Abstract
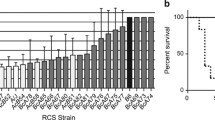
Recombinant inbred strains were used to demonstrate the existence of a major locus on chromosome 1, designated Sap, which controls the endogenous concentration of the mouse acute phase reactant, serum amyloid P-component (SAP). Levels of SAP were associated with alleles at the Ly-9 locus in two sets of RI strains: BXD (C57BL/6J × DBA/2) and BXH (C57BL/6J × C3H/HeJ). Low endogenous levels of SAP were present in the C57BL/6J progenitor strain and in most of the RI strains which inherited the Ly-9 ballele. High levels of SAP were present in the DBA/2J and C3H/HeJ progenitors and in most of the RI strains which inherited the Ly-9 aallele. In the BXD strains 91% of the genetic variation of SAP levels was accounted for by segregation at the Ly-9 locus while an additional 9% was attributed to genetic factors unlinked to Ly-9. In the BXH strains the percentage of genetic variation accounted for by Ly-9 segregation was reduced to 46%, while 54% was accounted for by other genetic factors. Because of background genetic variation it was not possible to detect any crossovers between Sap and Ly-9. However, in the BXD strains the linkage between Sap and Ly-9 appears to be quite close. The B6.C-H-25 ccongenic strain, which carries a segment of BALB/c chromosome 1 including the minor histocompatibility locus H-25 on a C57BL/6By background, had the same endogenous SAP level as the BALB/c donor strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, D. W.: Genetics of histocompatibility in mice. I. New loci and congenic lines. Immunogenetics 2: 249–256, 1975
Benson, M. D., Skinner, M., Shirahama, T., and Cohen, A. S.: P-component of amyloid: Isolation from human serum by affinity chromatography. Arthritis Rheum. 19: 749–755, 1976
Chirgwin, J. M., Schaefer, I. M., Rotwin, P. S., Piccini, N., Gross, K. W., and Naylor, S. L.: Human renin gene is on chromosome 1. Somatic Cell Mol. Genet. 10: 415–421, 1984
Crowle, A. J. and Miller, J. L.: Crossed immunoelectrophoresis of mouse serum. J. Immunol. Methods 43: 15–26, 1981
deBeer, F. C., Baltz, M. L., Holford, S., Feinstein, A., and Pepys, M. B.: Fibronectin and C4-binding protein are selectively bound by aggregated amyloid P-component. J. Exp. Med. 154: 1134–1149, 1981
Durda, P. J., Boos, S. C., and Gottlieb, P. D.: T100: A new murine cell surface glycoprotein detected by anti-LYT-2.1 serum. J. Immunol. 122: 1407–1412, 1982
Ferreira, A., Nussenzweig, V., and Gigli, I.: Structural and functional differences between the H-2 controlled Ss and Slp proteins. J. Exp. Med. 148: 1186–1197, 1978
Festenstein, H., Bishop, C., and Taylor, B. A.: Location of Mls locus on mouse chromosome 1. Immunogenetics 5: 357–361, 1977
Hind, C. R. K., Collins, P. M., Renn, D., Cook, R. B., Caspi, D., Baltz, M. L., and Pepys, M. B.: Binding specificity of serum amyloid P-component for the pyruvate acetal of galactose. J. Exp. Med. 159: 1058–1069, 1984
Hogarth, P. M., Craig, J., and McKenzie, I. F. C.: A monoclonal antibody detecting the Ly-9.2 (Lgp 100) cell-membrane alloantigen. Immunogenetics 11: 65–74, 1980
Kimura, S., Tada, N., Nakayama, E., Liu, Y., and Hämmerling, U.: A new mouse cell-surface antigen (Ly-m20) controlled by a gene linked to Mls locus and defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunogenetics 14: 3–14, 1981
Knott, T. J., Eddy, R. L., Robertson, M. E., Priestly, L. M., Scott, J., and Shows, T. B.: Chromosomal localization of the human apoprotein CI gene and of a polymorphic apoprotein AII gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 125: 299–301, 1984
Kozak, C. A., Davidson, W. F., and Morse, H. C.: Genetic and functional relationships of the retroviral and lymphocyte alloantigen loci on mouse chromosome 1. Immunogenetics 19: 163–168, 1984
Le, P. T. and Mortensen, R. F.: In vitro induction of hepatocyte synthesis of the acute phase reactant mouse serum amyloid P-component by macrophages and IL 1. J. Leuk. Biol. 35: 587–603, 1984
Le, P., Muller, M. T., and Mortensen, R. F.: Acute phase reactants of mice. I. Isolation of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) and its induction by a monokine. J. Immunol. 129: 665–672, 1982
Ledbetter, J. A., Goding, J. W., Tsu, T. T., and Herzenberg, L. A.: A new mouse lymphoid alloantigen (Lgp 100) recognized by a monoclonal rat antibody. Immunogenetics 8: 347–360, 1979
Lusis, A. J., Taylor, B. A., Wangenstein, R. W., and LeBoeuf, R. C.: Genetic control of lipid transport in mice. II. Genes controlling structure of high density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 258: 5071–5078, 1983
Mantzouranis, E. C., Dowton, S. B., Whitehead, A. S., Edge, M. D., Bruns, G. A. P., and Colten, H. R.: Human serum amyloid P-component. cDNA isolation, complete sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 7752–7756, 1985
Mortensen, R. F., Beisel, K., Zeleznik, N. J., and Le, P. T.: Acute phase reactants of mice. II. Strain dependence of serum amyloid P-component (SAP) levels and response to inflammation. J. Immunol. 130: 885–889, 1983
Painter, R. H., DeEscallion, I., Massey, A., Pinteric, L., and Stern, S. B.: The structure and binding characteristics of serum amyloid P protein. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 389: 199–215, 1982
Passmore, H. C. and Shreffler, D. C.: A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: Inheritance and association with the H-2 region. Biochem. Genet. 4: 351–365, 1970
Pepys, M. B. and Baltz, M. L.: Acute phase proteins with special reference to CRP and related proteins (pentraxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv. Immunol. 34: 141–212, 1983
Piccini, N., Kopf, J. L., and Gross, K. W.: A DNA polymorphism, consistent with gene duplication, correlates with high renin levels in the mouse submaxillary gland. Cell 30: 205–213, 1982
Roderick, T. H. and Davisson, M. L.: Linkage map of the mouse (Mus musculus). Genet. Maps 3: 343–355, 1984
Taylor, B. A.: Recombinant inbred strains: Use in gene mapping. In H. Morse (ed.): Origins of Inbred Mice, pp. 423–438, Academic Press, New York, 1978
Taylor, B. A.: Recombinant inbred strains of mice: Use in genetic analysis of diseases resistance. In: Genetic Control of Natural Resistance to Infection and Malignancy, pp. 1–7, Academic Press, Inc., New York, 1980
Traina, V. L., Taylor, B. A., and Cohen, J. C.: Genetic mapping of endogenous mouse mammary tumor viruses: Locus characterization, segregation, and chromosomal distribution. J. Virol. 40: 735–744, 1981
Whitehead, A. S., Pruns, G. A. P., Markham, A. F., Colten, H. R., and Woods, D. E.: Isolation of human C-reactive protein complementary DNA and localization of the gene to chromosome 1. Science 221: 69–71, 1983
Wilcox, F. H., Hirschorn, L., Taylor, B. A., Womack, J. E., and Roderick, T. H.: Genetic variation in alkaline phosphatase of the house mouse (Mus musculus) with emphasis on a manganese-requiring isozyme. Biochem. Genet. 17: 1093–1107, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortensen, R.F., Let, P.T. & Taylor, B.A. Mouse serum amyloid P-component (SAP) levels controlled by a locus on chromosome 1. Immunogenetics 22, 367–375 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430920
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00430920