Summary
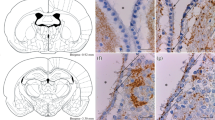
The histological patterns of supraependymal cell clusters (CC) in rats of different ages (untreated, androgenized, and treated with monosodium glutamate) were investigated with light (LM)-, scanning-and transmission electron microscopy (SEM, TEM). These clusters were a frequent but not a constant finding. In 18 day-and older embryos, CC were always found in the recess of the olfactory bulb immediately prior to its obliteration. All other CC appear in the infundibular recess between the 3rd and the 6th postnatal day. Independent of age, all cell clusters exhibit small aggregates of subependymal tissue protruding through the ependyma. Both neurons (light cells) and neuroglia (dark cells) were found in the CC. By use of SEM, in the region of the infundibular recess it is possible to distinguish four forms of supraependymal cell clusters according to localization, size, number of cells, and presence of intraventricular axons. CC may be 1) receptors or have an additional secretory function; 2) manifestations of a pathological type of reaction of the ventricular wall; 3) possible excrescences of the neural matrix, or 4) modifications of the ventricular wall in relation to the obliteration of the ventricular recesses. The first two interpretations are not tenable based on the present observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Card JP, Mitchell JA (1978) Electron microscopic demonstration of a supraependymal cluster of neuronal cells and processes in the hamster third ventricle. J Comp Neurol 180:43–58
Card JP, Mitchell JA (1979) Monosodium glutamate induced degeneration of intraventricular neurons of the median eminence of the neonate golden hamster. Anat Rec 193:496
Card JP, Mitchell JA (1980) Modular neuroglial complexes within the suprachiasmatic recess of the adult golden hamster brain. Anat Rec 196:27A
Chan-Palay V (1976) Serotonin axons in the supra-and subependymal plexuses and in the leptomeninges: Their roles in local alteration of cerebrospinal fluid and vasomotor activity. Brain Res 102:103–130
Coates PW (1978) Supraependymal cells and fiber processes in the fetal monkey third ventricle: Correlated scanning and transmission electron microscopy. SEM 11/II:143–150
Escourelle R, Poirier J (1977) Etude analytique des principales lésions du système nerveux central. In: Manuel élémentaire de neuropathologie, Masson Paris, pp 1–16
Friede RL (1975) Gross and microscopic development of the central nervous system. In: Developmental neuropathology, Springer, Wien New York, pp 1–23
Garfia A, Mestres P, Rascher K (1980) Trinitrophenol lesions of the ventricular wall: A SEM-TEM study. SEM 13/III:449–456
Gorski RA (1971) Gonadal hormones and the perinatal development of neuroendocrine functions. In: Martini L, Ganong WF (eds) Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. Oxford Univ Press, New York, pp 237–290
Leonhardt H (1968) Bukettförmige Strukturen im Ependym der Regio hypothalamica des III. Ventrikels beim Kaninchen. Z Zellforsch 88:297–317
Leonhardt H (1980) Neuroglia I. Ependym und Circumventrikuläre Organe. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen. Oksche A (ed) IV/10. Springer, Berlin, pp 197
Léranth C, Schiebler TH (1974) Über die Aufnahme von Peroxidase aus dem 3. Ventrikel der Ratte. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen. Brain Res 76:1–11
Meller K (1979) Scanning electron microscope studies on the development of the nervous system in vivo and in vitro. Int Rev Cytol 56:23–56
Mestres P (1965) Aportaciones al conocimiento de la superficie de contacto adenoneurohipofisaria en el hombre. Anales Anat XIV:579–598
Mitchell JA, Card JP (1978) Supraependymal neurons overlying the periventricular region of the third ventricle of the guinea pig: A correlative scanning-transmission electron microscopic study. Anat Rec 192:441–458
Olney JW (1969) Brain lesions, obesity and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science 164:719–721
Paull WK, Scott DE, Boldosser WG (1974) A cluster of supraependymal neurons located within the infundibular recess of the rat third ventricle. Am J Anat 140:129–133
Pilgrim C (1978) Transport function of hypothalamic tanycytic ependyma: how good is the evidence? Neurosci 3:277–283
Ramón y Cajal S (1929) Etudes sur la neurogenèse de quelques vertébrés, Chapt III, Tipografia artistica, Madrid, p 101
Ribas JL (1977) The rat epithalamus. I. Correlative scanning-transmission electron microscopy of supraependymal nerves. Cell Tissue Res 182:1–16
Scott DE, Kozlowski GP, Sheridan MN (1974) Scanning electron microscopy in the ultrastructural analysis of the mammalian cerebral ventricular system. Int Rev Cytol 37:349–388
Ule G (1974) Nervensystem. Entzündliche Erkrankungen des Nervensystems und seiner Häute. In: Doerr W (ed) Organpathologie Vol 3, Chapt 9, pp 46–48, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B (1974) The infundibular cerebrospinal-fluid contacting neurons. Adv in Anatomy Embryology and Cell Biology 50
Weindl A, Schinko I (1975) Vascular and ventricular neurosecretion in the organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis of the golden hamster. In: Knigge KM, Scott DE, Kobayashi H, Ishii S (eds) Brain-Endocrine Interaction II. The ventricular system in neuroendocrine mechanisms, Basel, Karger, pp 190–204
Wepler W (1958) Liquor: Krankheiten der Ventrikel. In: Kaufmann E, Staemmler M (eds) Lehrbuch der speziellen Pathologischen Anatomie, Vol III part 1, de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin, pp 78–89
Westergaard E (1970) The lateral cerebral ventricles and the ventricular walls. Thesis. Andelsbogtrykkeriet, Odense
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was generously supported by a grant from the DFG (Me 559/3). The authors are indebted to H. Jaeschke for her technical assistance and to J. Schäfer for her help in preparing the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mestres, P., Rascher, K. Supraependymal cell clusters in the rat brain. Cell Tissue Res. 218, 41–58 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210090
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210090