Summary
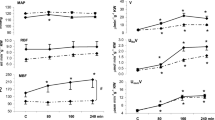
To evaluate the role of adrenergic mechanisms in the acute response of renin to furosemide, plasma renin activity (PRA) and plasma catecholamine concentrations were measured for 3 h after i.v. administration of furosemide 1 mg/kg to 8 patients with mild essential hypertension. Furosemide induced a prompt and long-lasting increase in renin, with PRA more than doubled at all times. The increase in PRA within the first 30 min paralleled the peak increases in urinary water and sodium flow rates, and significant decreases in plasma volume and central venous pressure. There was no change in plasma catecholamine concentrations. Plasma noradrenaline was increased significantly at 60 min and adrenaline at 90 min, once furosemide had induced a marked loss of body-fluid and ∼65% decrease in central venous pressure. Both catecholamines remained elevated until the end of the study, whereas urinary water and sodium flow rates had returned to their pre-treatment values by 150 min. Mean blood pressure was essentially unchanged throughout the study, whereas heart rate increased significantly after 90 min. The findings suggest that in mildly hypertensive patients adrenergic mechanisms are not involved in the initial renin response to furosemide, but they come into play later, probably as a result of reflex sympathetic activation triggered by marked volume depletion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keeton TK, Cambell WB (1981) The pharmacologic alteration of renin release. Pharmacol Rev 31: 81–227
Imbs JL, Schmidt M, Velly J, Schwartz J (1977) Comparison of the effects of two groups of diuretics on renin secretion in the anesthetized dog. Clin Sci Molec Med 52: 171–182
Callingham BA, Barrand MA (1979) The catecholamines. Adrenaline; noradrenaline; dopamine. In: Gray CH, James VHT (eds) Hormones in blood, vol. 2. Academic Press, London, pp 143–207
Muiesan G, Alicandri C, Agabiti-Rosei E, Motolese M, Valori C (1975) Effect of oxprenolol on catecholamines and plasma renin activity: acute response to furosemide in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci Molec Med 48: 85s-88s
Elmgreen J, Hesse B, Christensen NJ (1981) Lack of adrenergic influence on renin release after furosemide in normal man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20: 339–342
Hesse B, Nielsen I (1976) Unimpaired plasma renin increase after intravenous furosemide during saline replacement. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 36: 23–28
Rosenthal J, Raptis S, Escobar-Jimenez F, Pfeiffer EF (1976) Inhibition of furosemide-induced hyperreninemia by growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone in man. Lancet 1: 772–774
Zimlichman R, Rosler A, Rabinowitz D (1974) Renin response to furosemide and hypertonic saline infusion. Isr J Med Sci 10: 1562–1566
Frohlic RB, Tarazi ED, Dustan HP (1969) Re-examination of the hemodynamics of hypertension. Am J Med Sci 257: 9–17
Goldstein DS (1981) Plasma norepinephrine in essential hypertension. A study of studies. Hypertension 3: 48–52
Mancia G, Leonetti G, Picotti GB, Ferrari A, Galva MD, Gregorini L, Parati G, Pomidossi G, Ravazzani C, Sala C, Zanchetti A (1979) Plasma catecholamines and blood pressure responses to the carotid baroreceptor reflex in essential hypertension. Clin Sci 57: 165s-167s
Trimarco B, Volpe M, Ricciardelli B, Picotti GB, Galva MD, Petracca R, Condorelli M (1983) Studies of the mechanisms underlying impairment of beta-adrenoceptor mediated effects in human hypertension. Hypertension (in press)
Da Prada M, Zürcher G (1976) Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci 19: 1161–1174
Bühler HU, Da Prada M, Haefely W, Picotty GB (1978) Plasma adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine in man and different animal species. J Physiol 276: 311–320
Boyd GW, Fitz AE, Adamson AR, Pearts WS (1969) Radioimmunoassay determination of plasma renin activity. Lancet 1: 215–217
Davies R, Wiggins R, Slater JDH, Geddes D (1978) Nature of the adrenoceptor that mediates renin release in man. Cardiovasc Med 3: 571–575
Osborn JL, Hook JB, Bailie MD (1977) Control of renin release. Effects of d-propranolol and renal denervation on furosemide-induced renin release in the dog. Circ Res 41: 481–486
Brown MJ, Jenner DA, Allison DJ, Dollery CT (1981) Variations in individual organ release of noradrenaline measured by an improved radioenzymatic technique: Limitations of peripheral venous measurements in the assessment of sympathetic nervous activity. Clin Sci 61: 585–590
Leonetti G, Mayer G, Morganti A, Terzoli L, Zanchetti A, Bianchetti G, Di Salle E, Morselli PL, Chidsey CA (1975) Hypotensive and renin-suppressing activities of propranolol in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci Molec Med 48: 491–499
Stella A, Zanchetti A (1977) Effects of renal denervation on renin release in response to tilting and furosemide. Am J Physiol 232: H500-H507
Mancia G, Lorenz RR, Shepherd JT (1976) Reflex control of circulation by heart and lungs. In: Guyton AC, Cowley AW (eds) International review of science. Cardiovascular physiology II, vol. 9. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 111–144
Kircheim HR (1976) Systemic arterial baroreceptor reflexes. Physiol Rev 56: 100–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cannella, G., Galva, M.D., Campanini, M. et al. Sequential changes in plasma renin activity and plasma catecholamines in mildly hypertensive patients during acute, furosemide-induced body-fluid loss. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25, 299–302 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01037937
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01037937