Summary
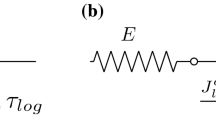
Mukudai and Yata have shown in the previous reports an interpretation of mechano-sorptive behavior that characteristic of viscoelastic behavior of wood under moisture change may be resulted from redistribution of applied stress in the cell wall because of change of friction between the S1 and S2 layers induced by moisture content change due to the looseness between the both layers, and have proposed a mechano-sorptive model based on the interpretation.
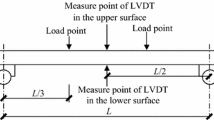
In this report, to find out evidence supporting the interpretation that mechano-sorptive behavior is resulted from the looseness between the S1 and S2 layers, surfaces of specimens fractured by increasing load during creep under moisture content change were observed with electron microscopes. And, characteristic features of mechano-sorptive creep and recovery deflection curves at 15%, 30% and 45% stress levels which were obtained by computer simulation were checked by comparison with those of the corresponding experiments.
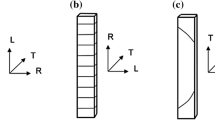
As the results, it could be observed that fractures took place at the interface of the S1 and S2 layers in cells of the tension side of beams, and splits at the interface of the S1 and S2 layers took place here and there in the fractured surfaces. Furthermore, the characteristic features of creep and recovery deflection curves obtained by the simulations agreed well with those of the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, L. D.; Christensen, G. N. 1961: Effect of moisture changes on creep in wood. Nature 191: 869–870
Barber, N. F.; Meylan, B. A. 1964: The anisotropic shrinkage of wood. Holzforschung 18: 146–156
Fengel, D.; Wegener, G. 1984: WOOD, chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. pp. 324–325. New York: Walter de Gruyter
Gibson, E. J. 1965: Creep of wood: role of water and effect of a changing moisture content. Nature 206: 213–215
Hearmon, R. F. S.; Paton, J. M. 1964: Moisture content changes and creep of wood. Forest Prod. J. 14: 357–359
Mukudai, J. 1983a: Evaluation on non-linear viscoelastic bending deflection of wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 17: 39–54
Mukudai, J. 1983b: Evaluation of linear and non-linear viscoelastic bending loads of wood as a function of prescribed deflections. Wood Sci. Technol. 17: 203–216
Mukudai, J.; Yata, S. 1986: Modeling and simulation of viscoelastic behavior (tensile strain) of wood under moisture change. Wood Sci. Technol. 20: 335–348
Mukudai, J.; Yata, S. 1987. Further modeling and simulation of viscoelastic behavior (bending deflection) of wood under moisture change. Wood Sci. Technol. 21: 49–63
Schniewind, A. P. 1960: On the nature of drying stresses in wood. Holzforschung 14: 161–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are indebted to Professor Arno P. Schniewind, Forest Products Laboratory, University of California, for reviewing the manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukudai, J., Yata, S. Verification of Mukudai's mechano-sorptive model. Wood Sci. Technol. 22, 43–58 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353227
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00353227