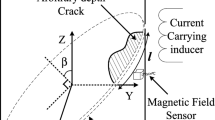
Abstract
In the ac field method of crack depth measurement by the Crack Microgauge, the area of the loop formed in the probe gives rise to an induced voltage, which can introduce errors into the depth measurement. In this paper, a method for measuring the probe area is given, and the quality of the probe is thereby characterized. The underlying theory was given previously, and it is applied here to the probe characterization problem. The probe area is determined by two voltage measurements taken on an artificial rectangular flaw machined in an arbitrary metal. By measurements on several such specimens with the same probe, it is confirmed that the area so obtained is a characteristic of the probe and is independent of the specimen material. Thereafter, measurements on various rectangular flaws with probes of different characteristic area were taken, and very good agreement between predicted and real depths was achieved. Both theory and experiments show that probe characterization is of particular importance when this method is used to measure surface crack depths in metals of low permeability such as aluminum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Mirshekar-Syahkal, D. H. Michael, and R. Collins, Parasitic voltages induced by artificial flaws when measured using the ac field technique,J. Nondestr. Eval. 2:195–202 (1981).
W. D. Dover, F. D. W. Charlesworth, K. A. Taylor, R. Collins, and D. H. Michael, The use of A.C. field measurements to determine the shape and size of a crack in a metal, inEddy Current Characterization of Materials and Structures, G. Birnbaurn and G. Free, eds., ASTM STP 722 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1981), pp. 401–427.
W. D. Dover, F. D. W. Charlesworth, K. A. Taylor, R. Collins, and D. H. Michael, The Measurement of Crack Length and Shape During Fracture and Fatigue, C. J. Beavers, ed. (Engineering Material Advisory Service, Warley, 1980), pp. 222–260.
R. Collins, D. H. Michael, and K. B. Ranger, The A.C. field around a semi-elliptical crack in metal, 13th Symposium on Nondestructive Evaluation, San Antonio, Texas (April 1981) pp. 470–479.
D. H. Michael, R. T. Waechter, and R. Collins, The measurements of surface cracks in metals using A.C. electric fields.Proc. Roy. Soc., London 1981, pp. 139–157.
F. D. W. Charlesworth and W. D. Dover, inSome Aspects of Crack Detection and Sizing Using A.C. Field Measurement, C. J. Beavers, ed. (Engineering Material Advisory Service, Warley), to be published.
C. J. Smithells,Metal Reference Book, 2nd ed. (Butterworths, London, 1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirshekar-Syahkal, D. Probe characterization in ac field measurements of surface crack depth. J Nondestruct Eval 3, 9–17 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566950
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566950