Abstract
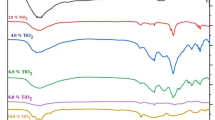
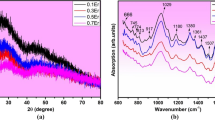
A study has been made of thermoluminescence from synthetic quartz with varying hydroxyl impurity concentrations up to approximately 300 H/106 Si which are associated with a “broad-band” IR absorption in the range 2600–3700 cm−1. These hydroxyl defects are known to be important in the hydrolytic weakening of quartz. We have found only minor differences in the glow curves of unheated crystals but significant intensity increases when “wet” crystals are heated sufficiently to cause bubble formation. It would seem that the electron traps are unaffected by the bubble formation, but the electron/luminescence centre radiative recombination probability is increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aines RD, Rossman GR (1986) Relationships between radiation damage and trace water in zircon, quartz and topaz. Am Mineral 71:1186–1193
Alonso PJ, Halliburton LE, Kohnke EE, Bossoli RB (1983) X-ray induced luminescence in crystalline SiO2. J Appl Phys 54:5369–5375
Compton AH, Allison SK (1936) X-rays in theory and experiment, 2nd edn. Van Nostrand, New York, p 802
Garlick GFJ, Gibson AF (1948) The electron trap mechanisms of luminescence in sulphide and silicate phosphors. Proc Phys Soc 60:574–590
Halperin A, Katz S (1988) The thermoluminescence and phosphorescence related to the [SiO4/Na]0 centre. J Lumin 40 and 41:341–342
Halperin A, Jani MG, Halliburton LE (1986) Correlated ESR and thermoluminescence study of the [SiO4/Li] centre in quartz. Phys Rev B 34:5702–5707
Hirsch PB (1981) Plastic deformation and electronic mechanisms in semiconductors and insulators. J Phys Colloq: C3 149–160
Hobbs BE (1981) The influence of metamorphic environment upon the deformation of minerals. Tectonophysics 78:335–383
Isoya J, Weil JA, Davies PH (1983) EPR of atomic hydrogen 1H and 2H in alpha quartz. Phys Chem Solids 44:335–343
Kats A (1962) Hydrogen in alpha quartz. Phillips Res Rep 17:133–195
Katz S, Halperin A (1988) The low temperature phophorescence and thermoluminescence of quartz crystals. J Lumin 39:137–143
Katz S, Halperin A, Ronen M (1983) Thermoluminescence from different growth sectors in synthetic quartz crystals. Proc 37th Ann Freq Control Symp: 181–184
Kekulawala KRSS, Paterson MS, Boland JN (1981) An experimental study of the role of water in quartz deformation. GeophysMonogr 24:49–60
King JC (1962) Electrolysis of synthetic quartz: Effect upon resonator performance. Proc IEE 109B suppl 22:295–301
McKeever SWS (1984) Thermoluminescence in quartz and silica. Radiat Protect Dosim 8:81–98
McKeever SWS (1985) Thermoluminescence in solids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
McLaren AC, Cook RF, Hyde ST, Tobin RC (1983) The mechanisms of the formation and growth of water bubbles and associated dislocation loops in synthetic quartz. Phys Chem Minerals 9:79–94
McLaren AC, Fitzgerald JD, Gerretsen J (1989) Dislocation nucleation and multiplication in synthetic quartz: relevance to water weakening. Phys Chem Minerals 16:465–482
Malik DM, Kohnke EE, Sibley WA (1981) Low temperature thermally stimulated luminescence of high quality quartz. J Appl Phys 52:3600–3605
Medlin WC (1962) Thermoluminescence in quartz. J Chem Phys 38:1132–1143
Newton-Howes JC, McLaren AC, Fleming RJ (1989) An investigation of the effects of the hydroxyl concentration and bubble formation on the electrical conductivity of synthetic quartz. Tectonophysics 158:335–342
Nuttall RHD, Weil JA (1981) The magnetic properties of the oxygen-hole aluminium centers in crystalline SiO2. Can J Phys 59:1696–1718
Paterson MS (1982) The determination of hydroxyl by infrared absorption in quartz, silicate glasses and similar materials. Bull Mineral 105:20–29
Randall JT, Wilkins MHF (1945) Phosphorescence and electron traps. Proc R Soc A184:366–407
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newton-Howes, J.C., Fleming, R.J. Thermoluminescence and hydroxyl defects associated with broad-band infra red absorption in synthetic quartz. Phys Chem Minerals 17, 27–33 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209222
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209222