Summary
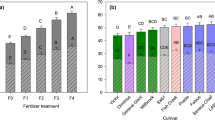
The energy characteristics of hybrid willow (Salix spp.) were evaluated to improve the selection and breeding program of this short-rotation species. The differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) has proven to be a valuable tool over the conventional adiabatic oxygen bomb calorimeter (AOB) based on its accounting for losses due to dissipated heat, incomplete combustion of pyrolysis and the loss of the heat of vaporization. The average heat content of the four unextracted hybrid willow determined by AOB and DSC was 4635 cal/g and 1609 cal/g respectively. Clone SP-3 is the superior tree based on its energy content per volume of biomass and energy content per square meter of land. Chemical composition of the wood was determined to elucidate its effects on the pyrolysis and combustion. Fuels with high extractive and lignin contents will not necessarily liberate the highest energy when burned. The ash, although representing only a minor proportion by weight, appears to be a major determinant in the combustion behaviour of a material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society for Testing and Materials, 1979: Standard method for preparation of extractive-free wood. ASTM D1105-56, pp. 367–368. Philadelphia, Pa.
American Society for Testing and Materials, 1977: Standard test method for lignin in wood. ASTM D1106-56, pp. 369–372. Philadelphia, Pa.
Browne, F. L. 1958: Theories of the combustion of wood and its control. Res. Pap. #2136, pp. 59. Wi: US Dept. of Ag., Forest Service
Browning, B. L. 1967: Methods of wood chemistry. Vol. II, pp. 385–823. New York: Interscience-Wiley
Dupont 990 Differential Scanning Calorimeter, 1974. Product Bulletin. Dupont
Dupont Instruments, 1974. Application Brief-Thermal Analysis. Heat content of coal. No. TA-55
Fong, P.; Ross, R. A. 1980: Pyrolysis of white birch in nitrogen and helium up to 900°C and 600 kPa in the presence of water vapour, Zinc (II) Chromite and Iron (III) Oxide. Wood Sci. 13 (2): 87–94
Huffman, D. 1979: Availability and fuel characteristics of eastern Canadian sawmill residues. Proceedings Energy Seminar, pp. 15–24. Halifax, Canada
Krigstin, S. G. 1985: Basic information on the factors responsible for the high energy in forest fuels. Master Thesis. Faculty of Forestry, The University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Kryla, J. M. 1983: Analysis and characterization of forest materials as a fuel source, pp. 22. Forintek Canada Corp., Eastern Lab., Ottawa, Canada
Maurice, T. M.; Page, C. M. 1983: Characterizing foods with thermal analysis. Canadian Research: 19–21
Pearl, I. A.; Busche, R. L. 1960: Studies on the chemistry of aspenwood, Part XI: The Klason lignin determination as applied to aspenwood with special reference to acid-soluble lignin. Tappi 43 (12): 961–970
Philipot, C. W. 1970: Influence of mineral content on the pyrolysis of plant materials. For. Sci. 16 (4): 461
Poole, H. 1907: The calorific power of fuels, pp. 268. John Wiley and Sons
Shafizadeh, F. 1978: Combustion, combustibility and heat release of forest fuels. AIChE Symposium Series: 74(177): 76–82
Shafizadeh, F. 1981: Basic principles of direct combustion. In: Safer, S. S., Zaborsky, C. R. (Ed.): Biomass conversion processes for energy and fuels, pp. 103–124. Plenum Publishing Corp
Shafizadeh, F. 1982: Introduction to pyrolysis of biomass. J. of Anal, and App. Pyrolysis 3:283–305
Shafizadeh, F.; Chin, P. P. S. 1977: Thermal deterioration of wood. In: Goldstein, I. S. (Ed.), ACS Symposium Series 43: Wood Technology: Chemical Aspects, pp. 57–81. Washington D.C.: ACS Press
Shafizadeh, F.; Chin, P. P. S.; DeGroot, W F. 1977: Effective heat content of green forest fuels. Forest Sci. 23 (1): 81–89
Susott, R. A. 1982: Differential scanning calorimetry of forest fuels. Forest Sci. 28 (4): 839–851
Susott, R. A. 1980: Thermal behaviour of conifer needle extractive. Forest Sci. 26 (3): 347–360
Tang, W. K. 1972: Forest products. In: MacKenzie, R.C. (Ed.): Differential thermal analysis. Vol. II, pp. 607. London: Academic Press
Tillman, D. A.; Rossi, A. J.; Kitto, W. D. 1981: Wood combustion — principles, processes and economics. In: Properties of wood fuels, pp. 17–47. New York: Academic Press
Wang, S.; Huffman, J. B.; Littell, R. C. 1981: Characterization of melaleuca biomass as a fuel for direct combustion. Wood Sci. 13 (4): 216–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Authors would like to thank Dr. L. Williams of the Department of Chemistry Engineering and Applied Chemistry for the unrestricted use of the DSC, without which this work could not have been completed. I would also like to extend my appreciation to Dr. S. K. Konar for his assistance throughout this work and Mr. D. Charles for facilitating the laboratory work. Our appreciation is extended to the Natural Science and Engineering Council for supporting this research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krigstin, S.G., Wong, B.M. & Roy, D.N. The contribution of the chemical components in juvenile hybrid Salix spp. to its total energy output. Wood Sci.Technol. 27, 309–320 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195310
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195310