Abstract
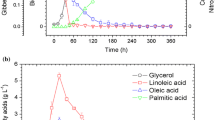
Metabolites (both intra- and extracellular) involved in penicillin biosynthesis were measured during fed-batch cultivations with a high-yielding strain of Penicillium chrysogenum. The fed-batch cultivations were carried out on a complex medium containing corn steep liqour. Three distinct phases were observed: (a) a rapid growth phase where free amino acids present in the medium are metabolized, (b) a linear growth phase, and (c) a stationary phase. The specific penicillin production (r p) is initially high and, during the rapid growth phase, it increases slightly. During the linear growth phase r p is approximately constant [4–6 mg penicillin V (g dry weight)−1 h−1 depending on the operating conditions], whereas it decreases during the stationary phase. During the cultivations the tripeptide Aad-Cys-Val (the first metabolite in penicillin biosynthesis) and 8-hydroxypenillic acid (formed by carboxylation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid, 6-APA) were found to accumulate in the medium, whereas the concentrations of isopenicillin N and 6-APA were found to be approximately constant and low. About 3% of the Aad-Cys-Val formed in the first step of the penicillin biosynthetic pathway is lost to the medium and 4% of the isopenicillin N formed in the second step of the pathway is lost as extracellular isopenicillin N, 6-APA or 8-hydroxypenillic acid. Also the cyclic form of α-aminoadipic acid, 6-oxopiperidine-2-carboxylic acid, was found to accumulate in the medium and it was found to be formed in an approximately constant ratio to penicillin V of 6 mol/100 mol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez E, Cantoral JM, Barredo, JL, Díez B, Martin JF (1987) Purification to homogeneity and characterization of acyl coenzyme A:6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase of Penicillium chrysogenum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:1675–1682
Alvarez E, Meesschaert B, Montenegro E, Gutiérrez S, Díez B, Barredo JL, Martin JF (1993) The isopenicillin-N acyltransferase, of penicillin chrysogenum has isopenicillin-N aminodohydrolase, 6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase and penicillin amidase activities, all of which are encoded by the single penDE gene. Eur J Biochem 215:323–332
Banko G, Demain AL, Wolfe S (1987) δ-(L-α-Aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase (ACV synthetase): a multifunctional enzyme with broad substrate specificity for the synthesis of penicillin and cephalosporin precursors. J Am Chem Soc 109:2858–2860
Brundidge SP, Gaeta FCA, Hook DJ, Sapino C, Elander RP, Morin RB (1980) Association of 6-oxo-piperidine-2-carboxylic acid with penicillin V production in Penicillium chrysogenum fermentations. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 23:1348–1351
Carlsen M, Meier H, Lantreibecq F, Johansen CL, Rong WM, Nielsen J (1993) On-line monitoring of penicillin V during penicillin fementations: a comparison of two different methods based on FIA. Anal Chim Acta 279:51–58
Christensen LH, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1991) Delay and dispersion in an in-situ membrane probe for bioreactors. Chem Eng Sic 46:3304–3307
Christensen LH, Mandrup G, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1994a) A robust LC method for studying the penicillin fermentation. Anal Chim Acta 296:51–62
Christensen LH, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1994b) Degradation of penicillin V in fermentation media, Biotechnol Bioeng 44, 165–169
Diez B, Gutiérrez S, Barredo JL, Solingen P Van, Voort LHM van der, Martin JF (1990) The cluster of penicillin biosynthetic genes. J Biol Chem 265:16356–16365
Erickson RC, Bennett RE (1965) Penicillin acylase activity of Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Microbiol 13:738–742
Gil-Espinosa S, Meesschaert BD, Matin JF (1993) Purification and characterization of a penicillin V acylase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Proceedings of the European Congress on Biotechnology IV, Florence, WE144
Hersbach GJM, Beek CP van der, Dijck PWM van (1984) The penicillins: properties, biosynthesis and fermentation. In: Vandamme EJ (ed) Biotechnology of industrial antibiotics. Dekker, New York, pp 45–140
Jaklitsch WM, Hampel W, Röhr M, Kubicek CP (1986) α-Aminoadipate pool concentration and penicillin biosynthesis in strains of Penicillium chrysogenum.Can J Microbiol 32:473–480
Johansen CL (1993) Monitoring and modelling of the penicillin fermentation. Ph D thesis. Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby
Jørgensen HS (1993) Metabolic fluxes in Penicillium chrysogenum. Ph D thesis. Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby
Lendenfeld T, Ghali D, Wolschek M, Kubicek-Pranz EM Kubicek CP (1993) Subcellular compartmentation of penicillin biosynthesis on Penicillium chrysogenum. J Biol Chem 268:665–671
Martin JF, Liras P (1989) Enzymes involved in penicillin, cephalosporin and cephamycin biosynthesis. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 39:153–188
Martinez-Blanco H, Reglero A, Fernández-Valverde M, Ferrero MA, Moreno MA, Peñalva MA, Leungo JM (1992) Isolation and characterization of the acetyl-CoA synthetase from Penicillium chrysogenum. J Biol Chem 267:5474–5481
Martin-Villacorta J, Reglero A, Luengo JM (1991) Biosynthesis of methoxybenzyl penicillins. Bio-technol Forum Europe 8:60–62
Müller WH, Krift TP van der, Krouwer AJJ, Wösten HAB, Voort LHM van der, Smaal EB, Verkleij AJ (1991) Localization of the pathway of the penicillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum. EMBO J 10:489–495
Nielsen J, Johansen CL Villadsen J (1994) Culture fluorescence measurements during batch and fed-batch cultivations with Penicillium chrysogenum, J Biotechnol 38:51–62
Nüesch J, Heim J, Treichler H-J (1987) The biosynthesis of sulfur-containing ß-lactams antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:51–75
Ramos FR, Lopez-Nieto M, Martin JF (1985) Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme that convert ACV to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:380–387
White RL, John E-MM, Baldwin JE, Abraham EP (1982) Stoichiometry of oxygen consumption in the biosynthesis of isopenicillin from a tripeptide. Biochem J 203:791–793
Zhang J, Demain AL (1992) ACV synthetase. CRC Crit Rev Bio technol 12:245–260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jørgensen, H., Nielsen, J., Villadsen, J. et al. Analysis of penicillin V biosynthesis during fed-batch cultivations with a high-yielding strain of Penicillium chrysogenum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 123–130 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170633
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170633