Summary
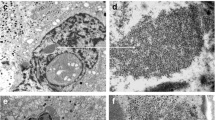
The ultrastructure of the pars intermedia (PI) of the normal VII +/+ and hereditary nephrogenic diabetes inspidus DI Os/+ mice has been studied with particular reference to the morphology of the glandular cells and their innervation. Four types of cells were observed in both the genotypes of mice, 1) the light glandular cell, 2) the dark cell, 3) a type of cell similar to ependymal cells and 4) a small percentage of typical ACTH cells, observed mostly on the PI border of the cleft and rarely in the centre of PI. The predominant light glandular cells contain mainly two types of membrane bound granules: 1) electron dense core granules, which measure 1500–2500 Å and 2) electron lucent vesicles, which measure 3000–4000 Å in diameter. Granules of intermediate size with various density are also present in both types of mice. The electron dense core granules are predominant in DI Os/+ mice, whereas, electron lucent vesicles are predominant in the normal VII +/+ mice. Similar uniform size membrane bound electron dense granules have been observed in ACTH cells of PI and pars distalis. From earlier experimental evidences and the present observations, it is concluded that the dense core granules in PI may be synthesizing ACTH or ACTH-like substance. It is also discussed that these dense core granules may further mature and give rise to MSH in the form of electron lucent vesicles. If it is so, PI light glandular cells may have dual functions, of producing MSH and ACTH. One of the functions of ependymal-like cells, may be the transport of PI secretion.
Three types of nerve endings are observed throughout the PI, making synaptic contact with the predominant cell type. The innervation is more in DI Os/+ mice than in normal mice. The classification of these nerves is according to Bargmann and co-workers 1) peptidergic neurosecretory fibers, contain mainly membrane bound dense core granules, measuring 1200 to 1800 Å, and are the classic neurosecretory granules; 2) adrenergic fibers, measuring 700–900 Å; 3) cholinergic fibers, measuring 300–400 Å. Adrenergic and cholinergic fibers are more towards the hypophysial cleft. The increased innervation, the synaptic contact, the extremely hypertrophied PI and the greater activity of its light glandular cells in the DI Os/+ mice show the PI is under the influence of the nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargmann, W.: Neurohypophysis. Structure and function. In: Neurohypophysial hormones and similar polypeptides (ed. B. Berde). Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol. 23, p. 1–39. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1968.
Bargmann, W., Lindner, E., Andres, K. H.: Über Synapsen an endokrinen Epithelzellen und die Definition sekretorischer Neurone. Untersuchungen am Zwischenlappen der Katzenhypophyse. Z. Zellforsch. 77, 282–298 (1967).
Cameron, E., Foster, C. L.: Some light and electron-microscopic observations on the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland of the rabbit. J. Endocr. 49, 479–485 (1971).
Duchen, L. W.: The effect of ingestion of hypertonic saline on the pituitary gland in the rat: a morphological study of the pars intermedia and posterior lobe. J. Endocr. 25, 161–168 (1962).
Foster, C. L.: Relationship between ultrastructure and function in the adenohypophysis of the rabbit. In: Subcellular organization and function in endocrine tissues (ed. H. Heller and K. Lederis). Memoirs of the Society for endocrinology, no. 19, p. 125–146. Cambridge: University Press 1971.
Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T.: Catecholamines in the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. In: Frontiers in neuroendocrinology (eds. W. F. Ganong and L. Martini), p. 47–96. New York-London-Toronto: Oxford University Press 1969.
Howe, A., Maxwell, D. S.: Electron microscopy of the pars intermedia of the pituitary gland in the rat. Gen. comp. Endocr. 11, 169–185 (1968).
Kagayama, M., Ando, A., Yamamoto, T. Y.: On the epithelial lining of the cleft between pars distalis and pars intermedia in the mouse adenohypophysis. Gunma Symp. Endocr. 6, 125–136 (1969).
Knowles, F.: Evidence for a dual control, by neurosecretion, of hormone synthesis and hormone release in the pituitary of the dogfish. Scylliorhinus stellaris. Phil. Trans. B 249, 435–456 (1965).
Kobayashi, Y.: Functional morphology of the pars intermedia of the rat hypophysis as revealed with the electron microscope. I. Ultrastructural changes after dehydration. Gunma Symp. Endocr. 1, 173–181 (1964).
Kobayashi, Y.: Functional morphology of the pars intermedia of the rat hypophysis as revealed with electron microscope. II. Correlation of the pars intermedia with the hypophysio-adrenal axis. Z. Zellforsch. 68, 155–171 (1965).
Kobayashi, Y.: Functional morphology of the pars intermedia of the rat hypophysis as revealed with the electron microscope. III. Effects of dexamethasone on the pars intermedia of rats under various experimental conditions. Arch. hist. jap. 29, 105–136 (1968).
Kobayashi, Y.: Functional morphology of the pars intermedia of the rat hypophysis as revealed with the electron microscope. IV. Effects of cortico-sterone on the pars intermedia of intact and adrenalectomized rats. Gunma Symp. Endocr. 6, 107–124 (1969).
Kraicer, J., Bencosme, S.. A., Gosbee, J. L.: The pars intermedia and ACTH secretion in the rat. Fed. Proc. 30, 533 (1971).
Kurosumi, K., Matsuzawa, T., Shibasaki, S.: Electron microscope studies on the fine structure of the pars nervosa and pars intermedia, and their morphological interrelation in the normal rat hypophysis. Gen. comp. Endocr. 1, 433–452 (1961).
Naik, D. V.: Pituitary-adrenal relationship in mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, with special emphasis on the pars intermedia. Amer. Zool. 6, 518 (1966).
Naik, D. V.: Pituitary-adrenal relationships in mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, with special emphasis on the neurohypophysis and pars intermedia. Z. Zellforsch. 107, 317–342 (1970a).
Naik, D. V.: Influence of neurosecretion on activity of pars intermedia. Proc. Canad. Fed. Biol. 13, 147 (1970b).
Naik, D. V.: Reversibility of the hypertrophied hypothalamo-hypophysial neurosecretory system in mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Anat. Rec. 166, 353 (1970c).
Naik, D. V.: Hypertrophied hypothalamo-hypophysial neurosecretory system and increased vasopressor activity accompanied by the hypertrophy of the adenohypophysis in the mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Anat. Rec. 169, 385 (1971b).
Naik, D. V.: Pituitary growth hormone and its hypothalamic releasing factor in mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus associated with increased vasopressor activity. Excerpta Medica Int. National Cong. Series, no. 231, p. 35 (1971a).
Naik, D. V.: Influence of neurosecretion on the activity of median eminence and pars intermedia in hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus mice with bilateral supraoptic lesions. Z. Zellforsch. 125, 460–479 (1972a).
Naik, D. V.: Salt and water metabolism and neurohypophysial vasopressor activity in mice with hereditary nephrogenic insipidus. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) 69, 434–444 (1972b).
Naik, D. V.: Electron microscopic studies on the pars intermedia and ACTH cells of the pituitary gland in the mouse. Arch. Mexicanos de Anatomia. 39, 31 (1972c).
Naik, D. V., Kobayashi, H.: Neurohypophysial hormones in the pars nervosa of the mouse with herediatry nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Neuroendocrinology 7, 322–328 (1971).
Naik, D. V., Sokol, H.: The hypothalamo-hypophysial neurosecretory system in mice with vasopressin resistant urinary concentrating defects. Gen. comp. Endocr. 15, 59–69 (1970).
Naik, D. V., Valtin, H.: Hereditary vasopressin resistant urinary concentration defects in mice. Amer. J. Physiol. 217, 1183–1189 (1969).
Novales, R. R.: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone and the intermediate lobe of the pituitary: chemistry effects and mode of action. In: Neuroendocrinology (eds. L. Martini and W. F. Ganong), vol. 2, p. 241–259. New York-London: Academic Press 1967.
Oshima, K., Gorbman, A.: Evidence for a doubly innervated secretory unit in the anuran pars intermedia. I. Electrophysiologic studies. Gen. comp. Endocr. 13, 98–107 (1969).
Soboleva, E. L.: Changes in the intermediate lobe of the hypophysis following experimental action of the adrenals. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. USSR. (Engl. Trans.) 149, 394–397 (1963).
Stewart, A. D., Stewart, J.: Studies on the syndrome of diabetes insipidus associated with oligosyndactyly in mice. Amer. J. Physiol. 217, 1191–1198 (1969).
Stoeckel, M. E., Dellman, H. D., Porte, A., Gertner, C.: The rostral zone of the intermediate lobe of the mouse hypophysis, a zone of particular concentration of corticotrophic cells. Z. Zellforsch. 122, 310–322 (1971).
Vincent, D. A., Anand-Kumar, T. C.: Electronmicroscopic studies on the pars intermedia of the ferret. Z. Zellforsch. 99, 185–197 (1969).
Wingstrand, K. G.: Microscopic anatomy, nerve supply and blood supply of the pars intermedia. In: The pituitary gland (eds. G. W. Harris and B. T. Donovan), vol. 3, p. 1–27. London: Butterworths 1966.
Yamada, K., Yamashita, K.: An electronmicroscopic study on the possible site of production of ACTH in the anterior pituitary of mice. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 29–43 (1967).
Ziegler, B.: Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an Pars intermedia und Neurohypophyse der Ratte. Z. Zellforsch. 59, 486–506 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by MRC of Canada Grant No. MA-3759.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, D.V. Electron microscopic studies on the pars intermedia in normal and in mice with hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Z.Zellforsch 133, 415–434 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307248
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307248