Abstract
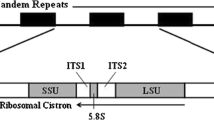
The determination of the secondary structure of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions separating nuclear ribosomal RNA genes of Chlorophytes has improved the fidelity of alignment of nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences from related organisms. Application of this information to sequences from green algae and plants suggested that a subset of the ITS-2 positions is relatively conserved. Organisms that can mate are identical at all of these 116 positions, or differ by at most, one nucleotide change. Here we sequenced and compared the ITS-1 and ITS-2 of 40 green flagellates in search of the nearest relative to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The analysis clearly revealed one unique candidate, C. incerta. Several ancillary benefits of the analysis included the identification of mislabelled cultures, the resolution of confusion concerning C. smithii, the discovery of mis-identified sequences in GenBank derived from a green algal contaminant, and an overview of evolutionary relationships among the Volvocales, which is congruent with that derived from rDNA gene sequence comparisons but improves upon its resolution. The study further delineates the taxonomic level at which ITS sequences, in comparison to ribosomal gene sequences, are most useful in systematic and other studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin B, Sanderson MJ, Porter JM, Wojciechowski MF, Campbell CS, Donoghue MJ (1995) The ITS region of nuclear ribosomal DNA: a valuable source of evidence on angiosperm phylogeny. Ann MO Bot Gard 82:247–277
Boudreau E, Turmel M (1996) Extensive gene rearrangements in the chloroplast DNAs of Chlamydomonas species featuring multiple dispersed repeats. Mol Biol Evol 13:233–243
Buchheim MA, Chapman RL (1991) Phylogeny of the colonial green flagellates: a study of 18S and 26S rRNA sequence data. BioSystems 25:85–100
Buchheim MA, Chapman RL (1992) Phylogeny of Carteria (Chlorophyceae) inferred from molecular and organismal data. J Phycol 28:362–374
Buchheim MA, Lemieux C, Otis C, Gutell RR, Chapman RL, Turmel M (1996) Phylogeny of the Chlamydomonadales (Chlorophyceae):a comparison of ribosomal RNA gene sequences from the nucleus and the chloroplast. Mol Phylogenet Evol 5:391–402
Buchheim MA, Turmel M, Zimmer EA, Chapman RL (1990) Phylo-genetic systematics of Chlamydomonas: an investigation based on cladistic analysis of nuclear 18S rRNA sequence data. J Phycol 26:689–699
Burrascano CG, VanWinkle-Swift KP (1984) Interspecific matings of five Chlamydomonas species. Genetics 107:sl5
Coleman AW (1996a) The Indian connection, crucial to reconstruction of the historical biogeography of freshwater algae: examples among Volvocaceae (Chlorophyta). Nova Hedwigia 112:477–488
Coleman AW (1996b) Are the impacts of events in the earth’s history discernable in the current distributions of freshwater algae? Hydrobiologia 336:137–142
Coleman AW, Suarez A, Goff LJ (1994) Molecular delineation of species and syngens in volvocacean green algae (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 30:80–90
Ettl H (1976) Die Gattung Chlamydomonas Ehrenberg. Beih Nova Hedwigia 49:1–1122
Friedl T (1996) Evolution of the polyphyletic genus Pleurastrum (Chlorophyta): inferences from nuclear-encoded ribosomal DNA sequences and motile cell ultrastructure. Phycologia 35:456–469
Gillham NW, Boynton JE, Harris EH (1987) Specific elimination of mitochondrial DNA from Chlamydomonas by intercalating dyes. Curr Genet 12:41–47
Goff LJ, Moon DA (1993) PCR amplification of nuclear and plastid genes from algal herbarium specimens and algal spores. J Phycol 29:381–384
Goodenough U, Ferris P, Woessner J, Armbrust EV (1996) Genes of the mating type locus in Chlamydomonas. J Phycol 32:sl9
Gross CH, Ranum LPW, Lefebvre PA (1988) Extensive restriction fragment length polymorphisms in a new isolate of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr. Genet 13:503–508
Harris EH (1989) The Chlamydomonas sourcebook. Academic Press, Inc., New York pp 780.
Harris EH, Boynton JE, Gillham NW, Burkhart BD, Newman SM (1991) Chloroplast genome organization in Chlamydomonas. Archiv Protistenkd 139:183–192
Hershkovitz MA, Zimmer EA (1996) Conservation patterns in angiosperm rDNA ITS2 sequences. Nuc Acids Res 24:2857–2867
Hershkovitz MA, Lewis LA (1996) Deep-level diagnostic value of the rDNA-ITS region. Mol Bio Evol 13:1276–1295
Hoshaw RW (1965) Mating types of Chlamydomonas from the collection of Gilbert M. Smith. J Phycol 1:194–196
Hoshaw RW, Ettl H (1966) Chlamydomonas smithii sp. nov.-a chlamydomonad interfertile with Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Phycol 2:93–96
Larson A, Kirk MM, Kirk DL (1992) Molecular phylogeny of the volvocine flagellates. Mol Biol Evol 9:85–105
Liss M, Kirk DL, Beyser K, Fabry S (1997) Intron sequences provide a tool for high resolution phylogenetic analysis of Volvocine algae. Curr Genet 31:214–227
Mai JC, Coleman AW (1997) The internal transcribed spacer 2 exhibits a common secondary structure in green algae and flowering plants. J Mol Evol 44:258–271
Rausch H, Larsen N, Schmitt R (1989) Phylogenetic relationships of the green alga Volvox carteri deduced from small-subunit ribosomal RNA comparisons. J Mol Evol 29:255–265
Ritland CE, Straus NA (1993) High evolutionary divergence of the 5.8S ribosomal DNA in Mimulus glaucescens (Scrophulariaceae). Plant Mol Biol 22:691–696
Ritland CE, Ritland K, Straus NA (1993) Variation in the ribosomal internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and ITS2) among eight taxa of the Mimulus guttatus species complex. Mol Biol Evol 10:1273–1288
Rumpf R, Vernon D, Schreiber D, Birky, Jr C (1996) Evolutionary consequences of the loss of photosynthesis in Chlamydomonadaceae: phylogenetic analysis of Rrn 18 (18S rDNA) in 13 Polytoma strains (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 32:119–126
Sack L, Zeyl C, Bell G, Sharbel T, Reboud X, Bernhardt T, Koelewyn H (1994) Isolation of four new strains of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyta) from soil samples. J Phycol 30:770–773
Schlosser UG (1984) Species-specific sporangium autolysins (cell-wall-dissolving enzymes) in the genus Chlamydomonas. In: Irvine, DEG, John, DM (eds) Systematics of the green algae. Academic Press, New York, pp 409–418
Spanier JG, Graham JE, Jarvik JW (1992) Isolation and preliminary characterization of three Chlamydomonas strains interfertile with Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 28:822–828
Starr RC, Marner FJ, Jaenicke L (1995) Chemoattraction of male gametes by a pheromone produced by female gametes of Chlamydomonas. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 92:641–645
Starr RC, Zeikus JA (1993) UTEX-the culture collection of algae at the University of Texas at Austin. J Phycol 29(Suppl): 1–106
Swofford DL (1993) PAUP: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Version 3.1.1 Computer program distributed by the Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, IL
Turmel M, Gutell RR, Mercier J-P, Otis C, Lemieux C (1993) Analysis of the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA gene from 17 Chlamydomonas taxa. J Mol Biol 232:446–467
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coleman, A.W., Mai, J.C. Ribosomal DNA and ITS-2 sequence comparisons as a tool for predicting genetic relatedness. J Mol Evol 45, 168–177 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006217
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006217