Abstract
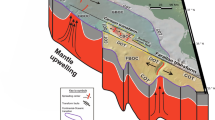
Morphologic, gravity, and seismic reflection/refraction data from ca. 10,000 km of Arctic passive continental margins suggest that the numerous oval free-air gravity anomalies, their +50–150 mGal extrema typically located just landward of shelf breaks, are caused by combinations of rapidly deposited Plio-Pleistocene glacial marine sediment loads, older post-breakup sediments, and perhaps causally related density anomalies (mascons) in the underlying oceanic crust. Dispersed seismicity associated with some gravity highs may reflect ongoing brittle, flexural adjustment to the loads. Multi-channel-seismic-controlled depocenter models for several prominent highs (including the Hornsund gravity high re-examined here) suggest that sediments alone do not suffice to explain the gravity highs, unless depocenter seismic velocities have been significantly underestimated. A flexural backstripping model for the Hornsund anomaly only roughly replicates observed gravity. Subjacent 'mascons', if present below some depocenters, may be caused by (1) anomalous subsidence of initially formed dense/thin crust; (2) depocenter blanketing of early-formed crust, mitigating hydrothermal fracturing and related density reduction; or (3) metastable phase transitions, converting basalt/gabbro to denser phases (Neugebauer–Spohn hypothesis), while cracks close or fill under the increased pressures and temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous, 1988, Gravity anomaly map of the Continenal Margin of Eastern Canada (Map), Geological Survey of Canada, Map 1708A, scale 1:5 000 000, Ottawa.
Basham, P. W., Forsyth, D. A. and Wetmiller, R. J., 1977, The seismicity of northern Canada, Can. J. Earth Sci. 14: 1646–1667.
Boucher, G., 1978, Rotation of Alaska and the opening of the Canada Basin, U.S. Geological Survey Open-file report 78–96, 12 pp.
Bungum, H., Alsaker, A., Kvamme, L. B. and Hansen, R. A., 1991, Seismicity and seismotectonics of Norway and nearby continental shelf areas, J. Geophys. Res. 96: 2249–2265.
Cherkis, N. Z. and Vogt, P. R., 1995, Regional bathymetry of the northern Norwegian-Greenland Sea (chart). In K. Crane and A. Solheim (eds.), Seafloor atlas of the Northern Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Norsk Polarinst. Med., Oslo, p. 137.
Childers, V. A., Peter, M. F. and Brozena, J. M. 1997, Error analysis of the NRL airborne gravity system, Proc. Int. Symp. on Kinetic Systems in Geodesy, Geomatics and Navigation, Banff, Canada, pp. 625–632.
Christensen, N. I. and Salisbury, M. H., 1975, Structure and composition of the lower oceanic crust, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 13: 57–86.
Eldholm, O., Faleide, J. I. and Myhre, A. M., 1987, Continent-ocean transition at the western Barents Sea/Svalbard continental margin, Geology 15: 1118–1122.
Eldholm, O., Skogseid, J., Sundvor, E. and Myhre, A. M., 1990, The Norwegian-Greenland Sea. In A. Grantz, G. L. Johnson and J. F. Sweeney (eds), The Arctic Ocean Region, Vol. L., The Geology of North America, Geol. Soc. Amer., Boulder, Colo., pp. 351–364.
Faleide, J. I., 1995, Free-air gravity field of the northern Norwegian-Greenland Sea, in Crane, K., and A. Solheim (ed.), Seafloor atlas of the Northern Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Norsk Polarinst. Med., 137, Oslo, pp. 17–20.
Faleide, J. I., Vågnes, E. and Gudlaugsson, S. T., 1993, Late Mesozoic-Cenozoic evolution of the south-western Barents Sea in a regional rift-shear tectonic setting, Mar. Pet. Geol. 10: 185–296.
Faleide, J. I., Solheim, A. Fiedler, A., Hjelstuen, B. O., Andersen, E. S. and Vanneste, K., 1996, Late Cenozoic evolution of the western Barents Sea-Svalbard continental margin, Global Planet. Change 12: 53–74.
Fujita, K., Cook, D. B., Hasegawa, H., Forsyth, D. and Wetmiller, R., 1990, Seismicity and focal mechanisms of the Arctic region and the North American plate boundary in Asia. In A. Grantz, G. L. Johnson and J. F. Sweeney (eds.), The Arctic Ocean Region, Vol. L, The Geology of North America, Geol. Soc. Amer., Boulder, Colo., pp. 79–100.
Gabrielsen, R. H., 1989, Reactivation of faults on the Norwegian continental shelf and its implications for earthquake occurrence. In S. Gregersen and P. W. Basham (eds.), Earthquakes at North-Atlantic passive margins: neotectonics and postglacial rebound, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp. 67–90.
Gardner, G. H. F., Gardner, L. W. and Gregory, A. R., 1974, Formation velocity and density-The diagnostic basics for stratigraphic traps, Geophysics 39: 770–780.
Grønlie, G. and Talwani, M., 1982, The free-air gravity field of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea and adjacent areas, Earth Evolution Sci. 2: 79–103.
Hamilton, E. L., 1978, Sound velocity-density relations in sea-floor sediments and rocks, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 63: 366–377.
Hjelstuen, B. O., Elverhøi, A. and Faleide, J. I., 1996, Cenozoic erosion and sediment yield in the drainage area of the Storfjorden fan, Global Planet. Change 12: 95–117.
Houtz, R. E., 1980, comparison of velocity-depth characteristics in western North Atlantic and Norwegian Sea sediments, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 68: 1409–1414.
Jackson, H. R., Faleide, J. I. and Eldholm, O., 1990, Crustal structure of the sheared southwestern Barents Sea continental margin, Mar. Geol. 93: 119–146.
King, E. L., Sejrup, H.P., Haflidason, H., Elverhøi, A. and Aarseth, I., 1996, Quaternary seismic stratigraphy of the North Sea fan; glacially-fed gravity flow aprons, hemipelagic sediments,and large submarine slides, Mar. Geol. 130: 229–315.
Larsen, H. C., 1990, The East Greenland shelf. In A. Grantz, G. L. Johnson and J. F. Sweeney (eds), The Arctic Ocean Region, Vol. L, The Geology of North America, Geol. Soc. Amer., Boulder, Colo., pp. 185–210.
Larter, R. D., Rebesco, M., Vanneste, L. E., Gamboa, L. A. P. and Barker, P. F., 1997, Cenozoic tectonic, sedimentary and glacial history of the continental shelf west of Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula, in Geology and Seismic Stratigraphy of the Antarctic Margin, Part 2, Antarctic Research Series 71: 1–27.
Laxon, S. and McAdoo, D., 1994, Arctic ocean gravity field derived from ERS-1 satellite altimetry, Science 265: 621–624.
Laxon, S. and McAdoo, D., 1998, Polar marine gravity from satellite altimetry, University College, London, http:msslsp.mssl.ucl.ac.uk/people/swl/polarg ravity.html.
Lindwall, D. A., 1988, A two-dimensional seismic investigation of crustal structure under the Hawaiian Islands near Oahu and Kauai, J. Geophys. Res. 93: 12107–12122.
Max, M. D., Ghidella, M., Kovacs, L., Paterlini, M. and Valladeres, J. A., 1999, Geology of the Argentine continental shelf and margin from aeromagnetic survey, Marine Petrol. Geol. 16: 41–64.
Myhre, A. M. and Eldholm, O., 1988, The western Svalbard margin (74°N–80°N), Mar. Pet. Geol. 5: 134–156.
Nafe, J. E. and Drake, C. L., 1957, Variation with depth in shallow and deep water marine sediments of porosity, density and velocities of compressional and shear waves, Geophysics 22: 523–552.
Neugebauer, H. J. and Spohn, T., 1981, Metastable phase transitions and progressive decline of gravitational energy: aspects of Atlantic type margin dynamics, AGU Geodynamics Ser. 6: 166–183.
Nicolas, A., 1985, Novel type of crust produced during continental rifting, Nature 315: 112–115.
Olesen, O. G., Gellein, J., Habrekka, H., Kihle, O., Skilbrei, J. R. and Smethurst, M. A., 1997, Magnetic anomaly map, Norway and adjacent ocean areas, Trondheim, Geol. Survey of Norway (map).
Perry, R. K., Fleming, H. S., Weber, J. R., Kristoffersen, Y., Hall, J. K., Grantz, A., Johnson, G.L., Cherkis, N. Z. and Larsen, B., 1985, Bathymetry of the Arctic Ocean, Geol. Soc. Amer. Map and Chart Ser., MC 56.
Purdy, G. M. and Ewing, J., 1986, Seismic structure of the ocean crust. In P. R. Vogt and B. T. Tucholke (eds.), The Western North Atlantic Region, Vol M., The Geology of North America, Geol. Soc. Amer., Boulder, Colo., pp. 313–330.
Rabinowitz, P. D., 1981, Gravity measurements bordering passive continental margins. In Dynamics of Passive Margins, Geodynamics Series, Vol. 6, Am. Geophys. Union, pp. 91–115.
Reid, I. and Jackson, R. R., 1981, Oceanic spreading rate and crustal thickness, Mar. Geophys. Res. 5: 165–172.
Sandwell, D. T. and Smith, W. H. F., 1997, Marine gravity anomaly from Geosat and ERS-1 satellite altimetry, J. Geophys. Res. 102: 10039–10054.
Sobczak, L. W., 1975, Gravity anomalies and passive continental margins, Canada and Norway. In C. J. Yorath, E. R. Parker and D. J. Glass (eds), Canada's Continental Margins and Offshore Petroleum Explorations, Mem. 4, Can. Soc. Pet. Geol., Calgary, pp. 743–761.
Sobczak, L. W., 1989, Stratigraphy and tectonic significance of Cretaceous volcanism in the Queen Elizabeth Islands, Canadian Arctic Archipelago: Discussion, Can. J. Earth Sci. 26: 2736–2739.
Sobczak, L. W., Mayr, U. and Sweeney, J. F., 1986, Crustal section across the polar continent-ocean transition in Canada, Can. J. Earth Sci. 23: 608–621.
Sobczak, L. W., Hearty, D. B., Forsberg, R., Kristoffersen, Y., Eldholm, O. and May, S. D., 1990, Gravity from 64°N to the North Pole. In A. Grantz, G. L. Johnson and J. F. Sweeney (eds.), The Arctic Ocean Region, Vol. L, The Geology of North America, Geol. Soc. Amer., Boulder, Colo., pp. 101–118.
Sobczak, L. W., Halpenny, J. F. and Henderson, D. M., 1991, Gravity interpretation along seismic refraction lines surveyed near the Canadian Ice Island during 1985, Geol. Surv. Canada Paper 90-12, 23 pp.
Spohn, T. and Neugebauer, H. J., 1978, Metastable phase transition models and their bearing on the development of Atlantic-type geosynclines, Tectonophysics 50: 387–412.
Stein, S., Cloetingh, S., Sleep, N. H. and Wortel, R., 1989, Passive margin earthquakes, stresses, and rheology. In S. Gregersen and P.W. Basham (eds.), Earthquakes at North-Atlantic Passive Margins: Neotectonics and Postglacial Rebound, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp. 231–259.
Stephenson, R. A., Coffin, K. C., Lane, L. S. and Dietrich, J. R., 1994, Crustal structure and tectonics of the southeastern Beaufort Sea continental margin, Tectonics 13: 389–400.
Stephenson, R. A. and Smolyaninova, E. I., 1999, Neotectonics and seismicity in the south-eastern Beaufort Sea, polar continental margin of north-western Canada, J. Geodyn. 27: 175–190.
Talwani, M. and Eldholm, O., 1977, Evolution of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea, Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull. 88: 969–999.
Talwani, M., Ewing, J., Sheridan, E., Holbrook, W. S. and Glover, L., III, 1995, The EDGE experiment and the U.S. East Coast magnetic anomaly, In E. Banda (eds.), Rifted Ocean-Continent Boundaries, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p. 155–181.
Turcotte, D. L., Ahern, J. L. and Bird, J. M., 1977, The state of stress at continental margins, Tectonophysics 42: 1–28.
Verhoef, J., Roest, W. R., MacNab, R., Arkani-Hamed, J. and Members of the Project Team, 1996, Magnetic anomalies of the Arctic and North Atlantic Oceans and adjacent land areas (CD-ROM), Geological Survey of Canada Open File 3125a.
Vogt, P. R., 1986, Geophysical and geochemical signatures and plate tectonics. In B. G. Hurdle (ed.), The Nordic Seas, Springer, New York, pp. 413–662.
Vogt, P. R. and Perry, R. K., 1978, Post-rifting accretion of continental margins in the Norwegian-Greenland and Labrador seas: Morphologic evidence (Abs), EOS 59: 120.
Vogt, P. R. and Jung, W.-Y., 1988, Glacial-marine sediment depocenters on high-latitude continental margins-Possible effects on gravity, seismicity, lithospheric flexure, and continental reconstructions (abs.), Alfred Wegener Conference on Geology of Polar Oceans: Arctic vs. Antarctic, Bremen, Germany, pp. 129–131.
Vogt, P. R., Johnson, G. L. and Kristjansson, L., 1980, Morphology and magnetic anomalies north of Iceland, J. Geophys. 47: 67–80.
Vogt, P. R., Crane, K. and Sundvor, E., 1994, Deep Pleistocene iceberg plowmarks on the Yermak Plateau: Sidescan and 3.5 kHz evidence for thick calving ice fronts and a possible marine ice sheet in the Arctic Ocean, Geology 22: 403–406.
Vogt, P. R., Cherkashev, G., Ginsburg, G., Ivanov, G., Milkov, A., Crane, K., Lein, L., Sundvor, E., Pimenov, N. and Egorov, A., 1997, Hâkon Mosby mud volcano provides unusual example of venting, EOS 78: 549, 556–557.
Vogt, P. R., Jung, W.-Y. and Brozena, J., 1998, Arctic margin gravity highs remain puzzling, EOS 79: 601, 605–606.
Vorren, T. O., Laberg, J. S., Blaume, F., Dowdeswell, J., Kenyon, N. H., Mienert, N., Rumohr, J. and Werner, G., 1998, The Norwegian-Greenland Sea continental margins: Morphology and late Quaternary sedimentary processes and environment, Quat. Sci. Rev. 17: 273–302.
Walcott, R. I., 1972, Gravity, flexure, and the growth of sedimentary basins at a continental edge, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 83: 1845–1848.
Watts, A. B., 1988, Gravity anomalies, crustal structure and flexure of the lithosphere at the Baltimore Canyon Trough, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 89: 221–238.
Watts, A. B. and ten Brink, U. S., 1989, Crustal structure, flexure, and subsidence history of the Hawaiian Islands, J. Geophys. Res. 94: 10473–10500.
Watts, A. B. and Fairhead, J. D., 1997, Gravity anomalies and magmatism along the western continental margin of the British Isles, J. Geol. Soc. London 154: 523–529.
Watts, A. B. and Ryan, W. B. F., 1976, Flexure of the lithosphere and continental margin basins, Tectonophysics 36: 25–44.
Watts, A. B. and Stewart, J., 1998, Gravity anomalies and segmentation of the continental margin offshore West Africa, Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 156: 239–252.
Watts, A. B, ten Brink, U. S., Buhl, P. and Brocher, T. M., 1985, A multichannel seismic structure study of lithosphere flexure across the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain, Nature 315: 105–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vogt, P.R., Jung, WY. & Brozena, J. Arctic margin gravity highs: Deeper meaning for sediment depocenters?. Marine Geophysical Researches 20, 459–477 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004775228851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004775228851