Abstract
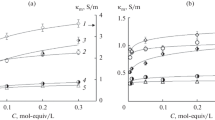
The separation of potassium and sodium ions from their mixture was performed by electrodialyzing a mixed solution of potassium chloride and sodium chloride in the presence of 18-crown-6 using a commercial cation-exchange membrane. After 18-crown-6 had been impregnated in the membrane, the mixed solution containing 18-crown-6 was electrodialyzed as the desalting-side solution. The permeation of potassium ions through the membrane decreased remarkably and the electrical resistance of the membrane increased during electrodialysis with increasing concentration of 18-crown-6 in the solution. Because potassium ions form a more stable complex with 18-crown-6 than sodium ions and because the complex permeated through the membrane with difficulty, sodium ions are thought to selectively permeate through the membrane. The current efficiency in electrodialysis was greater than 97.0%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 June 1999/Accepted in revised form: 13 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sata, T., Tanimoto, M., Kawamura, K. et al. Electrodialytic separation of potassium ions from sodium ions in the presence of crown ether using a cation-exchange membrane. Colloid Polym Sci 278, 57–60 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050008
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960050008