Abstract
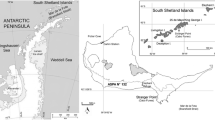
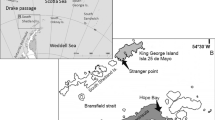
This study examined the diet of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, from an active breeding colony at Cape Shirreff (62°28′S, 60°48′W), Livingston Island, South Shetland Archipelago, Antarctica. It analysed faecal samples from five consecutive years (1997–2001) and length distribution of krill taken by trawl nets in the vicinity of Livingston Island. Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, was the most frequent prey item, followed by several myctophid species (Gymnoscopelus nicholsi, Electrona antarctica and Electrona carlsbergi), squid and penguin remains. From 1998 to 2001, a modal progression in krill size was evident, suggesting that A. gazella was depending on a strong krill cohort, at least over the study period. Analysis of size distribution and size selectivity of krill preyed upon by fur seals suggests a preference for larger krill (>34 mm), despite the broader size range of preys items available.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew DJ (1997) The CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Programme. Antarct Sci 9:235–242
Anonymous (1994) Annex to Recommendation XV-7, Site of Special Interest No. 32: Cape Shirreff, Livingston Island, South Shetland Islands. Antarctic Treaty System Handbook, 8th edn. U.S. Department of State
Bengtson JL, Ferm LM, Härkönen TJ, Stewart BS (1990) Abundance of Antarctic fur seals in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctic, during the 1986/87 austral summer. In: Kerry K, Hempel G (eds) Antarctic ecosystems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 265–270
Bonner WN (1968) The fur seal of South Georgia. British Antarctic Survey Scientific Report, no. 56
Boyd IL (1996) Temporal scales of foraging in a marine predator. Ecology 77:426–434
Casaux R, Baroni A, Carlini AR (1998) The diet of the Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus gazella, at Harmony Point, Nelson Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 20:424–428
Casaux R, Baroni A, Ramon A (2003) Diet of Antarctic fur seals Arctocephalus gazella at the Danco Coast, Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 26:49–54
Cherel Y, Guinet C, Tremblay Y (1997) Fish prey of Antarctic fur seals Arctocephalus gazella at Ile de Croy, Kerguelen. Polar Biol 17:87–90
Clarke A (1980) The biochemical composition of krill, Euphausia superba Dana, from South Georgia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 43:221–236
Croxall JP, McCann TS, Prince PA, Rothery P (1988) Reproductive performance of seabirds and seals at South Georgia and Signy Island, South Orkneys Islands, 1976–1987: implications for Southern Ocean Monitoring Studies. In: Sahrhage D (ed) Antarctic Ocean and resources variability. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 261–285
Croxall JP, Reid K, Prince PA (1999) Diet, provisioning and productivity responses of marine predators to differences in availability of Antarctic krill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 177:115–131
Daneri GA (1996) Fish diet of Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus gazella, in summer, at Stranger Point, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 16:353–355
Daneri GA, Carlini AR (1999) Spring and summer predation on fish by the Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus gazella, at King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Can J Zool 77:1157–1160
Daneri GA, Coria NR (1992) The diet of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, during the summer-autumn period at Mossman Peninsula, Laurie Island (South Orkneys). Polar Biol 11:565–566
Daneri GA, Coria NR (1993) Fish prey of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, during the summer-autumn period at Laurie Island, South Orkney Islands. Polar Biol 13:287–289
Daneri GA, Piatkowski U, Coria NR, Carlini AR (1999) Predation on cephalopods by Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, at two localities of the Scotia Arc, Antarctica. Polar Biol 21:59–63
Goebel ME, Costa DP, Crocker DE, Sterling JT, Demer DA (2001) Foraging ranges and dive patterns in relation to bathymetry and time-of-day of Antarctic fur seals, Cape Shirreff, Livingston Island, Antarctica. In: Davison W, Broady P (eds) Antarctic ecosystems: models for wider ecological understanding. New Zealand Natural Sciences, Canterbury University, Christchurch, pp 47–50
Green K, Burton HR, Williams R (1989) The diet of Antarctic fur seals Arctocephalus gazella (Peters) during the breeding season at Heard Island. Antarct Sci 1:317–361
Green K, Williams R, Burton HR (1991) The diet of Antarctic fur seals during the late autumn and early winter around Heard Island. Antarct Sci 3:359–361
Hamner WM, Hamner PP (2000) Behaviour of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba): schooling, foraging, and antipredatory behaviour. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57 [Suppl 3]:192–202
Hecht T (1987) A guide to the otoliths of Southern Ocean fishes. S Afr J Antarct Res 17:1–87
Hucke-Gaete R (1999) Dinámica poblacional del lobo fino antártico (Arctocephalus gazella (Peters, 1875)) en el Sitio de Especial Interés Científico no. 32, Isla Livingston, Shetland del Sur, Antártica: 1957–1999. Thesis, Universidad Austral de Chile
Hulley PA (1990) Family Myctophidae. In: Gon O, Heemstra PC (eds) Fishes of the Southern Ocean. J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology, Grahamstown, pp 146–178
Ichii T, Katayama K, Obitsu N, Ishii H, Nagabonu M (1998) Occurrence of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) concentrations in the vicinity of the South Shetland Islands: relationship to environmental parameters. Deep Sea Res I 45:1235–1262
King JC (1994) Recent climate variability in the vicinity of the Antarctic Peninsula. Int J Climatol 14:357–369
Kirkman SP, Wilson W, Klages NTW, Bester MN, Isaksen K (2000) Diet and estimated food consumption of Antarctic fur seals at Bouvetoya during summer. Polar Biol 23:745–752
Klages NTW, Bester MN (1998) Fish prey of fur seals Arctocephalus spp. at subantarctic Marion Island. Mar Biol 131:559–566
Knox GA (1970) Antarctic marine ecosystems. In: Holdgate MW (ed) Antarctic ecology. Academic, New York, pp 65–96
Loeb V, Siegel V, Holm-Hansen O, Hewitt R, Fraser W, Trivelpiece W, Trivelpiece S (1997) Effects of sea-ice extent and krill or salp dominance on the Antarctic food web. Nature 387:897–900
Murphy E J, Clarke A, Symon C, Priddle J (1995) Temporal variation in Antarctic sea-ice: analysis of a long term fast-ice record from the South Orkneys Islands. Deep Sea Res 42:1045–1062
Reid K (1995) The diet of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, during winter at South Georgia. Antarct Sci 7:241–249
Reid K (1996) A guide to the use of otoliths in the study of predators at South Georgia. British Antarctic Survey
Reid K, Arnould JPY (1996) The diet of Antarctic fur seals Arctocephalus gazella during the breeding season at South Georgia. Polar Biol 16:105–114
Reid K, Croxall JP (2001) Environmental responses of upper trophic-level predators reveals a system change in an Antarctic marine ecosystem. Proc R Soc Lond B 268:377–384
Reid K, Measures J (1998) Discriminating the sex of krill taken by predators using carapace measurements. Polar Biol 19:145–147
Siegel V (1987) Age and growth of the Antarctic Euphausiacea (Crustacea) under natural conditions. Mar Biol 4:483–495
Siegel V (1988) A concept of seasonal variation of krill (Euphausia superba) distribution and abundance west of the Antarctic Peninsula. In: Sahrhage D (ed) Antarctic Ocean and resources variability. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 145–163
Siegel V (2000) Krill (Euphausiacea) demography and variability in abundance and distribution. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57 [Suppl 3]:151–167
Siegel V, Loeb V (1994) Length and age at maturity of Antarctic krill. Antarct Sci 6:479–482
Siegel V, Loeb V (1995) Recruitment of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba and possible causes for its variability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 123:45–56
Siegel V, Loev V, Gröger J (1998) Krill (Euphausia superba) density, proportional and absolute recruitment and biomass in the Elephant Island region (Antarctic Peninsula) during the period 1977 to 1997. Polar Biol 19:393–398
Staniland IJ (2002) Investigating the biases in the use of hard prey remains to identify diet composition using Antarctic fur seals (Arctocephalus gazella) in captive feeding trials. Mar Mammal Sci 18:223–243
Torres D (1995) Antecedentes y proyecciones científicas de los estudios en el SEIC no. 32 y Sitio CEMP “Cabo Shirreff e islotes San Telmo”, isla Livingston, Antártica. Ser Cien INACH 45:143–169
Williams R, McEldowney A (1990) A guide to the fish otoliths waters off the Australian Antarctic Territory, Heard and Macquarie Islands. ANARE Res Notes 75
Acknowledgements
We thank Instituto Antártico Chileno (INACH) for supporting Project 018 without fail during more than 10 years. We also wish to thank all field colleagues and friends at Cape Shirreff (without whom this study would not have been possible), particularly those who endlessly helped collecting scats, and for helpful discussions: Veronica Vallejos, Juan Pablo Torres, Claudio Vera, Romeo Vargas, Olivia Blank, Jorge Acevedo, Mike Goebel and Rennie Holt. We also wish to thank Dr. Valerie Loeb who was kind enough to send us information regarding krill size distribution caught in trawl nets by the U.S. AMLR Program. Finally, we wish to thank two anonymous reviewers and A.R. Carlini for greatly improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osman, L.P., Hucke-Gaete, R., Moreno, C.A. et al. Feeding ecology of Antarctic fur seals at Cape Shirreff, South Shetlands, Antarctica. Polar Biol 27, 92–98 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-003-0555-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-003-0555-3