Summary
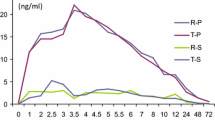
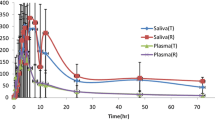
A previously described GLC method has been modified and applied to measurement of antipyrine levels in plasma, blood and saliva of man following administration of a single oral dose (10 mg/kg). The levels in blood and saliva were comparable to those in plasma at every time studied. The half life of antipyrine determined in blood, plasma or saliva in any given individual was similar. The intersubject variation in half-life was about two-fold (n=5). Antipyrine levels in saliva were not affected by the rate of saliva flow when collections were made continuously for 20 minutes. This study has demonstrated that kinetic data about antipyrine comparable to that from plasma may also be obtained from readily accessible tissue fluids, such as saliva and capillary blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vesell, E.S., Page, J.G.: Genetic control of drug levels in man: Antipyrine. Science161, 72–73 (1968)
Vesell, E.S., Page, J.G.: Genetic control of the phenobarbital-induced shortening of plasma antipyrine half-lives in man. J. clin. Invest.48, 2202–2209 (1969)
Kolmodin, B., Azarnoff, D.L., Sjöqvist, F.: Effect of environmental factors on drug metabolism: decreased plasma half-life of antipyrine in workers exposed to chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.10, 638–642 (1969)
Elfström, J., Lindgren, S.: Disappearance of phenazone from plasma in patients with obstructive jaundice. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 467–471 (1974)
Vesell, E.S., Passananti, G.T., Lee, C.H.: Impairment of drug metabolism by disulfiram in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.12, 785–792 (1971)
O'Malley, K., Stevenson, I.H., Crooks, J.: Impairment of human drug metabolism by oral contraceptive steroids. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.13, 552–557 (1972)
Soberman, R., Brodie, B.B., Levy, B.B., Axelrod, J., Hallander, V., Steele, J.M.: The use of antipyrine in the measurement of total body water in man. J. biol. Chem.179, 31–42 (1949)
Huffman, D.H., Sheeman, D.W., Azarnoff, D.L.: Correlation of the plasma elimination of antipyrine and the appearance of 4-hydroxy antipyrine in the urine of man. Biochem. Pharmacol.23, 197–201 (1974)
Buch Andreasen, P., Rabøl, A., Tønnesen, K., Keiding, S.: Michaelis-Menten kinetics of phenazone by the isolated perfused pig liver. Abstr. 6th Int. Congr. Pharmacol. 1975
Lindgren, S., Collste, P., Norlander, B., Sjöqvist, F.: Gas chromatographic assessment of the reproducibility of phenazone plasma half-life in young healthy volunteers. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.7, 381–385 (1974)
Rawlins, M.D., Collste, P., Bertilsson, L., Palmér, L.: Distribution and elimination kinetics of carbamazepine in man. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.8, 91–96 (1975)
De Angelis, R.L., Welch, R.M.: The salivary half-life of antipyrine as a convenient measure of drug metabolism in man. Fed. Proc.33, 534 (1974)
Shah, V.P., Riegelman, S.: GLC determination of theophylline in biological fluids. J. pharm. Sci.63, 1283–1285 (1974)
Levy, G., Ellis, E.F., Koysooko, R.: Indirect plasma-theophylline monitoring in asthmatic children by determination of theophylline concentration in saliva. Pediatrics53, 873–876 (1974)
Koysooko, R., Ellis, E.F., Levy, G.: Relationship between theophylline concentration in plasma and saliva of man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.15, 454–460 (1974)
Glynn, J.P., Boxtain, W.: Salivary excretion of paracetamol in man. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.25, 420–421 (1973)
Graham, G., Rowland, M.: Application of salivary salicylate data to biopharmaceutical studies of salicylates. J. pharm. Sci.61, 1210–1222 (1972)
Bochner, F., Hooper, W.D., Sutherland, J.M., Eadie, M.J., Tyrer, J.H.: Diphenylhydantoin concentrations in saliva. Arch. Neurol.31, 57–59 (1974)
Jusko, W.J., Gerbracht, L., Golden, L.H., Koup, J.R.: Digoxin concentrations in serum and saliva. Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol.10, 189–192 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Boxtel, C.J., Wilson, J.T., Lindgren, S. et al. Comparison of the half-life of antipyrine in plasma, whole blood and saliva of man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9, 327–332 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561668
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561668