Summary
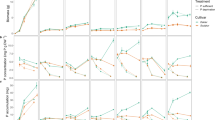
Five tropical grain legume species were grown for periods from 4 to 20 days in flowing-solution culture at 7 maintained phosphorus (P) concentrations, ranging from 0.25 μM to 16 μM. Critical external P requirements were 0.8 μM for cowpea cv. Vita 4 and soybean cv. Fitzroy, 1.0 μM for pigeon pea cv. Royes, 2.0 μM for mungbean cv. Regur and 3.0 μM for guar cv. Brooks. Plant responses to P deficiency included reduced growth rate, increased root percentage, and increased P uptake potential. The long-term P uptake rates of guar plants were lower than those of the other species at each external P concentration. Guar plants had a low P uptake potential as indicated by short-term32CP-labelled uptake rate studies from 15 μM P solutions. Cowpea by contrast had high short-term uptake rates indicating a high P uptake potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asher C J and Loneragan J F 1967 Response of plants to phosphate concentration in solution culture: I. Growth and phosphorus content. Soil Sci. 103 225–233.
Asher C J, Ozenne P G, and Loneragan J F 1965 A method for controlling the ionic environment of plant roots. Soil Sci. 100, 149–156, 204–207.
Barber S A, Walker J M and Vasey E H 1963 Mechanisms for the movement of plant nutrients from the soil and fertiliser to the plant root. J. Agric. Food Chem. 11, 204–207.
Borkert C M and Barber S A 1983 Effect of supplying P to a portion of the soybean root system on root growth and P uptake kinetics. J. Plant Nutr. 6, 895–910
Carter O G and Lathwell D J 1967 Effects of temperature on orthophosphate absorption by excised corn roots. Plant Physiol. 42, 1407–1412
Chantkam S, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1983 Response of selected tropical pasture legumes grown in flowing nutrient culture to constant solution phosphorus concentrations: I. Growth and phosphorus concentration. Thai J. Agric. Sci. 16, 217–231
Clarkson D T and Scattergood C B 1982 Growth and phosphorus transport in barley and tomato plants during the development of, and recovery from, phosphate-stress. J. Exp. Bot. 33, 865–875
Cogliatti D H Clarkson D T 1983 Physiological changes in, and phosphate uptake by potato plants during development of, and recovery from phosphate deficiency. Physiol. Plant. 58, 287–294
Edwards D G and Asher C J 1974 The significance of solution flow rate in flowing culture experiments. Plant and Soil 41, 161–175
Jintakanon S, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1979 An anomalous, high external phosphorus requirement for young cassava plants in solution culture.In V. Int. Symp. Tropical Root Crops. Eds. E H Belen and M Villanueva. pp 507–518 PCARR Los Banos, Philippines
Jintakanon S, Kerven G L, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1975 Measurement of low phosphorus concentrations in nutrient solutions containing silicon. Analyst 100, 408–414
Lefebvre D D and Glass A D M 1982 Regulation of phosphate influx in barley roots: Effects of phosphate deprivation and reduction of influx with provision of orthophosphate. Physiol. Plant. 54, 199–206
Loneragan J F 1968 Nutrient requirements of plants. Nature 220, 1307–1308
Reisenauer H M 1966 Mineral nutrients in soil solutionIn Environmental Biology. Eds. P L Altman and D S Dittmer. pp 507–508. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol., Bethesda
Ulrich A 1952 Physiological bases for assessing the nutritional requirements of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 3, 207–228
Watanabe F S and Olsen S R 1965 Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorus in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 677–678
Williams R F 1948 The effects of phosphorus supply on the rates of intake of phosphorus and nitrogen and upon certain aspects of phosphorus metabolism in gramineous plants. Aust. J. Sci. Res. B1, 333–361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fist, A.J., Smith, F.W. & Edwards, D.G. External phosphorus requirements of five tropical grain legumes grown in flowing-solution culture. Plant Soil 99, 75–84 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370155
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370155