Abstract
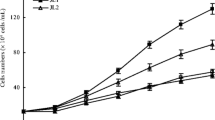
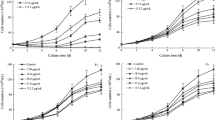
We tested the effects of solvent fractions (FA, FB, FC, and FD), which partitioned by liquid-liquid extraction from the methanol extract of Ulva pertusa, on the growth of red tide microalgae (Karenia mikimitoi, Skeletonema costatum, Alexandrium tamarense, Heterosigma akashiwo, Prorocentrum donghaiense), and FA, FB, and FC exhibited significantly antialgal activity. The chemical constituent analysis showed the existence of bioactive compounds such as phenols and alkaloids. Further, four solvent fractions were applied to silica gel column and repeated preparative TLC to produce 13 samples and their purity qualified as thin-layer chromatographic grade. Among these purified samples, FA111, FB411, FC411, FD111, and FD211 exhibited stronger antialgal activity. Furthermore, their functional groups were analyzed by colorimetric methods and UV spectra data. FD111 and FD211 were temptatively identified as alkaloids; the others were initially identified as phenolic acids. This is a preliminary study and the structure identification of these purified samples requires further investigation. While concentration of these purified samples in this algae was very small, they showed excellent effects against red tide microalgae.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegoke GO, Krishna AG (1998) Extraction and identification of antioxidants from spice Aframomum denielli. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75:1047–1052
Alamsjah MA, Ishibe K, Kim DK, Yamaguchi K, Ishibashi F, Fujity Y, Oda T (2007) Selecive toxic effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from Ulva fasciata on red tide phyotoplanker species. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:265–268
Anderson RJ, Monteiro PMS, Levitt GJ (1996) The effect of localized eutrophication on competition between Ulva lactuca (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta) and a commercial resource of Gracilaria verrucosa (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta). Hydrobiologia 326(327):291–296
Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (2012) Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Annu Rev Mater Sci 4:143–176
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Munro MHG, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR (2006) Review: Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 23(1):26–78
Chen AN (2011) The establishment of a miniaturized microalgal growth–inhibition bioassay and its application on effect of chemical ecology. Dissertation, Ocean University of China
Chiang IZ, Huang WY, Wu JT (2004) Allelochemiscals of Botryococcus braunii (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 40:474–480
Doan NT, Rickards RW, Rothschild JM, Smith GD (2000) Allelopathic actions of the alkaloid 12-epi-hapalindole Eisonitrile and calothrixin A from cyanobacteria of the genera Fische Val rella and Calothrix. J Appl Phycol 12(3/5):409–416
Etchegaray A, Rabello E, Dieckmann R, Moon DH, Fiore MF, Von Dohre H, Tsai SM, Neilan BA (2004) Algicide production by the filamentous cyanobacterium Fischerella sp. CENA 19. J App Phycol 16(3):237–243
Fong P, Donohoe RM, Zedler JB (1993) Competition with macroalgae and benthic cyanobacterial mats limits phytoplankton abundance in experimental microcosms. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 100:97–102
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatom. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol 17:309–314
Guven KC, Percot A, Sezik E (2010) Alkaloids in marine algae. Mar Drugs 8:269–284
Heisler J, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM, Anderson DM, Cochlan W, Dennison WC, Dortch Q, Gobler CJ (2008) Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 8:3–13
Jeong JH, Jin HJ, Sohn CH, Suh KH, Hong YK (2000) Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J Appl Phycol 12:37–43
Jin Q (2005) Studies on the allelopathic effects of macroalga Ulva pertusa on red tide microalgae and isolation and characterization of its allelochemicals. Dissertation, Ocean University of China
Jin Q, Dong SL (2003) Comparative studies on the allelopathic effects of two different strains of U. pertusa on Heterosigma akashiwo and Alexandrium tamarense. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 293:41–55
Kakisawa H, Asari F, Kusumi T, Toma T, Sakurai T, Oohusa T, Hara Y, Chihara M (1988) An allelopathic fatty acid from the brown alga Aladosiphon okaamuranus. Phytochemistry 27: 731–735
Kim KW, Kim KU (2000) Search for rice allelochemicals. In: Kim KU, Shin DH (Eds) Rice allelopathy. Taegn, pp 83–96
Ko¨rner S, Nicklisch A (2002) Allelopathic growth inhibition of selected phytoplankton species by submerged macrophytes. J Phycol 38:862–871
Lee V, Olsen S (1985) Eutrophication and management implications for the control of nutrient inputs to Rhode Island coastal lagoons. Estuaries 8:191–210
Lewitus AJ, Horner RA, Caron DA, Garcia-Mendoza E, Hickey BM, Hunter M, Huppert DD, Kudela RM, Langlois GW, Largier JL, Lessard EJ, RaLonde R, Jack Rensel JE, Strutton PG, Trainer VL, Tweddle JF (2012) Harmful algal blooms along the North American west coast region: history, trends, causes, and impacts. Harmful Algae 19:133–159
López A, Rico M, Rivero A, de Tangil MS (2011) The effects of solvents on the phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of Stypocaulon scoparium algae extracts. Food Chem 125(3):1104–1109
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1949) Further experiments on the fertilization of a sea loch (Loch Craiglin). J Mar Biol Assoc U K 27:360–379
Nakai S, Inoue Y, Hosomi M (2001) Algal growth inhibition effects and inducement modes by plant-producing phenols. Water Res 35(7):1855–1859
Nakamura T, Nagayama K, Uchida K, Tanaka R (1996) Antioxidant activity of phlorotannins isolated from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. Fish Sci 62(6):923–926
Nan CR, Zhang HZ, Zhao GQ (2004) Allelopathic interactions between the macroalga Ulva pertusa and eight microalgal species. J Sea Res 52:259–268
Nelson TA, Lee A (2001) A manipulative experiment proves that blooms of the macroalga Ulvaria obscura can reduce eelgrass shoot density. Aquat Bot 71:149–154
Nelson TA, Lee DJ, Smith BC (2003) Are “green tides” harmful algal blooms? Toxic properties of water–soluble extracts from two bloom–forming macroalgae, Ulva fenestrata and Ulvaria obscura (Ulvophyceae). J Phycol 39:874–879
Ravikumar S, Ramanathan G, Gnanadesigan M, Ramu A, Vijayakumar V (2011) In vitro antiplasmodial activity of methanolic extracts from seaweeds of South West Coast of India. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine 1: 862–865
Sun J, Wang YJ, Zhu LY, Yang RY (2007) Study on Antifungal and antioxidant activities of alcohol extract of Gelidium amansii. Chin Food Chem 28(10):53–56
Sun YY, Zhang J, Liu HJ, Li C, Wang CH (2011) Effects of macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis on the growth of the three species of red tide microalgae under laboratory conditions. Mar Sci Bull 30(3):328–333
Sun YY, Zhang J, Wang CH (2013) Growth inhibition of 6 kinds extracts of U. pertusa to three species of red tide microalgae. Environ Pollut Control 35(2):43–49
Suzuki M, Wakana I, Denboh T, Tatewaki M (1996) An allelopathic polyunsaturated fatty acid from red algae. Phytochemistry 43:63–65
Tang YZ, Gobler CJ (2011) The green macroalga, Ulva lactuca, inhibits the growth of seven common harmful algal bloom species via allelopathy. Harmful Algae 10:480–488
Valiela I, McClelland J, Hauxwell J, Behr PJ, Hersh D, Foreman K (1997) Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1105–1118
Wang CJ, Wang MY, Su JY, Li D, Zeng LM (1998) Chemical constituent of Acanthophora spicifera from the South China Sea. Chem Res 15(3):237–242
Wang RJ, Tang XX, Feng L, Xiao H, Qu L, Cai HJ (2006) Inhibitory effect of Surgassum thunbergii on Heterosigma akashiwo and Skeletonema costatum. Chin J App Ecol 17(12):2421–2425
Wang RJ, Xiao H, Wang Y, Zhou WL, Tang XX (2007) Effects of three macroalgae, Ulva linza (Chlorophyta), Corallina pilulifera (Rhodophyta) and Sargassum thunbergii (Phaeophyta) on the growth of the red tide microalga Prorocentrum donghaiense under laboratory conditions. J Sea Res 58:189–197
Wang HQ, Cheng SP, Zhang CH, Wang J, Hu CY, Ge FJ, Wu ZB (2010) Analysis of alkaloid from Elodea nuttallii by GC–MS and its alleloathic activity on Microcystin aeruginosa. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 34(2):361–366
Wang RJ, Tang XX, Sun JH (2011) Allelopathic effects of Sargassum thunbergii extracts on red tide microalga Alexandrium tamarense. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 17(5):694–699
Yang WD, Zhang XL, Liu JS (2005) The influence of allelochemicalo on the growth of Alexandrium tamarense. China Environ Sci 25(4):417–419
Yu F, Fang ZX, Yang HH, Zhang JJ, Ye XQ, Wu D (2010) Identification and determination of phenolic acids in purple yam. Sci Agric Sin 43(12):2527–2532
Yuan JF, Zhang ZS (1992) Biochemical interference of aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum on algae. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 13(1):45–50
Zhang TY, Wu AP, He M, Chen CP, Nie LW (2007) The allelopathy and its mechanism of phenolic acids on water–bloom algae. China Environ Sci 27(4):472–476
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. BinlunYan for his kind supply of U. pertusa, and Prof. Changhai Wang for his great help with the revision of the manuscript. This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20140446), a Project Funded by a Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the project of Jiangsu key laboratory of marine biotechnology of Huaihai Institute of Technology of China (2013HS010), and the Lianyungang Programs for Science and Technology Development (CG1310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ying-ying, S., Hui, W., Gan-lin, G. et al. Green alga Ulva pertusa—a new source of bioactive compounds with antialgal activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 10351–10359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4244-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4244-x