Abstract
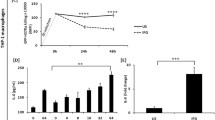
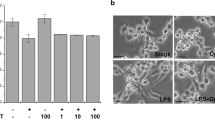
To clarify the effector pathway of Neospora caninum growth-inhibitory activity induced by interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in murine macrophages we examined the relationship between IFN-γ and nitric oxide (NO). Production of NO was enhanced in cultures of macrophages supplemented with IFN-γ, and dose-dependent growth inhibition was observed. These findings suggest that the inhibitory activity induced in macrophages by IFN-γ is mediated NO molecules. A competitive inhibitor of the L-arginine-dependent effector pathway, N G-monomethyl-L-arginine, virtually abolished the inhibitory effects induced by IFN-γ. From this finding it appears that the inhibitory effects induced by IFN-γ in macrophages may be mediated by an L-arginine-dependent effector pathway that involves NO production. In vivo, mice with a targeted disruption of the inducible NO synthase gene (iNOS−/−) were more susceptible than wild-type mice to N. caninum. Therefore, the production of NO in macrophages induced by IFN-γ is an important mechanism for the killing of intracellular N. caninum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 February 2000 / Accepted: 20 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, T., Nagasawa, H., Fujisaki, K. et al. Growth-inhibitory effects of interferon-γ on Neospora caninum in murine macrophages by a nitric oxide mechanism. Parasitol Res 86, 768–771 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360000242
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360000242