Abstract
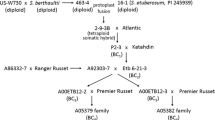
In tomato, Bulked Segregant Analysis was used to identify random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers linked to a quantitative trait locus (QTL) involved in the resistance to the Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus. F4 lines were distributed into two pools, each consisting of the most resistant and of the most susceptible individuals, respectively. Both pools were screened using 600 random primers. Four RAPD markers were found to be linked to a QTL responsible for up to 27.7% of the resistance. These markers, localized in the same linkage group within a distance of 17.3 cM, were mapped to chromosome 6 on the tomato RFLP map.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 August 1996 / Accepted: 4 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chagué, V., Mercier, J., Guénard, M. et al. Identification of RAPD markers linked to a locus involved in quantitative resistance to TYLCV in tomato by bulked segregant analysis. Theor Appl Genet 95, 671–677 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050611
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050611