Abstract
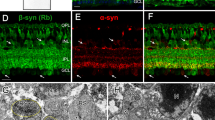
It is known that the retina contains the protein dystrophin in the ribbon synapse, but the ultrastructural analysis is not yet fully elucidated. Our previous study reported that dystrophin is localized under the rod cell membranes in rat retinas. In the present study, we have investigated the relationship between dystrophin-rich regions of rod cell membranes and other neuronal processes in mouse retinas with a monoclonal antibody raised against the human dystrophin C-terminus. Immunoblotting, immunofluorescence stainings, and immunoelectron microscopy were employed. Immunoblotting analysis indicated that mouse retinas possessed some of the dystrophin isoforms of approximately 260 kDa, 140 kDa, and 70 kDa molecular weight. Confocal images showed a punctate appearance in the outer plexiform layer, as previously described. Immunoelectron microscopy showed that dystrophin immunoreactive products were always observed at submembranous dense regions of the rod spherule abutting bipolar processes. These results suggest that retinal dystrophin may be closely involved in signal transmission from rods to bipolar cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 7 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, H., Baba, T., Terada, N. et al. Dystrophin in rod spherules; submembranous dense regions facing bipolar cell processes. Histochemistry 108, 243–248 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004180050164
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004180050164