Summary
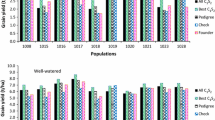
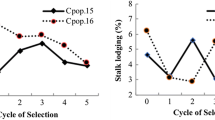
The maize (Zea mays L.) improvement program of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) develops broad-based maize populations and, until recently, improved all of them through full-sib family selection with international testing. The purpose of this study was to estimate the genetic and genetic × environment variance components for ten of those populations and to measure expected yield improvement from full-sib selection. Mean yield ranged from 3.35–6.81 t ha−1. For five populations the average yield in the last cycle was higher than in the initial cycles. Several populations showed no improvement or yielded less in the final cycle of selection, either because selection intensity was low or because strong selection pressure was applied simultaneously for several traits. Variation resulting from differences among family means within cycles and from interaction between families and locations within cycles were significant in all populations and cycles. Results indicate that variability among full-sib families was maintained throughout the cycles for all populations. The large σ 2ge /σ 2g ratio shown by most populations suggests that yield response per cycle could be maximized if the environments in which progenies are tested were subdivided and classified into similar subsets. The proportion of the predicted response realized in improved yield varied for each population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen FL, Comstock RE, Rasmusson DC (1978) Optimum environments for yields testing. Crop Sci 18:747–751
CIMMYT (1982) CIMMYT's maize program: An overview. CIMMYT, El Batan, Mexico
CIMMYT (1984) CIMMYT report on maize improvement 1980–81. CIMMYT, El Batan, Mexico
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1957) Experimental designs, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Comstock RE, Moll RH (1963) Genotype-environment interaction. In: Hanson WD, Robinson HF (eds) Statistical genetics and plant breeding. Nat Acad Sci — Nat Res Council, Washington/DC, pp 164–196
Crossa J, Gardner CO (1987) Introgression of an exotic germplasm for improving an adapted maize population. Crop Sci 27:187–190
Gardner CO (1978) Population improvement in maize. In: Walden DB (ed) Maize breeding and genetics. Wiley, New York, pp 207–228
Hallauer AR (1984) Reciprocal full-sib selection in maize. Crop Sci 24:755–759
Hallauer AR (1985) Compendium of recurrent selection methods and their application. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 3:1–33
Hallauer AR, Miranda JB (1981) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Moll RH, Smith OS (1981) Genetic variances and selection response in an advanced generation of a hybrid of widely divergent populations of maize. Crop Sci 21:387–391
Moll RH, Stuber CW (1971) Comparisons of response to alternative selection procedures initiated with two populations of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 11:706–710
Paliwal RL, Sprague EW (1982) Improving adaptation and yield dependability in maize in the developing world. CIMMYT Reprint Series, El Batan Mexico
Pandey S, Diallo AO, Islam TMT, Deutsch J (1986) Progress from selection in eight tropical maize populations using international testing. Crop Sci 26:879–884
Pandey S, Diallo AO, Islam TMT, Deutsch J (1987) Response to full-sib selection in four medium maturity maize populations. Crop Sci 27:617–622
Reeder LR, Hallauer AR, Lamkey KR (1987) Estimation of genetic variability on two maize populations. Hered 78:372–376
Sprague GF, Eberhart SA (1977) Corn Breeding. In: Sprague GF (ed) Corn and Corn Improvement. American Society of Agronomy, Madison/WI, pp 305–362
Vasal SK, Ortega A, Pandey S (1982) CIMMYT's maize germplasm management, improvement, and utilization program. CIMMYT Reprint Series, El Batan, Mexico
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. R. Hallauer
Journal Paper No. 8640, Nebraska Agric. Res. Div. Project No. 12-159. Research was supported in part by USAID/USDA/ CSRS Research Grant No. 86-CRSR-2-2789
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crossa, J., Gardner, C.O. Predicted and realized grain yield responses to full-sib family selection in CIMMYT maize (Zea mays L.) populations. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 77, 33–38 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292312
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292312