Abstract
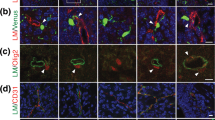
Laminin, a large glycoprotein of the basement membrane that promotes the growth of nerve cell processes in vitro has also been detected in the brains of developing embryos in situ where it is postulated to promote or guide neural outgrowth. We have investigated the histological and developmental patterns of a receptor to a specific pentapeptide sequence in the A chain of the laminin molecule (PA22-2 or IKVAV) that has been identified as a neuron growth-promoting sequence. Standard immunocytochemical procedures were used to localize the receptor by means of a polyclonal antibody to affinity-purified receptor (MR=110 kDa) from mouse brains. Results for postnatal stages (P) stages (P 1,7,8,25,30,and adult) show that the 110 kDa receptor is localized in fibers in the cortex and hippocampus, in astroglial cells at the surface of the cortex, and in neuronal cell bodies in the hippocampus. In contrast, the A-chain ligand is localized in cell bodies in the same regions at P stages. For embryonic stages (E) (E 14 and E 16) the receptor is localized in bundles of fibers in the superficial and deep cortical layers, and in cell bodies in these regions at E 14 only. Staining for the A chain ligand of the receptor was first seen postnatally. We speculate that the inverse histological pattern of receptor and ligand with respect to cell bodies and fibers may reflect a role in controlling axon guidance during development or repair during regeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron van Evercooren A, Kleinman HK, Ohno S, Marangos P, Schwartz JP, Dubois-Dalq ME (1982) Nerve growth factor, laminin and fibronectin promote neurite growth in human fetal sensory ganglia cultures. J Neurosci Res 8:179–184
Caviness VS Jr, Sidman RL (1973) Time of origin of corresponding cell classes in the cerebral cortex of normal and reeler mutant mice: An autoradiographic analysis. J Comp Neurol 148:141–152
Chung AE, Jaffe R, Freeman IL, Vergnes JP, Braginski JE, Carlin B (1979) Properties of a basement membrane related glycoprotein synthesized in culture by a mouse embryonal carcinoma-derived cell line. Cell 16:277–287
Douville PJ, Harvey WJ, Carbonetto S (1988) Isolation and partial characterization of high affinity laminin receptors in neural cells. J Biol Chem 263:14964–14969
Edgar D, Timpl R, Thoenen H (1984) The heparin-binding domain of laminin is reponsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J 3:1463–1468
Gehlsen KR, Dillner L, Engvall E, Ruoslahti E (1988) The human laminin receptor is a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. Science 241:1228–1229
Gordon-Weeks PR, Giffin C, Weekes SE, Barben C (1989) Transient expression of laminin immunoreactivity in the developing rat hippocampus. J Neurocytol 18:451–463
Graf J, Iwamoto Y, Sasaki M et al. (1987) Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis and receptor binding. Cell 48:989–996
Hagg T, Muir D, Engvall E, Varon S, Manthorpe M (1989) Laminin-like antigen in rat CNS neurons: Distribution and changes upon brain injury and nerve growth factor treatment. Neuron 3:721–732
Horwitz A, Duggan K, Greggs R, Decker C, Buck C (1985) The cell substrate attachment (CSAT) antigen has properties of a receptor for laminin and fibronectin. J Cell Biol 101:2134–2144
Jucker M, Kleinman HK, Höhann, Ordy JM, Ingram DK (1991) Distinct immunoreactivity to 110 kDa laminin-binding protein in adult and lesioned rat forebrain. Brain Res 555:305–312
Jucker M, Walker LC, Kibbey MC, Kleinman HK, Ingram DK (1993) Localization of a laminin-binding protein in brain. Neuroscience 56:1009–1022
Kleinman HK, Cannon FB, Laurie GW et al. (1985) Biological activities of laminin. J Cell Biochem 27:317–325
Kleinman HK, Ebihara I, Killen PD et al. (1987) Genes for basement membrane proteins are coordinately expressed in differentiating F9 cells but not in normal adult murine tissues. Devel Biol 122:373–378
Kleinman HK, Ogle RC, Cannon FB, Little CD, Sweeney TM, Luckenbill-Edds L (1988) Laminin receptors for neurite formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:1282–1286
Kleinman HK, Weeks BS, Cannon FB et al. (1991) Identification of a 110-kDa nonintegrin cell surface laminin-binding protein which recognizes an A chain neurite-promoting peptide. Arch Biochem Biophys 290:320–325
Lesot H, Kühl U, Mark K von der (1983) Isolation of a laminin binding protein from muscle cell membranes. EMBO J 2:861–865
Letourneau PC, Madsen AM, Palm SL, Furcht LT (1988) Immunoreactivity for laminin in the developing ventral longitudinal pathway of the brain. Dev Biol 125:135–144
Liesi P (1985) Do neurons in the vertebrate CNS migrate on laminin? EMBO J 4:1163–1170
Liesi P, Risteli L (1989) Glial cells of mammalian brain produce a variant form of laminin. Exper Neurol 105:86–92
Liesi P, Silver J (1988) Is astrocyte laminin involved in axon guidance in the mammalian CNS? Dev Biol 130:774–785
Liesi P, Kaakkola S, Dahl D, Vaheri A (1984) Laminin is induced in astrocytes of adult brain by injury. EMBO J 3:683–686
Malinoff HL, Wicha MS (1983) Isolation of a cell surface receptor protein for laminin from murine fibrosarcoma cells. J Cell Biol 96:1475–1479
Manthorpe M, Engvall E, Ruoslahti E, Longo FM, Favis GE, Varon S (1983) Laminin promotes neuritic regeneration from cultured peripheral and central neurons. J Cell Biol 97:1882–1890
Moody SA, Fisher M (1991) Distribution of laminin A, B1 and B2 chains in the developing mouse hindbrain. Soc Neurosci Abs 17:741
Murtomäki S, Risteli J, Koivisto U, Johansson S, Liesi P (1992) Laminin and its neurite outgrowth-promoting domain in the brain in Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome patients. J Neurosci Res 32:261–273
Pomeranz HD, Sherman DL, Smalheiser NR, Tennyson VM, Gershon MD (1991) Expression of a neurally related laminin binding protein by neural crest-derived cells that colonize the gut: Relationship to the formation of enteric ganglia. J Comp Neurol 313:625–642
Smalheiser NR, Schwartz NB (1987) Cranin: a laminin-binding protein of cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6457–6461
Suzuki H, Yamamoto T, Yamamoto H et al. (1990) Intraneuronal laminin-like immunoreactivity in the human central nervous system. Brain Res 520:324–329
Tashiro K, Sephel GE, Weeks B et al. (1989) A synthetic peptide containing the IKVAV sequence from a chain of laminin mediates cell attachment, migration, and neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem 264:16174–16182
Timpl R, Rohde H, Gehron RP, Rennard SI, Foidart JM, Martin GR (1979) Laminin—a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem 254:9933–9937
Zhou FC (1990) Four patterns of laminin-immunoreactive structure in developing rat brain. Devel Brain Res 55:191–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by the AOA Grant #89-08-296 and by the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luckenbill-Edds, L., Kaiser, C.A., Rodgers, T.R. et al. Localization of the 110 kDa receptor for laminin in brains of embryonic and postnatal mice. Cell Tissue Res 279, 371–377 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318494
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318494