Abstract
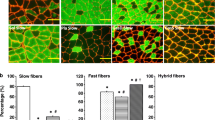
Indirect immunofluorescence was used to localize embryonic myosin heavy chains in soleus, adductor longus, tibialis anterior, plantaris, and extensor digitorum longus muscles of 6-month-old rats. A monoclonal antibody (2B6), specifically recognizing rat embryonic myosin, was applied to unfixed, transverse, frozen sections. The number of embryonic myosin-positive (EMP) extrafusal fibers was expressed as a percentage of the total number of fibers. EMP extrafusal fibers were only seen in the soleus and adductor longus muscles, both postural muscles. Approximately 1% of the soleus muscle fibers appeared positively stained for embryonic myosin. The majority of such fibers had a small diameter (<500 ν), appeared intensely fluorescent, and typically contained central nuclei. Re-expression of embryonic myosin due to spontaneous fiber denervation is not a likely factor in this study, since alpha-bungarotoxin and N-CAM localization were restricted to the motor end-plate region of EMP fibers. Since embryonic myosin was shown to disappear in all normal-sized myofibers by 2 to 3 months of age, the results suggest that the EMP extrafusal fibers seen in postural muscles of 6 to 12-month-old animals are regenerating myofibers. We speculate that a small number of muscle fibers may be regenerating in normal, adult postural muscles, in response to fiber damage possibly caused by excessive recruitment or overloading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler-Browne GS, Whalen RG (1984) Myosin isozyme transitions occurring during the postnatal development of the rat soleus muscle Dev Biol 102:324–334
Butler-Browne GS, Eriksson PO, Laurent C, Thornell LE (1988) Adult human masseter muscle fibers express myosin isozymes characteristic of development. Muscle Nerve 11:610–620
Cardasis CA, Padykula HA (1981) Ultrastructural evidence indicating reorganization at the neuromuscular junction in the normal rat soleus muscle. Anat Rec 200:41–59
Cerny L, Bandman E (1987) Expression of myosin heavy chain isoforms in regenerating myotubes of innervated and denervated chicken pectoralis muscle. Dev Biol 119:360–362
d'Albis A, Couteaux R, Janmot C, Roulet A (1989a) Specific programs of myosin expression in the postnatal development of rat muscle. Eur J Biochem 183:583–590
d'Albis A, Couteaux R, Janmot C, Mira JC (1989b) Myosin isoform transitions in regeneration of fast and slow muscles during postnatal development of the rat. Dev Biol 135:320–325
Gambke B, Rubinstein NA (1984) A monoclonal antibody to the embryonic myosin heavy chain of rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 259:12092–12100
Giddings CJ, Neaves WB, Gonyea WJ (1985) Muscle fiber necrosis and regeneration induced by prolonged weight-lifting exercise in the cat. Anat Rec 211:133–141
Gorza L, Sartore S, Triban C, Schiaffino S (1983) Embryonic-like myosin heavy chains in regenerating chicken muscle. Exp Cell Res 143:395–403
Granger BL, Lazarides E (1979) Desmin and vimentin co-exist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell 18:1053–1063
Jakubiec-Puka A, Kordewska J, Catani C, Carraro U (1990) Myosin heavy chain isoform composition in striated muscle after denervation and self-reinnervation. Eur J Biochem 193:623–628
Kirschbaum B, Schneider S, Izumo S, Mahdavi V, Nadal-Ginard B, Pette D (1990) Rapid and reversible changes in myosin heavy chain expression in response to increased neuromuscular activity of rat fast twitch muscle. FEBS Lett 268:75–78
LaFramboise W, Daood M, Guthrie R, Butler-Browne G, Whalen R, Ontell M (1990) Myosin isoforms in neonatal rat extensor digitorum longus, diaphragm, and soleus muscles. Am J Physiol 259:L116-L122
Lexell J, Jarvis J, Downham D, Salmons S (1993) Stimulation-induced damage in rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscles: a quantitative morphological study of the influence of pattern and frequency. Cell Tissue Res 273:357–362
Maier A, Gambke B, Pette D (1986) Degeneration-regeneration as a mechanism contributing to the fast to slow conversion of chronically stimulated fast-twitch rabbit muscle. Cell Tissue Res 244:635–643
Maier A, Gambke B, Pette D (1988) Immunohistochemical demonstration of embryonic myosin heavy chains in adult mammalian intrafusal fibers. Histochemistry 88:267–271
McCormick KM, Schultz E (1992) Mechanisms of nascent fiber formation during avian skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Dev Biol 150:319–334
McCormick K, Schultz E (1994) Role of satellite cells in altering myosin expression during avian skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Dev Dynam 199:52–63
Pette D, Vrbova G (1985) Neural control of phenotypic expression in mammalian muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve 8:676–689
Sanes J, Schachner M, Covault J (1986) Expression of several adhesive macromolecules (N-CAM, L1, J1, NILE, Uvomorulin, Laminin, Fibronectin, and a Heparin Sulfate Proteoglycan) in embryonic, adult, and denervated adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 102:420–431
Sartore S, Gorza L, Schiaffino S (1982) Fetal myosin heavy chains in regenerating muscle. Nature 298:294–296
Schiaffino S, Gorza L, Pitton G, Saggin L, Ausoni S, Sartore S, Lomo T (1988) Embryological and neonatal myosin heavy chains in denervated and paralyzed rat skeletal muscle. Dev Biol 127:1–11
Soussi-Yanicostas N, Barbet J, Laurent-Winter C, Barton P, Butler-Browne G (1990) Transition of myosin isozymes during development of human masseter muscle. Development 108:239–249
Whalen R, Sell S, Butler-Browne G, Schwartz K, Bouveret P, Pinset-Harstrom I (1981) Three myosin heavy chain isozymes appear sequentially in rat muscle development. Nature 292:805–809
Wieczorek D, Periasamy M, Butler-Browne G, Whalen R, Nadal-Ginard B (1985) Co-expression of multiple myosin heavy chain genes, in addition to a tissue-specific one, in extraocular musculature. J Cell Biol 101:618–629
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wanek, L.J., Snow, M.H. Presence of embryonic myosin in normal postural muscles of the adult rat. Cell Tissue Res 280, 541–548 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318358
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318358