Abstract
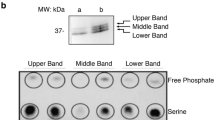
The study of human autoimmune diseases has benefited greatly from analysis of animal models. Mice that are homozygous for either the lpr (lymphoproliferation)1 or gld (generalized lymphoproliferative disease)2 mutant genes develop a disease characterized by massive lymphadenopathy and autoantibody formation. With age, the lyniphoid organs in these mice are replaced with a greatly expanded population of abnormal lymphocytes3–5. Recent work has shown that these cells are likely to be in the T-cell lineage. They rearrange and transcribe the genes for the α and β summits of the T-cell receptor (TCR) and a third, T-cell receptor-like gene, Tγ6,7. As determined by immunofliiorescence with anti-receptor antibodies the cells also express TCR on the cell surface. The murine T-cell receptor consists of the α and β chains, derived from the rearranged α and β genes, in non-covalent association with seven other chains; the δ chain, of relative molecular mass (Mr) 26,000 (26K), the ɛ chain (25K), a glycosylated 21K chain (gp21) which is probably the homologue of the γ chain of T3 (CD3), a 16K homodimer (ξ) and a 21K dimer (p21)8–10. This multichain complex is thought to be the murine analogue of the human T3 complex. After activation of normal T cells by antigen or lectin, p21 is phosphorylated on tyrosine residues and gp21 is phosphorylated on serine residues. In contrast, in the gld and lpr cells, p21 is phosphorylated even in the absence of antigen or lectin, whereas gp21 is not phosphorylated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy, E. D. & Roths, J. B. in Genetic Control of Autoimmune Disease (eds Rose, N. R., Bigazzi, P. E. & Warner, N. L.) 207–220 (Elsevier, New York, 1978).
Roths, J. B., Murphy, E. D. & Eicher, E. M. J. exp. Med. 159, 1–20 (1984).
Morse, H. C. III et al. J. Immun. 129, 2612–2615 (1982).
Davidson, W. F., Holmes, R. L., Roths, J. B. & Morse, H. C. III Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1219–1223 (1985).
Davignon, J. L. et al. J. Immun. 135, 2423–2428 (1985).
Nemazee, D. A., Studer, S., Steinmetz, M., Dembic, Z. & Kiefer, M. Eur. J. Immun. 15, 760–764 (1985).
Davidson, W. F., Dumont, F. J., Bedigian, H. G., Fowlkes, B. J. & Morse, H. C. III J. Immun. 136, 4075–4084 (1986).
Samelson, L. E., Patel, M. D., Weissman, A. M., Harford, J. B. & Klausner, R. D. Cell 46, 1083–1090 (1986).
Samelson, L. E., Weissman, A., Robey, F. A., Berkower, I. & Klausner, R. D. J. Immun. 137, 3254–3258.
Samelson, L. E., Harford, J. B. & Klausner, R. D. Cell 43, 223–231 (1985).
Samelson, L. E., Harford, J. B., Schwartz, R. H. & Klausner, R. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 1969–1973 (1985).
Patel, M., Samelson, L. E. & Klausner, R. D. (in preparation).
Brenner, M. B. et al. Nature 322, 145–149 (1986).
Lanier, L. L., Ruitenberg, J. J. & Phillips, J. H. J. exp. Med. 164, 339–344 (1986).
Hunter, T. & Cooper, J. A. A. Rev. Biochem. 54, 897–930 (1985).
Downward, J. et al. Nature 307, 521–527 (1984).
Cooper, J. A., Sefton, B. M. & Hunter, T. Meth. Enzym. 99, 387–402 (1983).
Samelson, L. E., Germain, R. N. & Schwartz, R. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 6972–6976 (1983).
Cleveland, D. W., Fischer, S. G., Kirchner, M. W. & Laemmli, U. K. J. biol. Chem. 252, 1102–1106 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samelson, L., Davidson, W., Morse, H. et al. Abnormal tyrosine phosphorylation on T-cell receptor in lymphoproliferative disorders. Nature 324, 674–676 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324674a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324674a0
This article is cited by
-
Insights into the initiation of TCR signaling
Nature Immunology (2014)
-
TCRζ mRNA splice variant forms observed in the peripheral blood T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (2006)
-
Ceramide-mediated clustering is required for CD95-DISC formation
Oncogene (2003)
-
Atypical signaling defects prevent IL-2 gene expression inIpr/Ipr CD4-CD8-cells
Journal of Biomedical Science (1998)
-
The phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor‐phenylarsine oxide restores defective phosphoinositide hydrolysis response in anergic C3H‐gld/gld lymphocytes
Immunology & Cell Biology (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.