Abstract
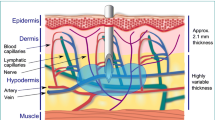
Microdialysis was applied to determine the in vivo transdermal absorption of methotrexate (MTX) in rats with or without a new penetration enhancer, l-[2-(decylthio)ethyl]azacyclopentan-2-one (HPE-101). A solution composed of 2.5 mM MTX and 3% (w/v) HPE-101 was applied to the shaved abdomen, in which a semipermeable membrane cannula of 10-mm length was inserted intracutaneously with the use of an L-shaped needle. Intradermal microdialysis was performed at a flow rate of 1.0 µL/min for 12 hr. The concentration of MTX in the dialysate was measured by fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA). HPE-101 (3%, w/v) significantly increased the dermal MTX concentration from 0.06±0.04 µM in the control to 56±26 µM in the dialysate from 8 to 12 hr. HPE-101 at concentrations of 0.75, 1.5, 2.25, and 3% (w/v) enhanced the total recovery of MTX in dermal dialysate from 0 to 10 hr by approximately 5, 18, 42, and 500 times compared with the control, respectively. The microdialysis system is useful for assessing in vivo transdermal drug absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. Nakashima, M. Nakano, K. Matsuyama, and M. Ichikawa. An application of the microdialysis system to the pharmacokinetic study on striatal distribution of L-DOPA with or without carbidopa in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 72:R5–R8 (1991).
J. M. Ault, C. E. Lunte, N. M. Meltzer, and C. M. Riley. Microdialysis sampling for the investigation of dermal drug transport. Pharm. Res. 9:1256–1261 (1992).
T. Yano, N. Higo, K. Furukawa, M. Tsuji, K. Noda, and M. Otagiri. Evaluation of a new penetration enhancer 1-[2-(decylthio)ethyl]azacyclopentan-2-one (HPE-101). J. Pharmacobio-Dyn. 15:527–533 (1992).
L. Slordal, P. S. Prytz, I. Pettersen, and J. Aarbakke. Methotrexate measurements in plasma: Comparison of enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique, TDx fluorescence polarization immunoassay, and high pressure liquid chromatography. Ther. Drug Monit. 8:368–372 (1986).
O. Chukwumerije, R. A. Nash, J. R. Matias, and N. Orentreich. Studies on the efficacy of methyl esters of n-alkyl fatty acids as penetration enhancers. J. Invest. Derm. 93:349–352 (1989).
E. M. Niazy, A. M. Molokhia, and A. S. El-Gorashi. Effect of Azone and other penetration enhancers on the percutaneous absorption of dihydroergotamine. Int. J. Pharm. 56:181–185 (1989).
L. Fry and R. M. H. McMinn. Topical methotrexate in psoriasis. Arch. Derm. 96:483–488 (1967).
E. J. Van Scott and R. P. Reinertson. Morphologic and physiologic effects of chemotherapeutic agents in psoriasis. J. Invest. Derm. 33:357–369 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuyama, K., Nakashima, M., Nakaboh, Y. et al. Application of in Vivo Microdialysis to Transdermal Absorption of Methotrexate in Rats. Pharm Res 11, 684–686 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018972112077
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018972112077