Abstract
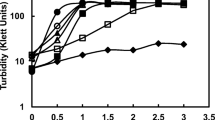
The effects of optimal sources and concentrations of major nutrients (supplying N, S, P, K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and inorganic carbon) and organic buffers on growth and secondary metabolite accumulation in Scytonema ocellatum strain FF-66-3 were determined. Nitrate, phosphate, magnesium, and sulfur had no specific stimulatory or inhibitory effects on scytophycin accumulation within the range of concentrations that supported optimal growth. Calcium concentrations greater than those required for growth (0.1 mM) stimulated scytophycin accumulation. Sodium carbonate concentrations in excess of 0.25 mM strongly inhibited growth. Ammonium (2.5 mM) inhibited both growth and product formation. 3-[N-Morpholino]propanesulfonic acid at 3–5 mM effectively controlled pH and facilitated both growth and product formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonowitz Y (1980) Nitrogen regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol 34:209–233
Bhattacharya M, Majumdar SK (1982) Studies on the nutritional requirements of Penicillium citrinum for the synthesis of citrinin toxin. J Food Sci Technol 19:61–63
Bloor S, England RR (1991) Elucidation and optimization of the medium constituents controlling antibiotic production by the cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:76–81
Carmeli S, Moore RE, Patterson GML (1990) Tolytoxin and new scytophycins from three species of Scytonema. J Nat Prod 53:1533–1542
Carmichael WW (1992) Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites-the cyanotoxins. J Appl Bacteriol 72:445–459
Castenholz RW (1988) Culture methods for cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol 167:68–93
Flores E, Wolk CP (1986) Production, by filamentous, nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, of a bacteriocin and of other antibiotics that kill related strains. Arch Microbiol 145:215–219
Foerster JW (1964) The use of calcium and magnesium hardness ions to stimulate sheath formation in Oscillatoria limosa (Roth) C. A. Agardh. Trans Am Microsc Soc 83:420–427
Fogg GE, Thake B (1987) Algal cultures and phytoplankton ecology, 3rd edn. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison
Garner HR, Fahmy M, Phillips RL, Koffler H, Tetrault PA, Bohonos N (1950) Chemical changes in the submerged growth of Streptomyces griseus. Bacteriol Proc 1:139–140
Gentile JH, Maloney TE (1969) Toxicity and environmental requirements of a strains of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Can J Microbiol 15:165–173
Gleason FD, Wood JM (1987) Secondary metabolism in cyanobacteria. In: Fay P, Van Baalen C (eds), The cyanobacteria. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 437
Hobbs G, Frazer CM, Gardner DCJ, Flett F, Oliver SG (1990) Pigmented antibiotic production by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): kinetics and the influence of nutrients. J Gen Microbiol 136:2291–2296
Jung JH, Moore RE, Patterson GML (1991) Scytophycins from a blue-green alga belonging to the Nostocaceae. Phytochemistry 30:3615–3616
Kratz WA, Myers J (1955) Nutrition and growth of several blue-green algae. Am J Bot 42:282–287
Kumar HD, Prakash G (1971) Toxicity of selenium to the blue-green algae, Anacystis nidulans and Anabaena variabilis. Ann Bot 35:697–705
Majumdar MK, Majumdar SK (1965) Effects of minerals on neomycin production by Streptomyces fradiae. Appl Microbiol 13:190–193
Manabe E, Hirano M, Takano H, Ishikawa-Doi N, Sode K, Matsunaga T (1992) Influence of ammonium chloride on growth and fatty acid production by Spirulina platensis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 34:273–281
Martín JF, Demain AL (1980) Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev 44:230–251
Neidhardt FC, Bloch PL, Smith DF (1974) Culture medium for Enterobacteria. J Bacteriol 119:736–747
Nomi R (1963) Streptomycin formation by intact mycelium of Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol 86:1220–1230
O'Flaherty LM, Phinney HK (1970) Requirements for the maintenance and growth of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae in culture. J Phycol 6:95–97
Patterson GML, Bolis C (1993a) Regulation of scytophycin accumulation in cultures of Scytonema ocellatum. I. Physical factors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:375–381
Patterson GML, Bolis C (1993b) Determination of scytophycins in cyanophyte cultures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr 16:475–486
Patterson GML, Baldwin CL, Bolis CM, Caplan FR, Karuso H, Larsen LK, Levine IA, Moore RE, Nelson CS, Tuang GD, Furusawa E, Furusawa S, Norton TR, Raybourne RR (1991) Antineoplastic activity of cultured blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). J Phycol 27:530–536
Patterson GML, Smith CD, Kimura LH, Britton BA, Carmeli S (1993a) Action of tolytoxin on cell morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and actin polymerization. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 24:39–48
Patterson GML, Baker KK, Baldwin CL, Bolis CM, Caplan FR, Larsen LK, Levine IA, Moore RE, Nelson CS, Tschappat KD, Tuang GD, Boyd MR, Cardellina JH II, Collins RP, Gustafson KR, Snader KM, Weislow OS (1993b) Antiviral activity of cultured blue-green algae (cyanophyta). J Phycol 29:125–130
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Schwartz RE, Hirsch CF, Sesin DF, Flor JE, Chartrain M, Fromtling RE, Harris GH, Salvatore MJ, Liesch JM, Yudin K (1990) Pharmaceuticals from cultured algae. J Ind Microbiol 5:113–124
Sivonen K (1990) Effects of light, temperature, nitrate, orthophosphate, and bacteria on growth of and hepatotoxin production by Oscillatoria agardhii strains. App Environ Microbiol 56:2658–2666
Smith CD, Carmeli S, Moore RE, Patterson GML (1993) Scytophycins: novel microfilament-depolymerizing agents which circumvent p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Res 53:1343–1347
Smith RJ (1988) Calcium-mediated regulation in the cyanobacteria? In: Rogers LJ, Gallon JR (eds) Biochemistry of the Algae and Cyanobacteria. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 185
Wälzlein G, Pistorius EK (1991) Inactivation of photosynthetic O2 evolution in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans PCC6301: influence of nitrogen metabolites and divalent cation concentration. z Naturforsch 46c:1024–1032
Wolk CP (1973) Physiology and cytological chemistry of blue-green algae. Bacteriol Rev 37:32–101
Yongmanitchai W, Ward OP (1991) Growth of and omega-3 fatty acid production by Phaeodactylum tricornutum under different culture conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:419–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patterson, G.M.L., Bolis, C.M. Regulation of scytophycin accumulation in cultures of Scytonema ocellatum. II. Nutrient requirements. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 692–700 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164775
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164775