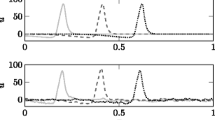
Abstract
A compartmental model of a terrapin motoneuron has been set up to compute membrane potential variations associated with synaptic input at different locations or with antidromic invasion. Membrane potential distributions obtained in that way were used to compute field potentials by means of a volume conduction formalism. The model was used to simulated field potentials measured in the spinal cord in response to stimulation of a muscle nerve with the intention to discriminate between different activation hypothesis for the generation of the spinal cord potential. Extracellular potentials calculated with an excitatory input distributed over the whole dorsal dendritic tree were found to give better reconstruction when compared with excitation restricted to the distal part of the dorsal dendrites, or with somatic inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, J.N., Crill, W.E.: Specific membrane properties of cat motoneurones. J. Physiol. 239, 301–324 (1974)
Brookhart, J.M., Fadiga, E.: Potential fields initiated during monosynaptic activation of frog motoneurons. J. Physiol. 150, 633–655 (1960)
Erulkar, S.D., Soller, R.W.: Neuronal interactions in a central nervous system model. In: Origin of cerebral field potentials, Speckmann, E.J., Caspers, H. (eds.), pp. 13–20, Stuttgart: Thieme 1979
Feenstra, B.W.A.: Field potential studies of the spinal cord of chelonia. In: Proc. of the 21st Dutch Fed. Meeting, Nijmegen, p. 123, 1980
Feenstra, B.W.A.: Analyses of cord dorsum potentials in the terrapin. In: Spinal projections of hindlimb afferents in the terrapin. Thesis State University of Utrecht, The Netherlands 1983a
Feenstra, B.W.A.: Distribution and sources of spinal cord potentials evoked by muscular and cutaneous nerves in the terrapin. In: Spinal projections of hindlimb afferents in the terrapin. Thesis State University of Utrecht, The Netherlands 1983b
Feenstra, B.W.A.: Spinal projections of chelonian muscle afferents studied by evoked potential analyses. J. Physiol. 350, 33 (1984)
Frank, E., Westerfield, M.: Synaptic organization of sensory and motor neurones innervating triceps brachii muscles in the bullfrog. J. Physiol. 324, 479–494 (1982)
Fukami, Y.: Postsynaptic potentials in toad's spinal motoneurons due to muscle afferent volleys. Jap. J. Physiol. 11, 596–604 (1961)
Grantyn, R., Shapovalov, A.I., Shiriaev, B.I.: Combined morphological and electrophysiological description of connections between single primary afferent fibres and individual motoneurons in the frog spinal cord. Exp. Brain Res. 48, 459–462 (1982)
Holsheimer, J., Boer, J., Lopes da Silva, F.H., Rotterdam, A. van: The double dipole model of theta rhythm generation: simulation of laminar field potential profiles in dorsal hippocampus of the rat. Brain Res. 235, 31–50 (1982)
Joseph, B.S., Whitlock, D.G.: The morphology of spinal afferent-efferent relationships in vertebrates. Brain Behav. Evol. 1, 2–18 (1968)
Kenins, P.: Reflex response to stretch of limb muscles in the australian blue tongue lizard. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 57 A, 383–390 (1977)
Kusuma, A., Donkelaar, H.J. Ten: Staining of the dorsal root primary afferent fibers by anterograde movement of horseradish peroxidase and retrograde labelling of motoneurons and preganglionic autonomic cells in the turtle spinal cord. Neurosci. Letters 14, 141–146 (1979)
Kusuma, A., Donkelaar, H.J. Ten: Dorsal root projections in various types of reptiles. Brain Behav. Evol. 17, 291–309 (1980)
Lux, H.D., Schubert, P., Kreutzberg, G.W.: Direct matching of morphological and electrophysiological data in cat spinal motoneurons. In: Excitatory synaptic mechanisms, Andersen, P., Jansen, J.K.S., (eds.), 5th Intern. Meet. Neurobiologists, pp. 189–198, Universitets forlaget Oslo 1970
Prohaska, O., Kohl, F., Szirmai, I., Urban, G., Vollmer, R.: Investigation of the inhomogenities of the tissue impedance within the rabbit's cortex. In: Proc. of the 5th Intern. Conf. on Electr. Bio-Impedance, pp. 117–120, Tokyo 1981
Rall, W.: Theory of physiological properties of dendrites. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 96, 1071–1092 (1962)
Rall, W., Shepherd, G.M.: Theoretical reconstruction of field potentials and dendrodendritic synaptic interactions in olfactory bulb. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 884–915 (1968)
Redman, S., Walmsley, B.: The synaptic basis of the monosynaptic stretch reflex. Trends Neurosci. 4, 248–251 (1981)
Rosenberg, M.E.: Excitation and inhibition of motoneurones in the tortoise. J. Physiol. 221, 715–730 (1972)
Rosenberg, M.E.: The distribution of the sensory input in the dorsal spinal cord of the tortoise. J. Comp. Neurol. 156, 29–38 (1974)
Rotterdam, A. van: A computer system for the analysis and synthesis of field potentials. Biol. Cybern. 37, 33–39 (1980)
Rotterdam, A. van: A one dimensional formalism for the computation of extracellular potentials: linear systems analysis applied to volume conduction. In: Progress Report Institute of Medical Physics TNO, No. PR6, Eijnsbergen, B. van, Lopes da Silva, F.H., (eds.), pp. 115–122, Utrecht 1978
Ruigrok, T.J.H., Crowe, A., Donkelaar, H.J. Ten: The distribution of motoneurons innervating hindlimb muscles in the terrapin Pseudemys scripta elegans. Neurosci. Letters 28, 157–162 (1982)
Ruigrok, T.J.H.: Organization and morphology of motoneurons and primary afferents in the lumbar spinal cord of the turtle Pseudemys Scripta Elegans. Thesis State University of Utrecht, The Netherlands 1984
Sypert, G.W., Munson, J.B., Fleshman, J.W.: Effect of presynaptic inhibition on axonal potentials, terminal potentials, focal synaptic potentials, and EPSP's in cat spinal cord. J. Neurophysiol. 44, 792–803 (1980)
Ulfhake, B., Kellerth, J.O.: A quantitative light microscopic study of the dendrites of cat spinal alfa-motoneurons after intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. J. Comp. Neurol. 202, 571–583 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feenstra, B.W.A., Hofman, F. & Van Leeuwen, J.J. Syntheses of spinal cord field potentials in the terrapin. Biol. Cybern. 50, 409–418 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335198
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00335198