Abstract
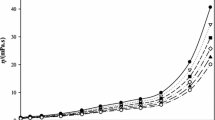
Densities and viscosities of mixtures of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) with water at 25°C have been determined. Limiting equivalent conductances of cesium chloride, potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium thiocyanate in these solvent mixtures at 25°C are presented together with corresponding values of ion association constants and distance of closest approach parameters. The transference number of the potassium ion has been determined in solvent mixtures ranging from 0 to 0.75 mol fraction in DMF in water at 25°C. The conductimetric Hittorf method has been used for both potassium bromide and potassium chloride in solutions of up to 0.496 mole fraction of DMF. For solutions of potassium thiocyanate in 0.5 and 0.75 mole fraction in DMF the cationic transference number has been determined using the moving boundary method. Stokes radii have been evaluated. Transport properties are examined in relation to-solvent properties such as composition, dielectric constant, excess volume of mixing and free volume.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. J. Steel and R. H. Stokes,J. Phys. Chem. 62, 450 (1958).
A. I. Vogel,A Textbook of Quantative Analysis, 3rd ed. (Longmans, London 1961), p. 944.
B. B. Owen and H. Zeldes,J. Chem. Phys. 18, 1083 (1950).
D. E. Mulcahy and B. J. Steel,J. Chem. Eng. Data 30, 191 (1985).
C. J. James, D. E. Mulcahy, and B. J. Steel,J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 17, 225 (1984).
J. E. Lind, J. J. Zwolenik, and R. M. Fuoss,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 81, 1557 (1959).
P. H. Dike,Rev. Sci. Inst. 2, 379 (1931).
J. L. Hawkes and R. L. Kay,J. Phys. Chem. 69, 2420 (1965).
R. H. Stokes,J. Phys. Chem. 65, 1242, 1277 (1961).
M. Spiro, inPhysical Methods of Chemistry, B. W. Rossiter and J. F. Hamilton, eds., Vol. 2 (J. Wiley and Sons, 1986) p. 765, Fig. 8.40b.
M. Spiro, inPhysical Methods of Chemistry, B. W. Rossiter and J. F. Hamilton, eds., Vol. 2 (J. Wiley and Sons, 1986), Fig. 8.40b. Reference 10, p. 746.
R. A. Robinson and R. H. Stokes,Electrolyte Solutions 2nd ed. (Butterworths, London, 1965), Chapter 7.
M. Spiro, inPhysical Methods of Chemistry, B. W. Rossiter and J. F. Hamilton, eds., Vol. 2 (J. Wiley and Sons, 1986), Fig. 8.40b. Reference 10, p. 745.
G. R. Leader and J. F. Gormley,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 73, 5731 (1951).
G. Douheret and M. Morenas,Compt. Rend. Ser. C. 264, 729 (1967).
C. de Visser, G. Perron, J. E. Desnoyers, W. J. M. Heuvelsland, and G. Somsen,J. Chem. Eng. Data.22, 74 (1977).
R. J. Raidon and K. A. Kraus, U.S. Office Saline Water,Res. Develop. Prog. Rep. 302, 52 (1968).
R. J. Fuoss and K. L. Hsia,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 57, 1550 (1967);58, 1818 (1967).
E. W. Washburn, ed.,International Critical Tables of Numerical Data, Physics, Chemistry and Technology, Vol. 5 (National Research Council, New York, 1929), p. 252.
B. Garb and M. Hlasko,Roczniki Chem. 10, 248 (1930).
M. Spiro, inPhysical Methods of Chemistry, B. W. Rossiter and J. F. Hamilton, eds., Vol. 2 (J. Wiley and Sons, 1986), Fig. 8.40b. Reference 10, p. 784.
J.-C. Justice and R. M. Fuoss,J. Phys. Chem. 67, 1707 (1963).
C. Treiner, J.-C. Justice, and R. M. Fuoss,J. Phys. Chem. 68, 3886 (1964).
E. Renard and J.-C. Justice,J. Solution Chem. 3, 633 (1974).
K. L. Hsia and R. J. Fuoss,J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 90, 3055 (1968).
J. E. Lind, Jr. and R. M. Fuoss,J. Phys. Chem. 65, 1414 (1961).
J. E. Prue and P. J. Sherrington,Trans. Faraday Soc. 57, 1795 (1961).
D. P. Ames and P. G. Sears,J. Phys. Chem. 59, 16 (1955).
D. F. Evans, T. Tominaga, J. B. Hubbard, and P. G. Wolynes,J. Phys. Chem. 83, 2669 (1979).
O. Ya. Samoilov,Structure of Aqueous Electrolyte Solutions and the Hydration of Ions, translated by D. J. G. Ives (Consultants Bureau, New York, 1965).
J. L. Kavanau,Water and Solute-Water Interactions, (Holden-Day Inc., San Francisco, 1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chittleborough, G., James, C. & Steel, B. Ion mobilities in DMF-water mixtures at 25°C. J Solution Chem 17, 1043–1057 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00647800
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00647800