Summary
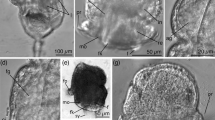
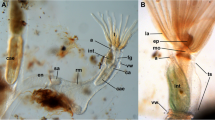
The larval morphology of the marine bryozoan Bowerbankia gracilis has been investigated by light and electron microscopy. The barrel-shaped larva (200 μm long and 150 μm in diameter) is light yellow without any apparent eyespots, although it is positively phototactic during its brief free-swimming existence. The primary morphological characteristics of the larva are: (1) a large corona that forms most of the larval surface, (2) a small apical disc without blastemas, (3) a deep pallial sinus lined by an extensive pallial epithelium, (4) an internal sac without regional specializations, and (5) a polypide rudiment in the oral hemisphere. This organization is characteristic of larvae of the ctenostome superfamily Vesicularioidea, and differs radically from the organization of all other bryozoan larvae examined. The major morphological differences occur in the size and organization of the apical disc, the pallial epithelium, and the internal sac. In most bryozoans, these regions of the larval epithelium represent rudiments of the polypide and the body wall epidermis of the ancestrula. The oral polypide rudiment, the extensive pallial epithelium, and the reduced internal sac in vesicularioid larvae indicate that their pattern of metamorphosis also differs radically from the metamorphoses of other bryozoans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB:
-
aboral
- acr:
-
axial ciliary rootlet
- ad:
-
apical disc
- anc:
-
aboral nerve cord
- ANT:
-
anterior
- arm:
-
apical retractor muscle
- b:
-
basal body
- bf:
-
basal foot process
- c:
-
corona
- cc:
-
ciliated cleft
- ce:
-
centriole
- ci:
-
cilium
- cl:
-
cupiform layer of the polypide rudiment
- cp:
-
ciliary pit
- cr:
-
ciliary rootlet
- enr:
-
equatorial neural ring
- g:
-
glandular cells of the pyriform organ
- gl:
-
glycocalyx
- go:
-
Golgi complex
- gr:
-
granule
- hcr:
-
horizontal ciliary rootlet
- ic:
-
intercoronal cell
- igf:
-
inferior glandular field
- ip:
-
infrapallial cells
- is:
-
internal sac
- jp:
-
juxtapapillary cells
- l:
-
lipid droplets
- L:
-
lateral
- m:
-
mesenchyme
- m′:
-
Type I mesenchyme cell
- m″:
-
Type II mesenchyme cell
- m‴:
-
Type III mesenchyme cell
- mb:
-
median band of the polypide rudiment
- mc:
-
marginal cells of the apical disc
- mi:
-
mitochondria
- mr:
-
microridge
- mv:
-
microvilli
- nn:
-
nerve nodule
- np:
-
neural plate
- nu:
-
nucleus
- O:
-
oral
- oce:
-
oral ciliated epithelium
- op:
-
opening to the internal sac
- ovc:
-
oral vesicular collarette
- p:
-
papilla of the pyriform organ
- pa:
-
pallial cell
- pe:
-
pallial epithelium
- po:
-
pyriform organ
- POS:
-
posterior
- pp:
-
parasagittal patches of undifferentiated cells
- pr:
-
polypide rudiment
- rer:
-
rough endoplasmic reticulum
- sc:
-
supracoronal cells
- sg:
-
secretory granules
- sgf:
-
superior glandular field
- sp:
-
suprapallial cells
- tc:
-
terminal cone
- tf:
-
transitional filaments
- u:
-
undifferentiated cells
- va:
-
vacuole
- vc:
-
vesicular cell
- wc:
-
wedge-shaped cells of the apical disc
- y:
-
yolk granule
- za:
-
zonula adhaerens
- Gp:
-
Glutaraldehyde-phosphate
- Os:
-
Osmium
References
Barrois J (1877) Recherches sur l'embryologie des Bryozoaires (Mémoire sur l'embryologie des Bryozoaires). Trav Stn Zool Wimereux 1:1–305 (Also: Thés Fac Sci Paris No. 396)
Barrois J (1882) Embryogénie des Bryozoaires. Essai d'une théorie génerale du developement basee sur l'étude de la métamorphose. J Anat Physiol Paris 18:124–157
Barrois J (1886) Mémoire sur la métamorphose de quelques Bryozoaires. Biblitque Éc ht Étud Paris Sect Sci Nat 32(5):1–94; 4 pls
Bogiavlenskii H (1905) To the knowledge of embryonic development, budding, and regeneration in Zoobotryon pellucidus. Obshchestro liubitele \({\text{izv}}{\text{sti}}\) estestvoznaniia, antropologii i etnografii, Moscow, izviestiia v. 108:1–90 (pls I–III) (Union List of Serials, vol 4, p 3131)
Braem F (1951) Über Victorella und einige ihrer nächsten Verwandten sowie die Bryozoenfauna des Ryck bei Greifswald. Zoologica (Stuttg) 102:1–59 (12 pls)
Brien P (1960) Classe des Bryozoaires. Traité de Zoologie 5(2):1053–1355. Masson et Cie, Paris
Calvet L (1900) Contribution à l'histoire naturelle des Bryozoaires Ectoproctes marins. Trav Inst Zool Univ Montpellier (N.S.) 8:1–488
Canu F, Bassler RS (1920) North American early Tertiary Bryozoa. US Natl Mus Bull 106:1–880
Cori CJ (1940) 3. Ordnung der tentaculata: Bryozoa. Handbuch der Zoologie III. 2(5):263–502
Corrêa DD (1948) A embryologia de Bugula flabellata (JV Thompson) (Bryozoa Ectoprocta). Univ Sao Paulo, Fac Filos Cienc Let Bol Zool 13:7–71
Gibbons IR (1961) The relationship between the fine structure and direction of beat in gill cilia of a lamellibranch mollusc. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 11:179–205
Hondt JL d' (1973) Étude anatomique, histologique, et cytologique de la larve d'Alcyonidium polyoum (Hassal 1841), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Arch Zool Exp Gén 114:537–602
Hondt JL d' (1974) La métamorphose de la larve et la réalisation du «cystide» chez Alcyonidium polyoum (Hassal 1841), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Arch Zool Exp Gén 115:577–605
Hondt JL d' (1975) Étude anatomique et cytologique comparée de quelques larves de Bryozoaires Cténostomes. In: Pouyet S (ed) Bryozoa 1974. Docum Lab Geol Sci Lyon H.S. 3(1). Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, pp 125–134
Hondt JL d' (1976) Evolution des lignées cellulaires larvaires des Bryozoaires Gymnolaemates au cours de la métamorphose et de l'organogenèse ancestrulaire. Bull Soc Zool Fr 101 (suppl. 5):41–47
Hondt JL d' (1977a) Valeur systématique de la structure larvaire et des particularités de la morphogenèse post-larvaire chez les Bryozoaires Gymnolaemates. Gegenbaurs Morph Jahrb 123(3):463–483
Hondt JL d' (1977b) Structure larvaire et histogenèse post-larvaire chez Bowerbankia imbricata (Adams 1798) Bryozoaire Cténostome (Vesicularines). Arch Zool Exp Gén 118:211–243
Hondt JL d' (1977c) Structure larvaire et organogenèse post-larvaire chez Flustrellidra hispida (Fabricius 1780), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Zoomorphologie 87:165–189
Hyman LH (1959) The lophophorate coelomates — phylum Ectoprocta. In: The invertebrates: smaller coelomate groups, Vol 5. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 275–515
Jebram D (1973) Stolonen-Entwicklung und Systematik bei den Bryozoa Ctenostomata. Sonderdruck aus Z. f Zool Systematik u Evolutionsforschung 11:1–48
Joliet L (1877) Contributions à l'histoire naturelle des bryozoaires des côtes de France. Arch Zool Exp Gén 6:193–304 (pls 6–13)
Kupelweiser H (1905) Untersuchungen über den feineren Bau und die Metamorphose des Cyphonautes. Zoologica (Stuttgart) 19:1–50
Loeb MJ, Walker G (1977) Origin, composition, and function of secretions from pyriform organs and internal sacs of four settling Cheilo-Ctenostome bryozoan larvae. Mar Biol 42:37–46
Marcus E (1941) Sôbre Bryozoa do Brasil. Bol Fac Phil Sc Latr Univer S Paulo XXII. Zoologia 5:3–208
Maturo FS (1971) Larval behavior and metamorphosis in the Cupuladriidae (Bryozoa, Anasca). Proc 2nd Int Conf Inter Bryozool Assoc 1971 (oral communication)
Osburn RC, Soule JD (1953) Order ectoprocta, suborder ctenostomata. In: Osburn RC (ed) Bryozoa of the pacific coast of America. Part 3: Cyclostomata, Ctenostomata, Entoprocta, and Addenda. Allan Hancock Pacific Expeditions 14(3):726–758. Los Angeles: The University of Southern California Press
Ostrooumoff MA (1885) Note sur la métamorphose du Cyphonautes. Zool Anz 8:219
Ostroumoff AA (1886) Contribution a l'etude zoologique et morphologique des bryozoaires du Golfe de Sebastopol. Archs Slaves Biol 1:557–569; 2:184–190; 2:329–355 (5 pls)
Prenant M, Bobin G (1956) Bryozoaires Entoproctes, Phylactolèmes, Cténostomes. In: Faune de France. Paul Lechevalier, Paris
Prouho H (1890) Recherches sur la larve de Flustrella hispida: Structure et métamorphose. Arch Zool Exp Gén 2 ser. 8:409–459
Prouho H (1892) Contribution à l'histoire des bryozoaires. Arch Zool Exp Gén 2 ser. 10:557–656
Reed CG (1978) Larval morphology and settlement of the bryozoan, Bowerbankia gracilis (Vesicularioidea, Ctenostomata): Structure and eversion of the internal sac. In: Chia FS, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, New York, pp 41–48
Reed CG (1980) The reproductive biology, larval morphology and metamorphosis of the marine bryozoan, Bowerbankia gracilis (Vesicularioidea, Ctenostomata). Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Reed CG, Cloney RA (1980) The role of ciliary motility in the metamorphosis of a bryozoan. Am Zool 20:953
Repiachoff W (1879) The embryology of Bowerbankia. Zool Anz 2:660–664
Repiachoff W (1880) On the morphology of bryozoans. Zap novoross Obshch Estest 6(11):1–71 (4 pls)
Ryland JS (1974) Behavior, settlement, and metamorphosis of bryozoan larvae: A review. Thalassia Jugoslavica 10:239–262
Ryland JS (1976) Physiology and ecology of marine bryozoans. Adv Mar Biol 14:285–443
Soule JD (1954) Post-larval development in relation to the classification of the Bryozoa Ctenostomata. Bull S Calif Acad Sci 53:13–34
Soule JD, Soule DF (1969) Systematics and biogeography of burrowing bryozoans. Am Zool 9:790–802
Soule JD, Soule DF (1975) Spathipora, its anatomy and phylogenetic affinities. In: Pouyet S (ed) Bryozoa 1974. Docum Lab Geol Sci Lyon H.S. 3(1). Universite Claude Bernard, Lyon, pp 247–253
Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (1971) Attachment and metamorphosis of the Cheiloctenostome bryozoan, Bugula neritina (Linne). J Morph 134:351–382
Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (1978) Metamorphosis of cellularioid bryozoans. In: Chia FS, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, New York, pp 49–63
Zimmer RL, Woollacott RM (1977a) Structure and classification of gymnolaemate larvae. In: Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (eds) Biology of bryozoans. Academic Press, New York, pp 57–89
Zimmer RL, Woollacott RM (1977b) Metamorphosis, ancestrulae, and coloniality in bryozoan life cycles. In: Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (eds) Biology of bryozoans. Academic Press, New York, pp 91–142
Zirpolo G (1933) Zoobothryon verticillatum (Delle Chiaje). Mem Accad Nuovi Lincei (2) 17:109–442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, C.G., Cloney, R.A. The larval morphology of the marine bryozoan Bowerbankia gracilis (Ctenostomata: Vesicularioidea). Zoomorphology 100, 23–54 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312198
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312198