Summary
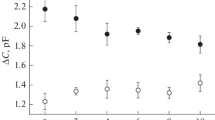
A Ca-activated, K-selective channel from plasma membrane of rat skeletal muscle was studied in artificial lipid bilayers formed from either phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) or phosphatidylserine (PS). In PE, the single-channel conductance exhibited a complex dependence on symmetrical K+ concentration that could not be described by simple Michaelis-Menten saturation. At low K+ concentrations the channel conductance was higher in PS membranes, but approached the same conductance observed in PE above 0.4m KCl. At the same Ca2+ concentration and voltage, the probability of channel opening was significantly greater in PS than PE. The differences in the conduction and gating, observed in the two lipids, can be explained by the negative surface charge of PS compared to the neutral PE membrane. Model calculations of the expected concentrations of K+ and Ca2+ at various distances from a PS membrane surface, using Gouy-Chapman-Stern theory, suggest that the K+-conduction and Ca2+-activation sites sense a similar fraction of the surface potential, equivalent to the local electrostatic potential at a distance of 9 Å from the surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apell, H.J., Bamberg, E., Läuger, P. 1979. Effects of surface charge on the conductance of the gramicidin channel.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552:369–378
Barrett, J.N., Magleby, K.L., Pallota, B.S. 1982. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle.J. Physiol. (London) 331:211–230
Begenisich, T. 1975. Magnitude and location of surface charges inMyxicola giant axons.J. Gen. Physiol. 66:47–65
Bell, J.E., Miller, C. 1984. Effects of phospholipid surface charge on ion conduction in the K+ channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum.Biophys. J. 45:279–287
Cecchi, X., Alvarez, O., Latorre, R. 1981. A three-barrier model for the hemocyanin channel.J. Gen. Physiol. 78:657–681
Edidin, M. 1974. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 3:179–201
Finkelstein, A., Andersen, O.S. 1981. The gramicidin A channel: A review of its permeability characteristics with special reference to the single-file aspect of transport.J. Membrane Biol. 59:155–171
Fohlmeister, J.F., Adelman, W.J., Jr. 1982. Periaxonal surface calcium binding and distribution of charge on the faces of squid axon potassium channel molecules.J. Membrane Biol. 70:115–123
Frankenhaeuser, B., Hodgkin, A.L. 1957. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of the squid axon.J. Physiol. (London) 137:218–244
Gilbert, D.L., Ehrenstein, G. 1969. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: Determination of surface charge.Biophys. J. 9:447–463
Grahame, D. 1947. The electric double layer and the theory of electrocapillarity.Chem. Rev. 41:441–501
Hahin, D.T., Campbell, D.T. 1983. Simple shifts in the voltage dependence of sodium channel gating caused by divalent cations.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:785–805
Hille, B., Woodhull, A.M., Shapiro, T. 1975. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: Divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B 270:301–318
Jost, P., Griffith, O.H., Capaldi, R.A., Vanderkooi, G. 1973. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70:480–484
Kistler, J.R., Stroud, M., Klykowsky, M.W., Lalancette, R.A., Fairclough, R.H. 1982. Structure and function of an acetylcholine receptor.Biophys. J. 37:371–383
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels.J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Latorre, R., Vergara, C., Hidalgo, C. 1982. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:805–809
Läuger, P., Stephan, W., Frehland, E. 1980. Fluctuations of barrier structure in ionic channels.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 602:167–180
Levitt, D.G. 1978. Electrostatic calculations for an ion channel. I. Energy and potential profiles and interactions between ions.Biophys. J. 22:209–219
Loosley-Millman, M.E., Rand, R.P., Parsegian, V.A. 1982. Effect of monovalent ion binding and screening and measured electrostatic forces between charged phospholipid bilayers.Biophys. J. 40:221–232
McLaughlin, S. 1977. Electrostatic potentials at membrane-solution interfaces.Curr. Top. Membr. Trans. 9:71–144
McLaughlin, S., Mulrine, G.A.N., Gresalfi, T., Vaio, G., McLaughlin, A. 1981. Adsorption of divalent cations to bilayer membranes containing phosphatidylserine.J. Gen. Physiol. 77:445–473
Methfessel, C., Boheim, G. 1982. The gating of single calcium-dependent potassium channels is described by an activation-blockade mechanism.Biophys. Struct. Mech. 9:35–60
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1983a. Saxitoxin and ouabain binding activity of isolated skeletal muscle membrane as indicators of surface origin and purity.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 732:412–420
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1983b. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes: Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:511–542
Mozhayeva, G.N., Naumov, H.P. 1970. Effect of surface charge on the steady-state potassium conductance of nodal membrane.Nature (London) 228:164–165
Mueller, P., Rudin, D.O. 1969. Translocators in bimolecular lipid membranes: Their role in dissipative and conservative bioenergy transductions.Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 3:157–249
Thomas, D.D., Bigelow, D.J., Squier, T.C., Hidalgo, C. 1982. Rotational dynamics of proteins and boundary lipid in sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane.Biophys. J. 37:217–225
Vergara, C. 1983. Characterization of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel from skeletal muscle membranes in artificial bilayers. Ph.D. Dissertation. Harvard University Cambridge, Massachusetts
Vergara, C., Latorre, R. 1983. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers: Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade.J. Gen. Physiol. 82:543–568
Vergara, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. 1984. Conduction, blockade and gating in a Ca2+-activated K+ channel incorporated into planar lipid bilayers.Biophys. J. 45:73–76
Warren, G.B., Toon, P.A., Birdsall, N.J.M., Lee, A.G., Meltcalfe, J.C. 1974. Reversible lipid titrations of the activity of pure adenosine triphosphatase-lipid complexes.Biochemistry 13:5501–5507
Wilson, D.L., Morimoto, K., Tsuda, Y., Brown, A.M. 1983. Interaction between calcium ions and surface charge as it relates to calcium currents.J. Membrane Biol. 72:117–130
Yellen, G.I. 1984. Ionic permeation and blockade in calcium-activated potassium channels of chromaffin cells. Ph.D. Dissertation. Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moczydlowski, E., Alvarez, O., Vergara, C. et al. Effect of phospholipid surface charge on the conductance and gating of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in planar lipid bilayers. J. Membrain Biol. 83, 273–282 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868701
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868701