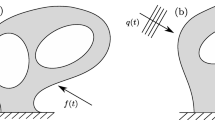
Abstract
This paper is devoted to problems of structuralacoustic coupling with emphasis on analysis, design sensitivity analysis and optimization. The paper is divided into two parts, and it is the aim of Part I to (i) give a brief survey of recent developments in sensitivity analysis and sound emission and NVH (Noise, Vibration and Harshness) design of acoustically loaded structures, and (ii) discuss alternative objective functions and optimization formulations for structural acoustics. The aims of Part II are to (i) present consistent numerical techniques commonly used for treatment of coupled structural and acoustic dynamics, (ii) use the structural optimization tool ODESSY for solution of several coupled problems, and (iii) compare the numerical efficiency of alternative techniques and the relevance of selected objective functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Constans, E.W.; Belegundu, A.D. 1996: Minimizing radiated sound from vibrating shells.Proc. 6-th AIAA/NASA/USAF Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Symp. (held in Bellevue, WA), pp. 1106–1115. (To appear inAIAA J.)
Coyette, J.P. 1992: Application of a new wave envelope formulation to exterior acoustic and elastoacoustic problems.J. de Physique IV 2, 1069–1072
Cunefare, K.A.; Koopman, G.H. 1991: A boundary element approach to optimization of active noise control sources on three-dimensional structures.ASME J. Vibr. & Acoustics 113, 387–394
Cunefare, K.A.; Koopmann, G.H. 1992: Acoustical design sensitivity for structural radiators,Trans. ASME, J. Vibr. & Acoustics 114, 179–186
Everstine, G.G.; Henderson, F.M. 1990: Coupled finite element/boundary element approach for fluid-structure interaction.J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 87, 1938–1948
Fahnline, J.B.; Koopmann, G.H. 1997:Designing quiet structures: A sound power minimization approach. London: Academic Press
Filippi, P.J.T.; Habault, D. 1989: Sound radiation by a baffled cylindrical shell: a numerical technique based on boundary integral equations. Parts I and II.J. Sound & Vibr. 131, 13–24; 25–36
Hahn, S.H.; Ferry A.A. 1994: Sensitivity analysis of coupled structural-acoustic problems using pertubations techniques.Proc. 3-rd Cong. on Air- and Structure-Borne Sound and Vibration, pp. 1799–1805
Jeans, R.; Mathews, I.C. 1991: Use of Lanczoz vectors in structural acoustic problems.NCA-12/AMD 128 Structural Acoustics ASME, 101–112
Jo, C.H.; Elliot, S.J. 1992: Active noise control of low frequency sound transmission between rooms.JASA 92, 1461–1472
Kliaus, K.M. 1996: Acoustic radiation by low-frequency vibration of slender source in fluid medium.Proc. 4-th Int. Cong. on Structure-Borne Sound and Vibration, pp. 931–936
Lamancusa, J.S. 1993: Numerical optimization techniques for structural-acoustic design of rectangular plates.Comp. & Struct. 48, 661–675
Ma, Z.D.; Hagiwara, I. 1991: Sensitivity analysis methods for coupled acoustic-structural systems,AIAA J. 29, 1787–1801
Matsumoto, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, Y. 1995: Design sensitivity analysis of steady-state acoustic problems using boundary integral equation formulation.JSME Int. J., Series C 38, 9–16
Mollo, C.G.; Bernard, R.J. 1989: Generalized methods of predicting optimal performance of active noise controlers.AIAA J. 27, 1473–1478
Nefske, D.J.; Sung, S.H. 1984: A coupled structural-acoustic finite element model for vehicle noise interior analysis.Trans. ASME 106, 314–31
Nefske, D.J.; Sung, S.H. 1986: Component mode synthesis of a vehicle structural-acoustic system model.AIAA J. 24, 1021–1026
Olson, L.G.: Bathe, K.-I. 1985: Analysis of fluid-structure interactions. A direct symmetric coupled formulation based on the fluid velocity potential.Comp. & Struct. 21, 21–32
Pal, C.; Hagiwara, I. 1994: Optimization of noise level reduction by truncated modal coupled structural-acoustic sensitivity analysis.JSME Int. J., Series C 37, 246–251
Salagame, R.R.; Belegundu, A.D.; Koopman, G.H. 1995: Analytical sensitivity of acoustic power radiated from plates.Trans. ASME, J. Vibr. & Acoustics 117, 43–48
Sandberg, G. 1995: A new strategy for solving fluid-structure problems.Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engrg. 38, 357–370
Sandberg, J.; Goransson, P. 1988: A symmetric finite element formulation for acoustic fluid-structure interaction analysis.J. Sound & Vibr. 123, 507–515
Schenck, H.A. 1968: Improved integral formulation for acoustic radiation problems.J. Acoust. Soc. Amer. 44, 41–58
Seybert, A.F. 1987: A note on methods for circumventing nonuniqueness when using integral equations.J. Sound & Vibr. 115, 171–172
Seybert, A.F.; Wu, T.W. 1985: An advanced computational method for radiation and scattering of acoustic waves in three dimensions.J. Acous. Soc. America 79, 362–368
Seybert, A.F.; Wu, T.W.; Li, W.L. 1991: A coupled FEM/BEM for fluid-structure interaction using Ritz vectors and eigenvectors.NCA 12/AMD 128.Structural Acoustics ASME, 171–178
Shaw, R.P.; Falby, W. 1978: F.E.-B.I.E.: combination of the finite element and boundary integral methods.J. Comp. & Fluids 6, 153–160
Slepyan, L.I.; Sorokin, S.V. 1995: Analysis of structural-acoustic coupling problems by a two-level boundary integral equations method. Parts 1 and 2.J. Sound & Vibr. 184, 195–211, 213–228
Smidt, D.C.; Bernard, R.J. 1992: Computation of acoustic shape design using a boundary element method.Trans. AMSE, J. Vibr. & Acous. 114, 127–132
Sorokin, S.V. 1993: A sensitivity analysis of thin-walled vibrating structures in the structural-acoustic coupling formulation.Proc. 1-st Cong. “Structural Optimization”, pp. 213–220
Sorokin, S.V. 1995: Analysis of vibrations of a spatial acoustic system by the boundary integral equations method.J. Sound & Vibr. 180, 657–667
St. Pierre, R.L.; Koopman, G.H. 1995: A design method for minimizing the sound power radiated from plates by adding optimally sized, discrete masses.Trans. ASME, J. Vibr. & Acous. 117, 243–251
Tanaka, M.; Masuda, Y. 1987: Boundary element analysis of some structural-acoustic coupling problems-theory and application of BEM.Proc. 1-st Japan-China Symp., pp. 407–419
Volkov, E.A.; Postnov, V.A. 1984: Numerical methods in analyses of marine structures.Trans. Leningrad Shipbuilding Inst., pp. 7–21 (in Russian)
Vorovich, I.I.; Tsionskij, A.Y.; Yudin, A.S. 1983: Method of natural modes for forced vibrations of stiffened shells of revolution in a liquid.Akusticheskij Zhurnal 29, 744–748 (in Russian)
Wang, S.; Hung, H.H.; Hwang, H.Y.; Park, Y.; Choi, K. 1994: Design sensitivity analysis of NVH of vehicle body structure.AIAA Paper 94-4385 CP, 1192–1202
Wilson, E.L.; Yuan, M.W.; Dickens, J.M. 1982: Dynamic analysis by direct superposi-tion of Ritz vectors.Earthquake Engrg. & Struct. Dynamics 10, 813–821
Yang, T.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Ling, S.F. 1995: A boundary-element-based optimization technique for design of enclosure acoustical treatments.J. ASA 98, 302–312
Xia, H.; Humar, J.L. 1992: Frequency dependent Ritz vectors.Earthquake Engrg. & Struct. Dynamics 21, 215–231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, S.T., Sorokin, S.V. & Olhoff, N. On analysis and optimization in structural acoustics — Part I: Problem formulation and solution techniques. Structural Optimization 16, 83–95 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01202818
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01202818