Summary
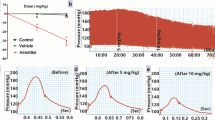
Intravenous etilefrine increases the pulse rate, cardiac output, stroke volume, central venous pressure and mean arterial pressure of healthy individuals. Peripheral vascular resistance falls during the infusion of 1 – 8 mg etilefrine but begins to rise at higher dosage. Marked falls in pulse rate, cardiac output, stroke volume and peripheral bloodflow, accompanied by rises in mean arterial pressure, occur when etilefrine is infused after administration of intravenous propranolol 2,5 mg. These findings indicate that etilefrine has both β1 and α adrenergic effects in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aperia, A.: Total peripheral resistance formula. Scand. Arch. Physiol.16 (Suppl.), 1 (1940)
Carrera, A.L., Aguilera, A.M.: Algunos effectos circulatorios de la m− oxifenil etanol etilmaina y sus modificaciones por el bloqueo α y β adrenergico. Arch. Inst. Cardiol. (Mexico)43 279–287 (1973)
Limbourg, von P., Just, H., Lang, K.F.: Positive inotrope Wirkung von Etilefrinhydrochlorid (EffortilR). Kardiol.586 1 (1973)
Mellander, S.: Comparitive effects of acetylcholine, butyl-nor-synephrine (Vasculat), noradrenaline, and ethyl-adrianol (Effortil) on resistance, capacitance and precapillary sphincter vessels and capillary filtration in cat skeletal muscle. Angiologia3 77–99 (1966)
Nusser, E., Donath, H., Russ, W.: Accion circulatorio del Effortil depot en pacientes con un trastorno regulador hipotonico de la circulacion. Med. Welt. (Berl.) 824–1827 (1965)
Offermeier, J., Dreyer, A.C.: A comparison of the effects of noradrenaline, adrenaline and some phenylephrine derivatives on alpha-, beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors. S.A. med. J.45 265–267 (1971)
Tarnow, J., Brückner, J.B., Eberlein, H.G., Patschke, D., Reinecke, A., Schmicke, P.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Beeinflussung der Hämodynamik in tiefer Halothannarkose durch Dopamin, Glucagon, Effortil, Noradrenalin und Dextran. Anaesthesist22 8–15 (1973)
Williams, J.C.P., O'Donovan, T.P.B., Wood, E.H.: A method for the calculation of areas under indicator dilution curves. J. appl. Physiol.21 695–699 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coleman, A.J., Leary, W.P. & Asmal, A.C. The cardiovascular effects of etilefrine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8, 41–45 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616413
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616413