Abstract
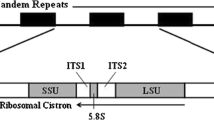
The ribosomal DNAs from Ch. thummi piger and Ch. th. thummi were cloned and analysed by a variety of restriction endonucleases. Comparison of rDNA clones from the two subspecies revealed a considerable length difference: the length of the analysed rDNA cistrons is approximately 9.0 kb for Ch. th. piger and approximately 14.5 kb for Ch. th. thummi. The nearly 5 kb additional DNA in Ch. th. thummi is clearly located within the non-transcribed spacer region, and consists of AT-rich, reptitive DNA elements. These elements with a basic repeat length of approximately 120 bp, are arranged tandemly in stretches of up to about 50 identical copies, which are characterized by a cleavage site for ClaI restriction endonuclease. They are found only in the Ch. th. thummi rDNA clones and not in the Ch. th. piger clones. Southern hybridizations between cloned ribosomal DNA and “centromeric” highly repetitive DNA have shown that the ribosomal repetitive Cla-elements are closely related to a highly repetitive DNA sequence family, which is present in various chromosomal sites particularly the centromeres. Sequence analysis has revealed more than 90% homology between the ribosomal Cla-elements and the “centromeric” Cla-elements. — Since it is clear from cytological investigations that Ch. th. piger with the small rDNA repeating unit is the phylogenetically older subspecies, we postulate a transposition of Cla-elements into the nucleolar DNA during the evolution of Ch. th. thummi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnheim, N., Seperack, P., Banerji, J., Lang, R.B., Miesfeld, R., Maren, K.B.: Mouse rDNA nontranscribed spacer sequences are found flanking immunoglobulin CH genes and elsewhere throughout the genome. Cell 22, 179–185 (1980)
Bach, R., Allet, B., Crippa, M.: Sequence organization of the spacer in the ribosomal genes of Xenopus clivii and Xenopus borealis. Nucl. Acids Res. 9, 5311–5330 (1981)
Barnett, T., Rae, P.M.M.: A 9.6 kb intervening sequence in Drosophila virilis rDNA, and sequence homology in rDNA interruptions of diverse species of Drosophila and other diptera. Cell 16, 763–775 (1979)
Bolivar, F., Backman, K.: Plasmids of E. coli as cloning vectors. In: Methods in enzymology (S.P. Colowick, N.O. Kaplan eds.), vol. 68, pp. 245–267. New York: Academic Press 1979
Boseley, P.G., Moss, T., Birnstiel, M.L.: 5'Labeling and Poly(dA) tailing. In: Methods in enzymology (S.P. Colowick, N.O. Kaplan eds.), vol. 65, p. 478, New York: Acedemic Press 1980
Boseley, P., Moss, T., Mächler, M., Portmann, R., Birnstiel, M.: Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell 17, 19–31 (1979)
Brutlag, D.L., Fry, K., Nelson, T., Hung, P.: Synthesis of hybrid bacterial plasmids containing highly repeated satellite DNA. Cell 10, 509–519 (1977)
Carroll, D., Brown, D.D.: Adjacent repeating units of Xenopus laevis 5S DNA can be heterogeneous in length. Cell 7, 477–486 (1976)
Coen, E.S., Thoday, J.M., Dover, G.: Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature (Lond.) 295, 564–568 (1982)
Cohen, A., Ram, D., Halvorson, H.O., Wensink, P.C.: Deletions within E. coli plasmids carrying yeast rDNA. Gene 3, 135–147 (1978)
Degelmann, A., Royer, H.-D., Hollenberg, C.P.: The organization of the ribosomal RNA genes of Chironomus tentans and some closely related species. Chromosoma (Berl.) 71, 263–281 (1979)
Denhardt, D.T.: A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 23, 641–646 (1966)
Glisin, V., Crkvenjakow, R., Byus, C.: Ribonucleic acid isolation by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry 13, 2633–2637 (1974)
Glover, D.M., Hogness, D.S.: A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell 10, 167–176 (1977)
Grunstein, M., Wallis, J.: Colony hybridization. In: Methods in enzymology (S.P. Colowick, N.O. Kaplan eds.), vol. 68, pp. 379–389. New York: Academic Press 1979
Hägele, K.: Differential staining of polytene chromosome bands in Chironomus by Giemsa banding methods. Chromosoma (Berl.) 59, 207–216 (1977)
Israelewski, N., Schmidt, E.R.: Spacer size heterogeneity in ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi is due to a 120 bp repeat homologous to a predominantly centromeric repeated sequence. Nucl. Acids Res. 10, 7689–7700 (1982)
Keyl, H.-G.: Chromosomenevolution bei Chironomus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 464–514 (1962)
Keyl, H.-G.: Duplikationen von Untereinheiten der chromosomalen DNS während der Evolution von Chironomus thummi. Chromosoma (Berl.) 17, 139–180 (1965)
Kunz, W., Petersen, G., Renkawitz-Pohl, R., Glätzer, K.H., Schäfer, M.: Distribution of spacer length classes and the intervening sequence among different nucleolous organizers in Drosophila hydei. Chromosoma (Berl.) 83, 145–158 (1981)
Long, E.O., Dawid, J.B.: Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 49, 727–764 (1980)
MacGregor, H.C., Mizuno, S.: In situ hybridization of “nick-translated” 3H-ribosomal DNA to chromosomes from salamanders. Chromosoma (Berl.) 54, 15–25 (1976)
Maxam, A.M., Gilbert, W.: Sequencing end-labelled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. In: Methods in enzymology (S.P. Colowick, N.O. Kaplan eds.) vol. 65, pp. 499–560. New York: Academic Press 1980
McCutchan, Th., Hsu, H., Thayer, R.E., Singer, M.F.: Organization of Africal green monkey DNA at junctions between α-satellite and other DNA sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 157, 195–211 (1982)
Prentki, P., Karch, F., Jida, S., Meyer, J.: The plasmid cloning vector pBR 325 contains a 482 base-pair-long inverted duplication. Gene 14, 289–299 (1981)
Radloff, R., Bauer, W., Vinograd, J.: A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA. The closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. (Wash.) 57, 1514–1521 (1967)
Rae, P.M.M., Barnett, Th., Murtif, V.L.: Nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma (Berl.) 82, 637–655 (1981)
Renkawitz-Pohl, R., Glätzer, K.-H., Kunz, W.: Characterization of cloned ribosomal DNA from Drosophila hydei. Nucl. Acids Res. 8, 4593–4611 (1980)
Renkawitz-Pohl, R., Matsumoto, L., Gerbi, S.: Two distinct intervening sequences in different ribosomal DNA repeat units of Sciara coprophila. Nucl. Acids Res. 9, 3747–3764 (1981)
Schaefer, J., Schmidt, E.R.: Different repetition frequencies of a 120 basepair DNA element and its arrangement in Chironomus thummi thummi and Chironomus thummi piger. Chromosoma (Berl.) 84, 61–66 (1981)
Schäfer, M., Wyman, A.R., White, R.: Length variation in the non-transcribed spacer of Calliphora erythrocephala ribosomal DNA is due to a 350 basepair repeat. J. Mol. Biol. 146, 179–199 (1981)
Schmidt, E.R.: The development of a 120 basepair repetitive DNA sequence in Chironomus thummi is correlated to the duplication of defined chromosomal segments. FEBS Lett. 129, 21–24 (1981)
Schmidt, E.R., Vistorin, G., Keyl, H.-G.: An AT-rich DNA component in the genomes of Chironomus thummi thummi and Chironomus thummi piger. Chromosoma (Berl.) 76: 35–45 (1980)
Suzuki, Y., Ohshima, Y.: Isolation and characterization of the silk fibroin gene with its flanking sequences. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 42, 947–957 (1977)
Tartof, K.D.: Evolution of transcribed and spacer sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila. Cell 17, 607–614 (1979)
Wellauer, P.K., Dawid, I.B.: The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 10, 193–212 (1977)
White, R.L., Hogness, D.S.: R-loop mapping of 18S and 28S sequences in the long and short repeating units of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell 10, 177–192 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, E.R., Godwin, E.A., Keyl, H.G. et al. Cloning and analysis of ribosomal DNA of Chironomus thummi piger and chironomus thummi thummi . Chromosoma 87, 389–407 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327181
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327181