Summary
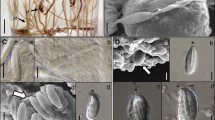
Microbasic p-mastigophores, euryteles of two size groups, holotrichous isorhizas and atrichous isorhizas, comprise the cnidom of Chironex fleckeri, a cubozoan that has been responsible for several human fatalities. In its undischarged state each microbasic mastigophore of C. fleckeri consists of a capsule containing matrix and an inverted tube possessing a smooth-walled butt which is loosely coiled helically and which narrows to form a thread that is tightly coiled helically and markedly pleated. Both butt and thread carry three helices of spines and contain a granular matrix. During discharge, the proximal butt spines form initially a piercing stylet. Granular material from the butt and thread is released prior to the release of capsular material. Each eurytele possesses a tube with a butt composed of three bulbs, the middle bulb bearing long spines. Each holotrichous isorhiza possesses a coiled tube bearing small spines along its length. Each atrichous isorhiza exhibits a tube that is devoid of spines and loosely folded in the undischarged condition. The probable role of each type of nematocyst is inferred from its structure and features that enable the ready separation of the nematocysts of C. fleckeri from those of scyphozoan jellyfish are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes JH (1966) Studies on three venomous Cubomedusae. Extraction of cnidarian venom from living tentacles. Symp Zool Soc London 16:307–332
Calder DR, Peters EC (1975) Nematocysts of Chiropsalmus quadrumanus with comments on the systematic status of the Cubomedusae. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 27:364–369
Carlgren O (1940) A contribution to the knowledge of structure and distribution of cnidae in the Anthozoa especially in the Actinaria. Lunds Univ Arsskr Avd 2 (N.S.) 36:1–62
Cleland JB, Southcott RV (1965) Injuries to man from marine invertebrates in the Australian region. Commonwealth of Australia, Canberra A.C.T. pp 43–116
Cormier SM, Hessinger DA (1980) Cellular basis for tentacle adherence in the Portugese man-of-war (Physalia physalis). Tissue Cell 12:713–721
Endean R (1981) The box jelly-fish or “sea-wasp”. In: Pearn J (ed) Animal toxins and man. Human poisoning by toxic Australian venomous creatures. Queensland Health Department, Brisbane, pp 46–54
Endean R, Duchemin C, McColm D, Fraser EH (1969) A study of the biological activity of toxic material derived from nematocysts of the cubomedusan Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 6:179–204
Endean R, Rifkin J (1975) Isolation of different types of nematocyst from the cubomedusan Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 13:375–376
Kingston CW, Southcott RV (1960) Skin histopathology in fatal jellyfish stinging. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 54:373–383
Mariscal RN (1974) Nematocysts. In: Muscatine L, Lenhoff HM (eds) Coelenterate biology: reviews and new perspectives. Academic Press, New York, pp 129–178
Mariscal RN, Conklin EJ, Bigger CH (1977) The ptychocyst, a new major category of cnida used in tube construction by a cerianthid anemone. Biol Bull (Woods Hole) 152:392–405
Picken LER, Skaer RJ (1966) A review of researches on nematocysts. Symp Zool Soc London 16:19–50
Southcott RV (1967) Revision of some Carybdeidae (Scyphozoa: Cubomedusae), including a description of the jelly fish responsible for the “Irukandji Syndrome”. Aust J Zool 15:651–671
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Tardent P, Holstein T (1982) Morphology and morphodynamics of the stenotele nematocyst of Hydra attenuata Pall (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Cell Tissue Res 224:269–290
Weill R (1934) Contribution à l'étude des cnidaires et le leurs nematocystes. I. Trav Sta Zool Wimereux 10:1–347
Werner B (1973) New investigations on the systematics and evolution of the class Scyphozoa and the phylum Cnidaria. Publ Seto Mar Biol Lab 20:35–61
Werner B (1975) Bau- und Lebensgeschichte von Tripedalia cystophora (Cubozoa). Helgoländer wiss Meeresunters 27:461–504
Westfall JA (1965) Nematocysts of the sea anemone Metridium. Amer Zoologist 6:377–393
Williamson JA, Callanan VI, Hartwick RF (1980) Serious envenomation by the northern Australian box-jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri). Med J Aust 1:13–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rifkin, J., Endean, R. The structure and function of the nematocysts of Chironex fleckeri Southcott, 1956. Cell Tissue Res. 233, 563–577 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212225
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212225