Summary
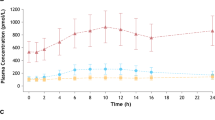
The diminished sympathomimetic pressor activity of monohydroxylated phenylalkylamines after oral administration has been attributed to incomplete enteric absorption. Therefore, urinary excretion of the unchanged drug and its metabolites has been compared after intravenous and oral administration of3H-m-octopamine to eight patients. Identical amounts of3H-activity (80% of the dose) were excreted after the two routes of dosing, so enteric absorption has been assumed to be complete. Significant differences were found in the fraction of free urinarym-octopamine, which amounted to 10.5% of the dose after infusion and 0.58% after oral administration. The only metabolic pathways form-octopamine are deamination and conjugation. Following oral administration the percentage of conjugates was considerably higher than after intravenous infusion. This metabolic pattern appears typical of all phenylalkylamines with a hydroxyl group in themeta position. Ring hydroxylation to catecholamines was not observed. The enzymes mainly responsible for conjugation after oral administration are located in the gut wall. The resulting “first pass effect”, i.e. metabolism prior to the access to the central compartment, can account for the diminished pharmacodynamic effect after dosing by this route.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod, J.: Enzymatic formation of adrenaline and other catechols from monophenols. Science140 499–500 (1963)
Bray, G.: A simple efficient liquid scientillator for counting aqueous solutions in a liquid scintillation counter. Analyt. Biochem.1 279–285 (1960)
Conway, W.D., Minatoya, H., Lands, A.M., Shekosky, J.M.: Absorption and elimination profile of isoproterenol. III. The metabolic fate of dlisoproterenol-7-H3 in the dog. J. pharm. Sci.57 1135–1141 (1968)
Credner, K. Renwanz, G., Hinze, H.J.: Untersuchungen über das Verhalten des m-Hydroxyphenyl (1)-äthanol) (1)-amin (2) hydrochlorids im Organismus. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch.Pharmak.243 85–90 (1962)
Credner, K., Neugebauer, K.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die Kreislauf- und Stoffwechselwirkungen des p- und m-Oxyphenylaminoäthynol-HCL. Arzneimittel-Forsch.3 462–465 (1953)
Dengler, H. J.: Zur Methodik der Katecholaminbestimmung beim Phaeochromocytom. Ergebn. Labor.-Med.3 55–63 (1967)
Dengler, H.J.: Resorption, Verteilung und Ausscheidung von Tritium-markiertem 1-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-isopropylaminoäthanol (Alupent). Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path.255 9 (1965)
Engelman, K., Jéquier, E., Udenfriend, S., Sjoerdsma, A.: Metabolism of α-methyltyrosine in man: Relationship to its potency as an inhibitor of catecholamine biosynthesis. J. clin. Invest.47 568–576 (1968)
Hengstmann, J.H., Konen, W., Konen, C., Eichelbaum, M., Dengler, H.J.: The physiological disposition ofp-octopamine in man. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol.283 93–106 (1974)
Hengstmann, J.H., Weyand, U., Dengler, H.J.: Enteral absorption and metabolism of DL-1-(m-hydroxyphenyl)-2-ethylaminoethanol in the human. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmac.274, R51 (1972)
Ikeda, M., Levitt, M., Udenfriend, S.: Hydroxylation of phenyl alanine by purified preparations of adrenal and brain tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.18 482–488 (1965)
Jones, R.L., Bory, P., Brown, W.T., Mc.Geer, P.L.: Failure to detect p-methoxyphenylethylamine derivatives in human urine. Canad. J. Biochem.47 185–195 (1969)
Kaczmarek, E., Puppe, H.: Klinisch-experimentelle Messungen zur Kreislaufwirkung des Novadrals. Arzneimittel-Forsch.3 208–210 (1953)
Pisano, J.J., Crout, J.R., Abraham, D.: Determination of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxymandelic acid in urine. Clin. chim. Acta7 285–291 (1962)
Richter, D.: The inactivation of adrenaline in vivo in man. J. Physiol. (Lond.)98 361–370 (1940)
Ruthven, C.R.J., Sandler, M.: The estimation of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylglycol and total metadrenalines in human urine. Clin. chim. Acta12 318–324 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hengstmann, J.H., Konen, W., Konen, C. et al. Bioavailability of m-octopamine in man related to its metabolism. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 8, 33–39 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616412
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00616412