Summary
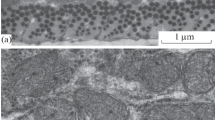
The ultrastructure and vascular supply of the different fibre types in the lateral muscles of the sturgeon Acipenser stellatus were studied by light- and electron microscopy and morphometry. Three fibre types form separate layers without intermingling. The red fibres are superficial, the white fibres deep and the intermediate fibres between them. From morphometric analyses, the mitochondrial volume fraction in red fibres is 30%, in intermediate fibres 3.7% and in white fibres 0.7%. Z lines are most fuzzy in the red fibres. Triads of the sarcotubular system are always situated at the level of the Z discs. In red fibres the three elements are arranged in a series along the myofibrils, whereas in white fibres they are arranged transversely and in the intermediate fibres they are aligned obliquely. The number of capillaries surrounding each fibre is 2.3, 0.9 and 0.2 for the red, intermediate and white fibres, respectively. In red fibres 16% of the surface is directly covered by capillaries. The corresponding percentages for intermediate and white fibres are 5 and 1, respectively. Per unit volume of the fibre, the directly vascularised fibre surface in red fibres is about ten times larger than that of white fibres.
The degree of vascularisation of the fibre types is directly related to the volume fraction of mitochondria, and thus to their aerobic capacities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akster HA, Osse JWM (1978) Muscle fibre types in head muscles of the perch Perca fluviatilis (L), Teleostei. Neth J zool 29:94–110
Bone Q (1966) On the function of the two types of myotomal muscle fibre in elasmobranch fish. J Mar Biol Ass U K 46:321–349
Bone Q (1978) Locomotor muscle. In: Fish Physiology, Academic Press, Inc, Vol VII, 361–424
Bone Q, Chubb A (1978) The histochemical demonstration of myofibrillar ATPase in elasmobranch muscle. Histochem J 10:489–494
Flood PR (1979) The vascular supply of the three fibre types in the parietal trunk muscle of the atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa, L.) Microvasc Res 17:55–70
Flood PR, Mathisen JS (1962) A third type of muscle fibre in the parietal muscle of the atlantic hagfish Myxine glutinosa L Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 58:638–640
Johnston IA, Ward PS, Goldspink G (1975) Studies on the swimming musculature of the rainbow trout. I. Fibre types. J Fish Biol 7:451–458
Johnston IA, Dawison W, Goldspink G (1977) Energy metabolism of carp swimming muscles. J Comp Physiol 114:203–216
Kilarsky W (1973) Cytomorphometry of sarcoplasmic reticulum in extrinsic eye muscles of the teleost (Tinca tinca L.) Z Zellforsch 143:273–290
Korneliussen H (1972) Identification of muscle fibre types in “semithin” sections stained with p-phenylene diamine. Histochemie 32:95–98
Korneliussen H, Nicolaysen K (1973) Ultrastructure of four types of striated muscle fibres in the Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa L.) Z Zellforsch 143:273–290
Korneliussen H, Dahl HA, Paulsen JE (1978) Histochemical definition of muscle fibre types in the trunk musculature of a teleost fish (cod, Gadus morhua, L.). Histochemistry 55:1–16
Kryvi H (1975) The structure of the myosatellite cells in axial muscles of the shark Galeus melastomus. Anat Embryol 147:35–44
Kryvi H (1977) Ultrastructure of the different fibre types in axial muscles of the sharks Etmopterus spinax and Galeus melastomus. Cell Tissue Res 184:287–300
Kryvi H, Totland GK (1977) Histochemical studies with microphotometric determinations of the lateral muscles in the sharks Etmopterus spinax and Galeus melastomus. J Mar Biol Ass U K 57:261–271
Kryvi H, Totland GK (1978) Fibre types in locomotory muscles of the cartilaginous fish Chimaera monstrosa. J Fish Biol 12:257–265
Mosse PRL (1978) The distribution of capillaries in the somatic musculature of two vertebrate types with special reference to teleost fish. Cell Tissue Res 187:281–303
Mosse PRL, Hudson RCL (1977) The functional role of different fibre types identified in the myotomes of marine teleosts: a behavioral, anatomical and histochemical study. J Fish Biol 11:417–430
Nag AC (1972) Ultrastructure and adenosinetriphosphatase activity in red and white muscle fibres of the caudal region of a fish, Salmo gairdneri. J Cell Biol 55:42–57
Stanfield PR (1972) Electrical properties of white and red muscle fibres of the elasmobranch fish Scyliorhinus canicula. J Physiol (London), 222:161–186
Stevens ED (1968) The effect of exercise on the distribution of blood to various organs in rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol 25:615–625
Wardle CS (1978) Non-release of lactic acid from anaerobic swimming muscle of plaice Pleuronectes platessa L: A stress reaction. J Exp Biol 77:141–155
Weibel ER (1967) Stereological techniques for electron microscopic morphometry. In: Hayat HA (ed), Principles and techniques of electron microscopy. Van Nostrand Reinold Comp, New York, Vol III
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kryvi, H., Flood, P.R. & Gulyaev, D. The ultrastructure and vascular supply of the different fibre types in the axial muscle of the sturgeon Acipenser stellatus, Pallas. Cell Tissue Res. 212, 117–126 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234038
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00234038