Abstract
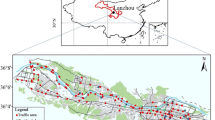
Fifty-one tree leaves were sampled in the industrial area, residential area, and Fenhe River ecological zone, for the purpose of a magnetic study on atmospheric pollution in Linfen City, Shanxi Province, China. Measurements of mass-specific magnetic susceptibility (γ) show a significant variation range (from 11.6 × 10−8 m3/kg to 129.7 × 10−8 m3/kg). Overall values of magnetic susceptibility decline in the following sequence: industrial area > residential area > Fenhe River ecological zone. The relatively elevated concentration-related magnetic parameters (saturation isothermal remanent magnetization, anhysteretic remanent magnetization and magnetic susceptibility) appear in the industrial area, with their highest values in the vicinity of Linfen Steel Mill. Magnetic particles are dominated by multidomain, magnetite-like minerals. Magnetic particle concentration and grain size both decrease with the increasing distance from industrial area, indicating the industrial area, especially Linfen Steel Mill, is the main source of atmospheric particle pollution. Residential area and Fenhe River ecological zone are also affected by industrial emission to a certain extent. The results of this study indicate that magnetic measurements of tree leaves are practicable for monitoring and determination of atmospheric pollution in Linfen City.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeson W L, Abbey D E, Knutsen S F, 1998. Long term concentrations of ambient air pollutants and incident lung cancer in Californian adults: Results from the AHSMOG study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 106(12): 813–822. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106813
Curtis L, Rea W, Smith-Willis P et al., 2006. Adverse health effects of outdoor pollutants. Environment International, 32(6): 815–830. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2006.03.012
Day R, Fuller M, Schmidt V A, 1977. Hysteresis properties of titanomagnetites: Grain-size and compositional dependence. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 13(4): 260–267. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(77)90108-X
Donaldson K, Li X Y, MacNee W, 1998. Ultrafine (nanometre) particle mediated lung injury. Journal of Aerosol Science, 29(5–6): 553–560. doi: 10.1016/S0021-8502(97)00464-3
Du X L, Lu C H, Wang H R et al., 2012. Trends of urban air pollution in Zhengzhou City in 1996–2008. Chinese Geographical Science, 22(4): 402–413. doi: 10.1007/s11769-012-0542-0
Dunlop D J, 2002. Theory and application of the Day plot (Mrs/Ms versus Hcr/Hc) 1. Theoretical curves and tests using titanomagnetite data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107 (B3): 1–22. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000486
Eriksson G, Jensen S, Kylin H et al., 1989. The pine needle as a monitor of atmospheric pollution. Nature, 341: 42–44. doi: 10.1038/341042a0
Evans M E, Heler F, 2003. Environmental Magnetism: Principle and Application of Enviromagnetics. New York: Academic Press, 1–299.
Gautam P, Blaha U, Appel E, 2005. Magnetic susceptibility of dust-loaded leaves as a proxy of traffic-related heavy metal pollution in Kathmandu city, Nepal. Atmospheric Environment, 39(12): 2201–2211. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.01.006
Goddu S R, Appel E, Jordanova D et al., 2004. Magnetic properties of road dust from Visakhapatnam (India)-Relationship to industrial pollution and road traffic. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 29(13–14): 985–995. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2004.02.002
Hanesch M, Scholger R, Rey D, 2003. Mapping dust distribution around an industrial site by measuring magnetic parameters of tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 37(36): 5125–5133. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.07.013
Hansard R, Maher B A, Kinnersley R, 2011. Biomagnetic monitoring of industry-derived particulate pollution. Environmental Pollution, 159(6): 1673–1681. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.039
Harrison R M, Jones M, 1995. The chemical composition of airborne particles in the UK atmosphere. Science of the Total En vironment, 168(3): 195–214. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(95)04536-A
Harrison R M, Yin J X, 2000. Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? The Science of the Total Environment, 249(1–3): 85–101. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00513-6
Hu S Y, Duan X M, Shen M J et al., 2008. Magnetic response to atmospheric heavy metal pollution recorded by dust-loaded leaves in Shougang industrial area, western Beijing. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(10): 1555–1564. doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0140-9
Huhn G, Schulz H, Staerk H J et al., 1995. Evaluation of regional heavy metal deposition by multivariate analysis of element contents in pine tree barks. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 84(3–4): 367–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00475349
Jordanova D, Petrov P, Hoffmann V et al., 2010. Magnetic signature of different vegetation species in polluted environment. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica, 54(3): 417–442. doi: 10.1007/s11200-010-0025-7
Ju Yitai, Wang Shaohuai, Zhang Qingpeng et al., 2004. Mineral magnetic properties of polluted topsoils: A case study in Sanming City, Fujian Province, Southeast China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(2): 282–288. (in Chinese)
Kardel F, Wuyts K, Maher B A et al., 2011. Leaf saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM) as a proxy for particulate matter monitoring: Inter-species differences and in-season variation. Atmospheric Environment, 45(29): 5164–5171. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.06.025
Karr C, Lumley T, Shepherd K et al., 2006. A case-crossover study of wintertime ambient air pollution and infant bronchiolitis. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(2): 277–281. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8313
King J, Banerjee S K, Marvin J et al., 1982. A comparison of different magnetic methods of determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials: Some results from lake sediments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 59(2): 404–419. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90142-X
King J G, Williams W, 2000. Low-temperature magnetic properties of magnetite. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B7): 16427–16436. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900006
King J W, Channell J E T, 1991. Sedimentary magnetism, environmental magnetism and magnetostratigraphy. Reviews of Geophysics, 29: 358–370.
Knox E G, 2006. Roads, railways and childhood cancers. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 60(2): 136–141. doi: 10.1136/jech.2005.042036
Knutsen S, Shavlik D, Chen L H et al., 2004. The association between ambient particulate air pollution levels and risk of cardiopulmonary and all-cause mortality during 22 years follow-up of a non-smoking cohort. Epidemiology, 15(4): S45.
Liu Qingsong, Deng Chenglong, 2009. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(4): 1041–1048. (in Chinese).
Lu S G, Zheng Y W, Bai S Q, 2008. A HRTEM/EDX approach to identification of the source of dust particles on urban tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 42(26): 6431–6441. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.04.039
Maher B A, Moore C, Matzka J, 2008. Spatial variation in vehicle-derived metal pollution identified by magnetic and elemental analysis of roadside tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 42(2): 364–373. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.013
Matzka J, Maher B A, 1999. Magnetic biomonitoring of roadside tree leaves: Identification of spatial and temporal variations in vehicle-derived particulates. Atmospheric Environment, 33(28): 4565–4569. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00229-0
Mitchell R, Maher B A, 2009. Evaluation and application of biomagnetic monitoring of traffic-derived particulate pollution. Atmospheric Environment, 43(13): 2095–2103. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.01.042
Mitchell R, Maher B A, Kinnersley R, 2010. Rates of particulate pollution deposition onto leaf surfaces: Temporal and inter-species magnetic analyses. Environmental Pollution, 158(5): 1472–1478. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.12.029
Moreno E, Sagnotti L, Dinares-Turell J et al., 2003. Biomonitoring of traffic air pollution in Rome using magnetic properties of tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, 37(21): 2967–2977. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00244-9
Morris W A, Versteeg J K, Bryant D W et al., 1995. Preliminary comparisons between mutagenicity and magnetic susceptibility of respirable airborne particulate. Atmospheric Environment, 29(23): 3441–3450. doi: 10.1016/1352-2310(95)00203-B
Pope III C A, Burnett R T, Thun M J et al., 2002. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. Journal of American Medical Association, 287(9): 1132–1141.
Pope III C A, Dockery D W, 1999. Epidemiology of particle effects. In: Holgate S T et al. (eds.). Air Pollution and Health. London: Academic Press, 673–705.
Pope III C A, Thun M J, Namboodiri M et al., 1995. Particulate air pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of US adults. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 151(3): 669–674.
Power A L, Worsley A T, Booth C, 2009. Magneto-biomonitoring of intra-urban spatial variations of particulate matter using tree leaves. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31(2): 315–325. doi: 10.1007/s10653-008-9217-2
Prajapati S K, Pandey S K, Tripathi B D, 2006. Monitoring of vehicles derived particulates using magnetic properties of leaves. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 120(1–3): 169–175. doi: 10.1007/s10661-005-9055-y
Robinson S G, 1986. The late Pleistocene palaeoclimatic record of North Atlantic deep-sea sediments revealed by mineral-magnetic measurements. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 42(1–2): 22–47. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9201(86)80006-1
Sagnotti L, Taddeucci J, Winkler A et al., 2009. Compositional, morphological, and hysteresis characterization of magnetic airborne particulate matter in Rome, Italy. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 10(8): Q08Z06. doi: 10.1029/2009GC002563Q08Z06.
Schwartz J, 1996. Air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory disease. Epidemiology, 7(1): 20–28.
Schwarze P, Ovrevik J, Lag M et al., 2006. Particulate matter properties and health effects: Consistency of epidemiological and toxicological studies. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 25(10): 559–579. doi: 10.1177/096032706072520
Seaton A, MacNee W, Donaldson K, 1995. Particulate air pollution and acute health effects. Lancet, 345(8943): 176–178. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)90173-6
Shen Mingjie, Hu Shouyun, Blaha Ulrich et al., 2006. A magnetic study of a polluted soil profile at the Shijingshan industrial area, western Beijing, China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(6): 1665–1673. (in Chinese)
Sun Zhiming, Hu Shouyun, Ma Xinghua, 1996. A rock-magnetic study of recent lake sediments and its palaeoenvironmental implication. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 39(2): 178–187. (in Chinese)
Szonyi M, Sagnotti L, Hirt A M, 2008. A refined biomonitoring study of airborne particulate matter pollution in Rome, with magnetic measurements on Quercus Ilex tree leaves. Geophysical Journal International, 173(1): 127–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03715.x
Thompson R, Oldfield F, 1986. Environmental Magnetism. London: Allen & Unwin, 1–227.
Tian Lili, Zhu Rixiang, Pan Yongxin, 2002. Rock-magnetic properties of Hannuoba basalt in Zhangbei section. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 45(6): 832–838. (in Chinese)
Urbat M, Lehndorff E, Schwark L, 2004. Biomonitoring of air quality in the Cologne conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler-Part I: Magnetic properties. Atmospheric Environment, 38(23): 3781–3792. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.061
Wichmann H E, Peters A, 2000. Epidemiological evidence of the effects of ultrafine particle exposure. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 358(1775): 2751–2769. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2000.0682
Wilson J G, Kingham S, Pearce J et al., 2005. A review of intraurban variations in particulate air pollution: Implications for epidemiological research. Atmospheric Environment, 39(34): 6444–6462. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.07.030
Woodruff T J, Parker J D, Schoendorf K C, 2006. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution and selected causes of postneonatal infant mortality in California. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(5): 786–790. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8484
Xia D S, Chen F H, Bloemendal J et al., 2008. Magnetic properties of urban dustfall in Lanzhou, China, and its environmental implications. Atmospheric Environment, 42(9): 2198–2207. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.11.040
Yu Lizhong, Xu Yu, Zhang Weiguo, 1995. Magnetic measurement on lake sediment and its environmental application. Progress in Geophysics, 10(1): 11–22. (in Chinese)
Zhang C X, Huang B C, Li Z Y et al., 2006. Magnetic properties of highroad-side pine tree leaves in Beijing and their environmental significance. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(24): 3041–3052. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2189-7
Zhang Chunxia, Huang Baochun, Liu Qingsong, 2009. Magnetic properties of different pollution receptors around steel plants and their environmental significance. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(11): 2826–2839. (in Chinese)
Zhao P S, Feng Y C, Zhu T et al., 2006. Characterizations of resuspended dust in six cities of North China. Atmospheric Environment, 40(30): 5807–5814. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.026
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40972216), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Project (NO. AP 34/21)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, G., Hu, S., Cao, L. et al. Magnetic properties of tree leaves and their significance in atmospheric particle pollution in Linfen City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 59–72 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0588-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0588-7