Summary
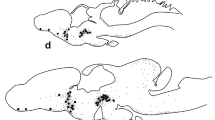
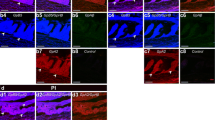
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) cells were immunostained in the anterior pituitary lobe of the California leaf-nosed bat with antisera against the specific beta (β) subunits of rat LH and rat FSH employing the unlabeled immunoperoxidase technique. Selective immunochemical staining by both antisera was localized primarily in the same cell type. However, some cells consistently reacted solely with antisera to either LH-β or FSH-β. Whereas the immunoreactive LH-β cells, in general, stained more intensely than FSH-β cells they were usually less numerous. These cells were alcian-blue and PAS-positive, staining pink to purple. The LH/FSH cells were pleomorphic with eccentric nuclei, often with cytoplasmic extensions. They were found throughout the pars distalis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzali G (1971) Citologie adenoiponsaria dei chirotteri con particolare riguardo alle cellule FSH, LH, ACTH e LTH. Ateneo Parmense Sezione I, Acta Biomed 42:169–229
Baker BL (1974) Functional cytology of the hypophysial pars distalis and pars intermedia. In: Greep RO, Astwood EB (eds) Handbook of Physiology, American Physiological Society, Washington, DC, Sect 7, Vol IV, Part 1, pp 45–80
Baker BL (1977) Cellular composition of the human pars tuberalis as revealed by immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 182:151–163
Baker BL, Karsch KJ, Hoffman DL, Beckman WC (1977) The presence of gonadotropic and thyrotropic cells in the pituitary pars tuberalis of the monkey (Macaco mulatta). Biol. Reprod 17:232–240
Bugnon C, Lenys D, Kerdelhue B, Dessy C, Fellmann D (1974) Étude cytoimmunologique des cellules gonadotropes du Renard roux. CR Soc Biol (Paris) 168:814–818
Bugnon C, Bloch B, Fellman D (1977a) Cyto-immunological study of the ontogenesis of the gonadotropic hypothalamo-pituitary axis in the human fetus. J Steroid Biochem 8:565–575
Bugnon C, Fellman D, Lenys D, Bloch B (1977b) Étude cyto-immunologique des cellules gonadotropes et des cellules thyréotropes de l'adénohypophyse du Rat. C R Soc Biol (Paris) 171:907–913
Dacheux F (1978) Ultrastructural localization of gonadotrophic hormones in the porcine pituitary using the immunoperoxidase technique. Cell Tissue Res 191:219–232
Dacheux F (1980) Ultrastructural localization of LH and FSH in the porcine pituitary. In: Jutisz M, McKerns KW (eds) Synthesis and release of adenohypophyseal hormones Plenum Press, New York and London, pp 187–195
Dubois PM, Begeot M, Dubois MP, Herbert DC (1978) Immunocytological localization of LH, FSH, TSH and their subunits in the pituitary of normal and anencephalic human fetuses. Cell Tissue Res 191:249–265
El Etreby MF, Fath El Bab MR (1977a) Effect of cyproterone acetate on cells of the pars distalis of the adenohypophysis in the beagle bitch. Cell Tissue Res 183:177–189
El Etreby MF, Fath El Bab MR (1977b) Localization of gonadotrophic hormones in the dog pituitary gland: a study using immunoenzyme histochemistry and chemical staining. Cell Tissue Res 183:167–175
El Etreby MF, Fath El Bab MR (1977c) The utility of antisera to canine growth hormone and canine prolactin for immunocytochemical staining of the dog pituitary gland. Histochemistry 53:1–15
El Etreby MF, Fath El Bab, MR (1978) Effect of 17β-estradiol on cells stained for FSHβ and/or LHβ in the dog pituitary gland. Cell Tissue Res 193:211–218
Girod C, Dubois MP (1976) Identification, en immunofluorescence, de différentes catégories de cellules adénohypophysaires (cellules somatotropes, à prolactine, corticotropes, mélanotropes, gonadotropes et thréotropes) chez le Spermophile (Citellus variegatus) et la Graphiure (Graphiurus murinus). C R Séanc Soc Biol 170:1236–1238
Herbert DC (1975) Localization of antisera to LHβ in the rat pituitary gland. Am J Anat 194:379–385
Herbert DC (1976) Immunocytochemical evidence that luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) are present in the same cell type in the rhesus monkey pituitary gland. Endocrinology 98:1554–1557
Herlant M (1956) Corrélations hypophysogénitales chez la femelle de la chauve-souris Myotis muotis (Borkhausen). Arch Biol 67:89–180
Herlant M (1960) Étude critique de deux, techniques nouvelles destinées à mettre en évidence les différentes catégories cellulaires présentes dans la glande pituitaire. Bull Micr Appl Ser 2, 10:37–44
Krutzsch PH, Sulkin SE (1958) The laboratory care of the Mexican free-tailed bat. J Mammal 39:262–265
Merchant FW (1974) Prolactin and luteinizing hormone cells of pregnant and lactating rats as studied by immunohistochemistry and radioimmunoassay. Am J Anat 139:245–268
Moriarty GC (1975) Electron microscopic-immunocytochemical studies of rat pituitary gonadotrophs: a sex difference in morphology and cytochemistry of LH cells. Endocrinology 97:1215–1225
Moriarty GC (1976) Immunocytochemistry of the pituitary glycoprotein hormones. J Histochem Cytochem 24:846–863
Nakane PK (1970) Classification of anterior pituitary cell types with immunoenzyme histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 18:9–20
Patil DR (1974) Comparison of pituitary gland cytology in three species of leaf-nosed bat (Hipposideridae). J Anat 118:33–51
Pelletier G, Leclerc R, Labrie F (1976) Identification of gonadotropic cells in the human pituitary by immunoperoxidase technique. Mol Cell Endocrinol 6:123–128
Petrusz P, DiMeo P, Ordronneau P, Weaver C, Keefer DA (1975) Improved immunoglobulin-enzyme bridge method for light microscopic demonstration of hormone-containing cells of the rat adenohypophysis. Histochemistry 46:9–26
Phifer RF, Midgley AR, Spicer SS (1973) Immunohistologic and histologic evidence that folliclestimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone are present in the same cell type in the human pars distalis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 36:125–141
Purandare T, Sar M, Stumpf WE (1978) Immunohistochemical localization of FSH and LH in rat pituitary. Mol Cell Endocrinol 10:57–62
Rennels EG, Herbert DC (1980) Functional correlates of anterior pituitary cytology. In: Greep RO (ed) Reproductive Physiology III. International Review of Physiology. Vol 22 University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 1–40
Richardson BA (1979) The anterior pituitary and reproduction in bats. J Reprod Fertil 56:379–389
Robyn C, Leleux P, Vanhaelst L, Golstein J, Herlant M, Pasteels JL (1973) Immunohistochemical study of the human pituitary with anti-luteinizing hormone, anti-follicle stimulating hormone, antithyrotrophin sera. Acta Endocrinol (Kbh.) 72:625–642
Sternberger LA, Hardy PH, Jr, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1979) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Tougard C (1980) Immunocytochemical identification of LH-and FSH-secreting cells at the light-and electron-microscope levels. In: Jutisz M, McKerns KW (eds) Synthesis and release of adenohypophyseal hormones. Plenum Press, New York and London, pp 15–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Submitted to the Graduate College at The University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree. This work was supported in part by a Grant from the University of Arizona Graduate College to the author, USPHS GRS Grant RR-05675 and Grant No. 302867 from The University of Arizona Alumni Association and University Foundation to P.H. Krutzsch
The author would like to extend his appreciation to Dr. P.H. Krutzsch for his counsel and assistance throughout the course of this study. The author also wishes to thank Dr. A.F. Parlow who kindly supplied the antisera and antigens utilized in this study under the auspices of the Hormone Distribution Program of NIAMDD and Dr. L.A. Sternberger for the PAP complex. Dr. R.J. Reiter is acknowledged for his critical review and Nancy Elms for her skillful typing of this manuscript
The author is presently a NIH Postdoctoral Fellow (1 F32ND05900)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richardson, B.A. Localization of gonadotrophic hormones in the pituitary gland of the California leaf-nosed bat (Macrotus californieus). Cell Tissue Res. 220, 115–123 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209970
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209970