Abstract
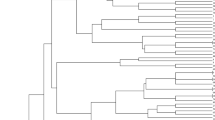
Genetic diversity of a set of 71 wheat accessions, including 53 biotype 2 Russian wheat aphid (RWA2)-resistant landraces and 18 RWA2 susceptible accessions, was assessed by examining molecular variation at multiple microsatellite (SSR) loci. Fifty-one wheat SSR primer pairs were used, 81 SSR loci were determined, and 545 SSR alleles were detected. These SSR loci covered all the three genomes, 21 chromosomes, and at least 41 of the 42 chromosome arms. Diversity values averaged over SSR loci were high with mean number of SSR alleles/locus = 6.7, mean Shannon’s index (H) = 1.291, and mean Nei’s gene diversity (He) = 0.609. The three wheat genomes ranked as A > D > B and the homoeologous groups ranked as 7 > 3 > 1 > 2 > 6 > 5 > 4 based on the number of alleles per locus. Xgwm136 on chromosome arm 1AS is the most polymorphic SSR locus with the largest number of observed and effective alleles and the highest H and He. Among all 2485 pairs of wheat accessions, genetic distance (GD) ranged from 0.054 to 1.933 and averaged 0.9832. A dendrogram based on GD matrix showed that all the wheat accessions could be grouped into distinct clusters. Most of the susceptible cultivars (13/18) were clustered into groups that contains all or mostly susceptible accessions. Most of the U.S. cultivars belong to a group that is distinguishable from all the different RWA2 resistant groups. Diversity analysis was also conducted separately for subgroups containing 53 RWA2-resistant accessions and 18 RWA2-susceptible accessions. Association mapping revealed 28 SSR loci significantly associated with leaf chlorosis, and 8 with leaf rolling. New chromosome regions associated with RWA2 resistance were detected, and indicated existence of new RWA resistance genes located on chromosomes of all other homoeologous groups in addition to the groups 1 and 7 in bread wheat. This information is helpful for development of mapping populations for RWA2 resistance genes from different phylogenetic groups, and for wise utilization of the RWA-resistant germplasm in wheat breeding programs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AM:
-
Association mapping
- LC:
-
Leaf chlorosis
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- LR:
-
Leaf rolling
- GD:
-
Genetic distance
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PIC:
-
Polymorphic information content
- RWA:
-
Russian wheat aphid
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- UPGMA:
-
The un-weighted pair-group method with arithmetic average
References
Akkaya MS, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE, Bhagwat AA, Cregan PB (1995) Integration of simple-sequence repeat DNA markers into a soybean linkage map. Crop Sci 35:1439–1445
Alamerew S, Chebotar S, Huang XQ, Röder MS, Börner A (2004) Genetic diversity in Ethiopian hexaploid and tetraploid wheat germplasm assessed by microsatellite markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 51:559–567
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Anderson GR, Papa D, Peng JH, Tahir M, Lapitan NLV (2003) Genetic mapping of Dn7, a rye gene conferring resistance to the Russian wheat aphid in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 107:1297–1303
Arzani A, Peng JH, Lapitan NLV (2004) DNA and morphological markers for a Russian wheat aphid resistance gene. Euphytica 139:167–172
Basky Z (2003) Biotypic and pest status differences between Hungarian and South African populations of Russian wheat aphid, Diuraphis noxia (Kurdjumov) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pest Manag Sci 59:1152–1158
Bell CJ, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19:137–144
Bertin P, Grégoire D, Massart S, de Froidmont D (2004) High level of genetic diversity among spelt germplasm revealed by microsatellite markers. Genome 47:1043–1052
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Bryan GJ, Collins AJ, Stephenson P, Orry A, Smith JB, and Gale MD (1997) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites from hexaploid bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 94:557–563
Collins MB, Haley SD, Peairs FB, Rudolph JB (2005a) Biotype 2 Russian wheat aphid resistance among wheat germplasm accessions. Crop Sci 45:1877–1880
Collins MB, Haley SD, Randolph TL, Peairs FB, Rudolph JB (2005b) Comparison of Dn4- and Dn7-carrying spring wheat genotypes artificially infested with Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) biotype 1. J Econ Entol 98:1698–1703
Edwards K, Johnstone C, Thompson C (1991) A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucl Acids Res 19:1349
Fahima T, Röder MS, Grama A, Nevo E (1998) Microsatellite DNA polymorphism divergence in Triticum dicoccoides accessions highly resistant to yellow rust. Theor Appl Genet 96:187–195
Fahima T, Röder MS, Wendehake K, Kirzhner VM, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellite polymorphism in natural populations of wild emmer wheat (Triricum dicoccoides) in Israel. Theor Appl Genet 104:17–29
Graybosch RA, Peterson CJ, Hansen LW, Mattern PJ (1990) Relationships between protein solubility characteristics, 1BL/1RS, high molecular weight glutenin composition, and end-use quality in winter wheat germplasm. Cereal Chem 67:342–349
Guyomarc’h H, Sourdille P, Charmet G, Edwards K, Bernard M (2002) Characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from Aegilops tauschii and transferability to the D-genome of bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:1164–1172
Haley SD, Peairs FB, Walker CB, Rudolph JB, Randolph TL (2004) Occurrence of a new Russian wheat aphid biotype in Colorado. Crop Sci 44:1589–1592
Huang XQ, Börner A, Röder MS, Ganal MW (2002) Assessing genetic diversity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:699–707
Jannink JL, Bink M, Jansen RA (2001) Using complex plant pedigrees to map valuable genes. Trends Plant Sci 6:337–342
Jyoti JL, Michaud JP (2005) Comparative biology of a novel strain of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on three wheat varieties. J Econ Entomol 98:1032–1039
Khlestkina EK, Huang XQ, Quenum FJB, Chebotar S. Röder MS, Börner A (2004a) Genetic diversity in cultivated plants—loss or stability? Theor Appl Genet 108:1466–1472
Khlestkina EK, Röder MS, Efremova TT, Börner A, Shumny VK (2004b) The genetic diversity of old and modern Siberian varieties of common spring wheat as determined by microsatellite markers. Plant Breed 123:122–127
Kimura M, Crow JF (1964) The number of alleles that can be maintained in a finite population. Genetics 49:725–738
Lapitan NLV, Peng JH, Sharma V (2007) A high-density map and PCR markers for Russian wheat aphid resistance gene Dn7 on chromosome 1RS/1BL. Crop Sci 47:809–818
Li YC, Röder MS, Fahima T, Kirzhner VM, Beiles A, Korol AB, Nevo E (2000a) Natural selection causing microsatellite divergence in wild emmer wheat at the ecologically variable microsite at Ammiad, Israel. Theor Appl Genet 100:985–999
Li YC, Fahima T, Peng JH, Röder MS, Kirzhner VM, Beiles A, Korol AB, Nevo E (2000b) Edaphic microsatellite DNA divergence in wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides, at a microsite: Tabigha, Israel. Theor Appl Genet 101:1029–1038
Litt M, Luty JA (1989) A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiacmuscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet 44:397–401
Liu XM, Smith CM, Gill BS, Tolmay V (2001) Microsatellite markers linked to six Russian wheat aphid resistance genes in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102:504–510
Liu J, Liu L, Hou N, Zhang A, Liu C (2007) Genetic diversity of wheat gene pool of recurrent selection assessed by microsatellite markers and morphological traits. Euphytica 155:249–258
Marais GF, Horn M, Du Toit F (1994) Intergeneric transfer (rye to wheat) of a gene(s) for Russian wheat aphid resistance. Plant Breed 113:265–271
Marais GF, Wessels WG, Horn M (1998) Association of a stem rust resistance gene (Sr45) and two Russian wheat aphid resistance genes (Dn5 and Dn7) with mapped structural loci in common wheat. S Af J Plant Soil 15:67–71
Morrissey JH (1981) Silver stain for protein in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem 117:307–310
Morrison WP, Peairs FB (1998) Response model concept and economic impact. In: Quisenberry SS, Peairs FB (eds) A response model for an introduced pest—The Russian wheat aphid Thomas Say Publ in Entomology, Entomology Soc Am. Lanham, MD, pp 1–11
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106:283–292
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Peng JH, Lapitan NLV (2005) Characterization of EST-derived microsatellites in the wheat genome and development of eSSR markers. Funct Integr Genomics 5:80–96
Peng JH., Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Dahan A, Grama A, Ronin YI, Korol AB, Nevo E (1999) Microsatellite tagging of stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides, and suggestive negative crossover interference on chromosome 1B. Theor Appl Genet 98:862–872
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Huang QY, Dahan A, Grama A, Nevo E (2000a) High-density molecular map of chromosome region harboring stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 and Yr15 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicccoides. Genetica 109:199–210
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Grama A, Nevo E (2000b) Microsatellite high-density mapping of stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 region on chromosome 1B and evaluation of its marker-assisted selection in F2 generation in wild emmer wheat. New Phytologist 146:141–154
Peng JH, Korol AB, Fahima T, Röder MS, Ronin YI, Li YC, Nevo E (2000c) Molecular genetic maps in wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides: Genome-wide coverage, massive negative interference, and putative quasi-linkage. Genome Res 10:1509–1531
Peng JH, Ronin YI, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Nevo E, Korol AB (2003) Domestication quantitative trait loci in Triticum dicoccoides, the progenitor of wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2489–2494
Peng JH, Wang H, Haley SD, Peairs FB, Lapitan NLV (2007) Molecular mapping of the Russian wheat aphid resistance gene Dn2414 in wheat. Crop Sci 47:2418–2429
Plaschke J, Ganal MW, Röder MS (1995) Detection of genetic diversity in closely related bread wheat using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:1001–1007
Prichard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–659
Puterka GJ, Burd JD, Burton RL (1992) Biotypic variation in a worldwide collection of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 85:1497–1506
Qureshi JA, Michaud JP, Martin TJ (2006) Resistance to biotype 2 Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in two wheat lines. J Econ Entomol 99:544–550
Rafalski JA (2002) Novel genetic mapping tools in plants: SNPs and LD-based approaches. Plant Sci 162:329–333
Reif JC, Zhang P, Dreisigacker S, Warburton ML, van Ginkel M, Hoisington D, Bohn M, Melchinger AE (2005) Wheat genetic diversity trends during domestication and breeding. Theor Appl Genet 110:859–864
Risch NJ (2000) Searching for genetic determinants in the new millennium. Nature 405:847–856
Röder MS, Plaschke J, König SU, Börner A, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD, Ganal MW (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Roussel V, Koenig J, Beckert M, Balfourier F (2004) Molecular diversity in French bread wheat accessions related to temporal trends and breeding programmes. Theor Appl Genet 108:920–930
Roussel V, Leisova L, Exbrayat F, Stehno Z, Balfourier F (2005) SSR allelic diversity changes in 480 European bread wheat varieties released from 1840 to 2000. Theor Appl Genet 111:162–170
Senior ML, Heun M (1993) Mapping maize microsatellites and polymerase chain reaction confirmation of the targeted repeats using a CT primer. Genome 36:884–889
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. Univ of Illinois Press, Urbana
Shufran KA, Burd JD, Webster JA (1997) Biotypic status of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in the United States. J Econ Entomol 90:1684–1689
Smith CM, Belay T, Stauffer C, Stary P, Kubeckova I, Starkey S (2004) Identification of Russian wheat aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations virulent to the Dn4 resistance gene. J Econ Entomol 97:1112–1117
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Song QJ, Fickus EW, Cregan PB (2002) Characterization of trinucleotide SSR motifs in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:286–293
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T, Brown-Guedira GL, Gay G, Qi L, Gill BS, Dufour P, Murigneux A, Bernard M (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic–physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Funct Integr Genom 4:12–25
Teklu Y, Hammer K, Huang XQ, Röder MS (2006) Analysis of microsatellite diversity in Ethiopian tetraploid wheat landraces. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1115–1126
Waines JG, Hegde SG (2003) Intra-specifi c gene flow in bread wheat as aff ected by reproductive biology and pollination ecology of wheat flowers. Crop Sci 43:451–463
Webster JA, Starks KJ, Burton RL (1987) Plant resistance studies with Diuraphis noxia(Homoptera: Aphididae) a new United States wheat pest. J Econ Entomol 80:944–949
Wu KS, Tanksley SD (1993) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet 241:225–235
Yeh FC, Yang RC (2000) POPGENE Version 1.32. University of Albert and Center for International Research, http://www.ualberta.ca/∼fyeh/
You GX, Zhang XY, Wang LF (2004) An estimation of the minimum number of SSR loci needed to reveal genetic relationships in wheat varieties: Information from 96 random accessions with maximized genetic diversity. Mol Breed 14:397–406
Zhang P, Dreisigacker S, Buerkert A, Alkhanjari S, Melchinger AE, Warburton ML (2006) Genetic diversity and relationships of wheat landraces from Oman investigated with SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1351–1360
Zondervan KT, Cardon LR (2004) The complex interplay among factors that influence allelic association. Nat Rev Genet 5:89—100
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Chinese Academy of Sciences under the Important Directional Program of Knowledge Innovation Engineering Grant No. KSCX2-YW-Z-0722, the Colorado Wheat Research Foundation, the U.S. Department of Agriculture under Cooperative Agreements USDA Contract No. 2001–52100-11293 and USDA Contract No. 2003-34205-13636, the National Research Initiative of USDA’s Cooperative State Research, Education and Extension Service, CAP Grant No. 2006-55606-16629, and Hatch Funds Project No. 644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Appendix 3
Appendix 4
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J.H., Bai, Y., Haley, S.D. et al. Microsatellite-based molecular diversity of bread wheat germplasm and association mapping of wheat resistance to the Russian wheat aphid. Genetica 135, 95–122 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9262-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-008-9262-x