Abstract
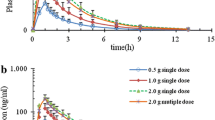
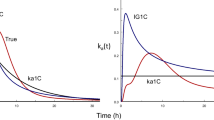
This study examined the absorption kinetics of cefatrizine, an amino-β-lactam antibiotic, after oral administration of a single 500-mg dose to 12 healthy volunteers. Plasma concentrations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography. The plots of the percentage of drug unabsorbed and the apparent rate of cefatrizine absorption as a function of time showed, first, a delay and, then, an almost constant rate of absorption with a tendency to move toward first-order kinetics at the end of the process. Three compartmental models incorporating a lag time and first-order elimination kinetics, but differing in their input rate, were used for analysis of the time course of cefatrizine plasma concentrations. The model with first-order absorption kinetics was clearly inadequate. The results were improved with the model for which the rate of absorption is constant, but a model incorporating saturable absorption kinetics of the Michaelis-Menten type improved the fit further. This last model was statistically superior to the constant-rate input model in 6 out of 12 subjects, according to the likelihood-ratio method. Because of the innovative feature of the model incorporating the Michaelis-Menten equation, simulations of the effect of altering the model parameters and the dose administered on the concentration-time profile, were performed. Different hypotheses which might explain why cefatrizine absorption kinetics fits the Michaelis-Menten equation were examined. The observation of saturable absorption kinetics is consistent with a carrier-mediated transport previously reported to occur in the gastrointestinal tract of rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Rowland and T. N. Tozer.Clinical Pharmacokinetics: Concepts and Applications, 2nd ed., Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, 1989, p. 34.
P. J. McNamara, W. A. Colburn, and M. Gibaldi. Absorption kinetics of hydroflumethiazide.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 18:190 (1978).
M. Ehrnebo, S. O. Nilsson, and L. O. Boréus. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin and its prodrugs bacampicillin and pivampicillin in man.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:429–451 (1979).
H. Ehrsson, S. O. Nilsson, M. Ehrnebo, I. Wallin, and G. Wennerstein. Effect of food on kinetics of 8-methoxsalen.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 25:167–171 (1979).
J. P. Reymond, J. L. Steimer, and W. Niederberger. On the dose dependency of cyclosporin A absorption and disposition in healthy volunteers.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 16:331–353 (1988).
E. Krüger-Thiemer. Kinetic aspects of absorption, distribution and elimination of drugs. InKinetics of Drug Action, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1977, p. 98.
S. Shadomy, G. Wagner, and M. Caver. In vitro activities of five oral cephalosporins against aerobic pathogenic bacteria.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 12:609–613 (1977).
J. P. Santella and B. Tanrisever. Cefatrizine, a clinical overview.Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 11:441–446 (1985).
V. Mastrandrea. Pharmacokinetics of ceftrizine after oral administration in human volunteers.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 5:319–323 (1985).
R. C. Gaver and G. Deeb. Disposition of carbon-14 labelled cefatrizine in man.Drug Metab. Dispos. 8:157–162 (1980).
M. Pfeffer, R. C. Gaver, and J. Ximenez. Human intravenous pharmacokinetics and absolute oral bioavailability of cefatrizine.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24:915–920 (1983).
W. Couet, B. G. Reigner, M. A. Lefebvre, J. Bizouard, and J. B. Fourtillan. Pharmacocinétique de la cefatrizine administrée en doses répétées.Pathol. Biol. 36:513–516 (1988).
T. Kimura, T. Yamamoto, M. Mizuno, Y. Suga, S. Kitade, and H. Sezaki. Characterisation of aminocephalosporin transport across rat small intestine.J. Pharmaco. biodyn. 6:246–253 (1983).
A. Tsuji and T. Yamana. Gastrointestinal absorption ofβ-lactam antibiotics. In S. Mitshuhashi (ed.),Beta-Lactam Antibiotics, Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981, pp. 235–258.
J. Sjövall, G. Alvan, and D. Westerlund. Oral cyclacillin interacts with the absorption of oral ampicillin, amoxicillin and bacampicillin.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 29:495–502 (1985).
J. G. Wagner and E. Nelson. Percent absorbed time plots derived from blood level and/or urinary excretion data.J. Pharm. Sci. 52:610–611 (1963).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier, Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., Marcel-Dekker, New York, 1982, pp. 34, 42.
G. E. Forsyte, M. A. Malcolm, and C. B. Moler.Computer Methods for Mathematical Computations, Prentice-Hall, Engelwood Cliffs, NJ, 1977.
R. Gomeni. An interactive program for individual and population parameter estimation. In M. J. Von Bommel, N. O. Ball, and N. Wigertz (eds.),Medinfo 83, North-Holland, Amsterdam 1983, pp. 1022–1025.
M. J. D. Powell. An efficient method for finding the minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives.Comput. J. 7:155–162 (1964).
L. B. Sheiner. Analysis of pharmacokinetics data using parametric models. II. Point estimates of an individual's parameters.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 13:515–540 (1985).
H. G. Boxenbaum, S. Riegelman, and R. M. Elashoff. Statistical estimation in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:123–149 (1974).
L. B. Sheiner. Analysis of pharmacokinetics data using parametric models. III. Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:539–555 (1986).
V. W. Steinijans and E. Diletti. Statistical analysis of bioavailability studies: parametric and nonparametric confidence interval.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 24:127–136 (1983).
J. C. K. Loo and S. Riegelman. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:918–928 (1968).
J. G. Wagner. Properties of the Michaelis-Menten equation and its integrated form which are useful in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:103–121 (1972).
W. D. Mason, J. D. Conklin, and F. J. Hailey. Relative bioavailability of four macrocrystalline nitrofurantoin capsules.Int. J. Pharm. 36:105–111 (1987).
W. A. Mahon, J. S. Leeder, M. M. Brill-Edwards, J. Correia, and S. M. McLeod. Comparative bioavailability study of three sustained release quinidine formulations.Clin. Pharmacokin. 13:118–124 (1987).
J. Sjövall, G. A. Alvan, and D. Westerlund. Dose-dependent absorption of amoxycillin and bacampicillin.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 38:241–250 (1985).
M. Mayersohn. Ascorbic acid absorption in man—Pharmacokinetic implications.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 19:140–142 (1972).
J. H. Wood and K. M. Thakker. Michaelis-Menten absorption kinetics in drugs: examples and implications.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 23:183–188 (1982).
G. Levy and W. J. Jusko. Factors affecting the absorption of riboflavine in man.J. Pharm. Sci. 55:285–289 (1966).
A. Tsuji, E. Nakashima, I. Kagami, and T. Yamana. Intestinal absorption mechanism of amphotericβ-lactam antibiotics I: comparative absorption absorption and evidence for saturable transport of amino-β-lactam antibiotics byin situ rat small intestine.J. Pharm. Sci. 70:768–772 (1981).
P. J. Sinko and G. L. Amidon. Characterization of the oral absorption of β-lactam antibiotics. I. Determination of intrinsic membrane absorption parameters in the rat intestinein situ.Pharm. Res. 5:645–650 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reigner, B.G., Couet, W., Guedes, JP. et al. Saturable rate of cefatrizine absorption after oral administration to humans. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 18, 17–34 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063620
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063620