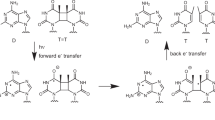
Summary
Non-photoreactivable endonuclease V-sensitive sites have been detected in the DNA of wild type bacteriophage T4 irradiated with near UV light (320 nm). Such sites were not detected in the DNA of (a) wild type T4 irradiated with far UV (254 nm) or (b) in T4 mutants in which non-glucosylated 5-hydroxy-methylcytosine (5HMC) or cytosine replaces glucosylated 5HMC normally present in T4, irradiated with 320 nm or 254 nm light. Although the non-photoreactivable sites accounted for ∼50% of the endonuclease V-sensitive sites in the DNA of glucosylated T4 irradiated with near UV, there was very little difference in the sensitivities of T4 containing glucosylated 5HMC, non-glucosylated 5HMC and cytosine to near UV (313 nm). We propose that the photoproduct responsible for the non-photoreactivable, but endonuclease V-sensitive, sites in glucosylated DNA is formed from glucosylated 5HMC and that a similar photoproduct is formed from non-glucosylated 5HMC or cytosine in the appropriate phage strains. We further propose that the glucosylated 5HMC photoproduct is non-photoreactivable whereas the cytosine and non-glucosylated 5HMC photoproducts are photoreactivable and are therefore possibly cyclobutane dimers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cabrera-Juárez, E., Setlow, J.K.: Formation of a thymine photoproduct in transforming DNA by near ultraviolet irradiation. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 475, 315–322 (1977)
Carrier, W.L., Setlow, R.B.: Endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus which has activity toward ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid: Purification and properties. J. Bact. 102, 178–186 (1970)
Cavilla, C.A., Johns, H.E.: Inactivation and photoreactivation of the T-even phages as a function of the inactivating ultraviolet wavelength. Virology 24, 349–358 (1964)
Childs, J.D.: Conditional lethal mutants of bacteriophage T4 unable to grow on a streptomycin resistant mutant of Escherichia coli. Mutation Res. 44, 165–176 (1977)
Childs, J.D., Birnboim, H.C.: Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of intact bacteriophage T4D particles. J. Virol. 16, 652–661 (1975)
Cook, J.S., Worthy, T.E.: Deoxyribonucleic acid photoreactivating enzyme. A quantitative chemical assay and estimation of molecular weight of the yeast enzyme. Biochemistry (Wash.) 11, 388–393 (1972)
Doermann, A.H., Eiserling, F.A., Boehner, L.: Genetic control of capsid length in bacteriophage T4. J. Virol. 12, 374–385 (1973)
Eisenstark, A., Ananthaswamy, H.N.: Cell damage by near-ultraviolet radiation and a tryptophan photoproduct (hydrogen peroxide). In: Symposium on biological effects and measurement of light sources, Rockville, Maryland, pp. 145–155. Published by. U.S. Dept. of Health, Education and Welfare (1976)
Eker, A.P.M., Fichtinger-Schepman, A.M.J.: Studies on a DNA photoreactivating enzyme from Streptomyces griseus. II. Purification of the enzyme. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 378, 54–63 (1975)
Friedberg, E.C.: Studies on the substrate specificity of the T4 excision repair endonuclease. Mutation Res. 15, 113–123 (1972)
Friedberg, E.C., King, J.J.: Endonucleolytic cleavage of UV-irradiated DNA controlled by the V+ gene in phage T4. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 37, 646–651 (1969)
Fukasawa, T.: The course of infection with abnormal bacteriophage T4 containing non-glucosylated DNA on Escherichia coli strains. J. molec. Biol. 9, 525–536 (1964)
Georgopoulos, C.P.: Isolation and preliminary characterization of T4 mutants with nonglucosylated DNA. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 28, 179–184 (1967)
Harm, W.: Mutants of phage T4 with increased sensitivity to ultraviolet. Virology 19, 66–71 (1963)
Hattman, S., Fukasawa, T.: Host-induced modification of T-even phages due to defective glucosylation of their DNA. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 50, 297–300 (1963)
Hill, R.F.: Ultraviolet-induced lethality and reversion to prototrophy in Escherichia coli strains with normal and reduced dark repair ability. Photochem. Photobiol. 4, 563–568 (1965)
Howard-Flanders, P., Boyce, R.P., Simson, E., Theriot, L.: A genetic locus in E. coli K12 that controls the reactivation of UV-photoproducts associated with thymine in DNA. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 2109–2115 (1962)
Meistrich, M.L.: Contribution of thymine dimers to the ultraviolet light inactivation of mutants of bacteriophage T4. J. molec. Biol. 66, 97–106 (1972)
Meistrich, M.L., Drake, J.W.: Mutagenic effects of thymine dimers in bacteriophage T4. J. molec. Biol. 66, 107–114 (1972)
Paterson M.C.: Use of purified lesion-recognizing enzymes to monitor DNA repair in vivo. Adv. Radiat. Biol. 7, 1–53 (1978)
Paterson, M.C., Lohman, P.H.M., Sluyter, M.L.: Use of a UV endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus to monitor the progress of DNA repair in UV-irradiated human cells. Mutation Res. 19, 245–256 (1973)
Revel, H.R.: Restriction of nonglucosylated T-even bacteriophage: Properties of permissive mutants of Escherichia coli B and K12. Virology 31, 688–701 (1967)
Runnels, J., Snyder, L.: Isolation of a bacterial host selective for T4 phage containing cytosine in its DNA. J. Virol. 27, 815–818 (1978)
Setlow, R.B.: Cyclobutane-type pyrimidine dimers in polynucleotides. Science 153, 379–386 (1966)
Setlow, R.B.: Photoproducts in DNA irradiated in vivo. Photochem. Photobiol. 7, 643–649 (1968)
Setlow, R.B.: Analysis of irradiated material. In: Research progress in organic biological and medicinal chemistry, Vol. 3, part 1, pp. 71–99. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Co. 1970
Setlow, R.B., Carrier, W.L.: The v-gene controls dimer excision in T4 phage. Biophys. J. 6, 68 (Abs.) (1966)
Setlow, R.B., Carrier, W.L.: The excision of pyrimidine dimers in vivo and in vitro. In: Replication and recombination of genetic material, pp. 134–141. (W.J. Peacock and R.D. Brock, eds.) Canberra: Australian Academy of Science 1968
Shedlovsky, A., Brenner, S.: A chemical basis for the host-induced modification of T-even bacteriophages. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 50, 300–305 (1963)
Snyder, L., Gold, L., Kutter, E.: A gene of bacteriophage T4 whose product prevents true late transcription on cytosine-containing T4 DNA. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.). 73, 3098–3102 (1976)
Unrau, P., Wheatcroft, R., Cox, B.S.: Methods for the assay of ultraviolet-induced pryimidine dimers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 269, 311–321 (1972)
Volkin, E.: The linkage of glucose in coliphage nucleic acids. J. Amer. chem. Soc. 76, 5892–5893 (1954)
Vosberg, H.P., Hoffmann-Berling, H.: DNA synthesis in nucleotide-permeable Escherichia coli cells. I. Preparation and properties of ether-treated cells. J. molec. Biol. 58, 739–753 (1971)
Wang, S.I. (Ed.) Photochemistry and photobiology of nucleic acids, Vols. 1 and 2. New York: Academic Press 1976
Webb, R.B., Brown, M.S.: Sensitivity of strains of Escherichia coli differing in repair capacity to far UV, near UV and visible radiations. Photochem. Photobiol. 24, 425–432 (1976)
Webb, R.B., Brown, M.S., Tyrrell, R.M.: Lethal effects of pyrimidine dimers induced at 365 nm in strains of E. coli differing in repair capability. Mutation Res. 37, 163–172 (1976)
Winkler, V., Johns, H.E., Kellenberger, E.: Comparative study of some properties of bacteriophage T4D irradiated with monochromatic ultraviolet light. Virology 18, 343–358 (1962)
Wood, W.B.: Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: Bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J. molec. Biol. 16, 118–133 (1966)
Wood, W.B., Revel, H.R.: The genome of bacteriophage T4. Bact. Rev. 40, 847–868 (1976)
Wyatt, G.R., Cohen, S.S.: The bases of the nucleic acids of some bacterial and animal viruses: The occurrence of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Biochem. J. 55, 774–782 (1953)
Yasuda, S., Sekiguchi, M.: Mechanism of repair of DNA in bacteriophage. II. Inability of ultraviolet-sensitive strains of bacteriophage in inducing an enzyme activity to excise pyrimidine dimers. J. molec. Biol. 47, 243–255 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
AECL Refence No. 6370
Communicated by B.A. Bridges
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Childs, J.D., Paterson, M.C., Smith, B.P. et al. Evidence for a near UV-induced photoproduct of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in bacteriophage T4 that can be recognized by endonuclease V. Molec. Gen. Genet. 167, 105–112 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270326
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270326