Abstract
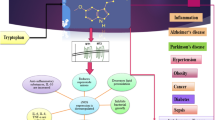
1. Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH), synthesized in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), is released in response to physiological stimuli through medianeminence nerve terminals to control thyrotropin or prolactin secretion from the pituitary.
2. Several events participate in the metabolism of this neuropeptide: regulation of TRH biosynthesis and release as well as modulation of its inactivation by the target cell.
3. Upon a physiological stimulus such as cold stress or suckling, TRH is released and levels of TRH mRNA increase in a fast and transient manner in the PVN; a concomitant increase in cfos is observed only with cold exposure.
4. Hypothalamic cell cultures incubated with cAMP or phorbol esters show a rise in TRH mRNA levels; dexamethasone produces a further increase at short incubation times.TRH mRNA are thus controlled by transsynaptic and hormonal influences.
5. Once TRH is released, it is inactivated by a narrow specificity ectoenzyme, pyroglu-tamyl peptidase II (PPII).
6. In adenohypophysis, PPII is subject to stringent control: positive by thyroid hormones and negative by TRH; other hypothalamic factors such as dopamine and somatostatin also influence its activity.
7. These combined approaches suggest that TRH action is modulated in a coordinate fashion.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Anderson, R. G. W., and Orci, L. (1988). A view of acidic intracellular compartments. J. Cell Biol. 106:539–543.
Aragay, A. M., Katz, A., and Simon, M. I. (1992). The Gq and G11 proteins couple the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C in GH3 rat pituitary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267:24983–24988.
Arancibia, S., Tapia-Arancibia, L., Assenmacher, I., and Astier, H. (1983). Direct evidence of short-term cold-induced TRH release in the median eminence of unanesthetized rats. Neuroendocrinology 37:225–228.
Arancibia, S., Tapia-Arancibia, L., Astier, H., and Assenmacher, I. (1989). Physiological evidence for α1-adrenergic facilitatory control of the cold-induced TRH release in the rat, obtained by push-pull cannulation of the median eminence. Neurosci. Lett. 100:169–174.
Arenander, A. T., and Herchman, H. R. (1993). Primary response gene expression in the nervous system. In Loughlin, S. E., and Fallon, J. H. (eds.), Neurotrophic Factors, Academic Press, New York, pp. 89–128.
Barofsky, A.-L., Taylor, J., and Massari, V. J. (1983). Dorsal raphe-hypothalamic projections provide the stimulatory serotonergic input to suckling-induced prolactin release. Endocrinology 113:1894–1903.
Bauer, K. (1976). Regulation of degradation of thyrotropin releasing hormone by thyroid hormones. Nature 259:591–593.
Bauer, K. (1987). Adenohypophyseal degradation of thyrotropin releasing hormone regulated by thyroid hormones. Nature 330:375–377.
Bauer, K. (1988). Degradation and biological inactivation of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH): Regulation of the membrane-bound TRH-degrading enzyme from rat anterior pituitary by estrogens and thyroid hormones. Biochimie 70:69–74.
Bauer, K. (1994). Purification and characterization of the thyrotropin releasing hormone degrading ectoenzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 224:387–396.
Bauer, K., and Nowak, P. (1979). Characterization of a thyroliberin-degrading serum enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of thyroliberin at the pyroglutamyl-histidine bond. Eur. J. Biochem. 99:239–246.
Bauer, K., Carmeliet, P., Schulz, M., Baes, M., and Denef, C. (1990). Regulation and cellular localization of the membrane bound thyrotropin-releasing hormone-degrading enzyme in primary cultures of neuronal, glial and adenohypophyseal cells. Endocrinology 127:1224–1233.
Bhat, R. V., Tausk, F. A., Baraban, J. M., Mains, R. E., and Eipper, B. A. (1993). Rapid increases in peptide processing enzyme expression in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 61:1315–1322.
Birch, N. P., Tracer, D. J., Hakes, D. J., and Loh, Y. P. (1991). Coordinate regulation of mRNA levels of pro-opiomelanocortin and the candidate processing enzymes PC2 and PC3, but not furin, in rat pituitary intermediate lobe. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 178:1311–1319.
Boler, J., Enzmann, K., Bowers, C. Y., and Schally, A. V. (1969). The identity of chemical and hormonal properties of the thyrotropin releasing hormone and pyroglutamyl-histidyl-proline-amide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 37:705–710.
Bradley, D. J., Young, W. S., III, and Weinberger, C. (1989). Differential expression of α and β thyroid hormone receptor genes in rat brain and pituitary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:7250–7254.
Braks, J. A. M., and Martens, G. J. M. (1994). 7B2 is a neuroendocrine chaperon that transiently interacts with prohormone convertase PC2 in the secretory pathway. Cell 78:263–273.
Brunh, T. O., Taplin, J. H., and Jackson, I. M. D. (1991). Hypothyroidism reduces content and increases in vitro release of pro-thyrotropin-releasing hormone peptides from the median eminence. Neuroendocrinology 53:511–515.
Bulant, M., Delfour, A., Vaudry, H., and Nicolas, P. (1988). Processing of thyrotropin releasing hormone prohormone generates pro-TRH-connecting peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 263:17189–17191.
Bulant, M., Toussel, J. P., Astier, H., Nicolas, P., and Vaudry, H. (1990). Processing of thyrotropin-releasing hormone prohormone (pro-TRH) generates a biological active peptide, prepro-TRH-(160–169), which regulates TRH-induced thyrotropin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4439–4443.
Burgus, R., Dunn, T., Desiderio, D., and Guillemin, R. (1969). Structure moleculaire du facteur hypothalamique hypophysiotrope TRF d'origine ovine: mise en évidence par spectrometrie de masse de la sequence PCA-His-Pro-NH2. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 269:1870–1873.
Canonico, P. L., Judd, A. M., Koike, K., Valdenegro, C. A., and Macleod, R. M. (1986). Arachidonate stimulates prolactin release in vitro: A role for the fatty acid and its metabolites as intracellular regulator(s) in mammotrophs. Endocrinology 116:218–220.
Charli, J. L., Ponce, G., Joseph-Bravo, P., and McKelvy, J. F. (1984). Accumulation of thyrotropin releasing hormone by rat hypothalamic slices. J. Neurochem. 42:981–986.
Charli, J. L., Mendez, M., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Wilk, S. (1987). Specific inhibitors of pyroglutamyl peptidase I and prolyl endopeptidase do not change the in vitro release of TRH or its content in rodent brain. Neuropeptides 9:373–378.
Charli, J. L., Cruz, C., Vargas, M., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1988). The narrow specificity pyroglutamate aminopeptidase degrading TRH in brain is an ectoenzyme. Neurochem. Int. 13:237–242.
Charli, J. L., Méndez, M., Vargas, M. A., Cisneros, M., Assai, M., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Wilk, S. (1989). Pyroglutamyl peptidase II inhibition specifically increases recovery of TRH released from rat brain slices. Neuropeptides 14:191–196.
Charli, J. L., Cruz, C., Redondo, J. L., Guerra, C., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1995). Homologous conditioned medium enhances expression of TRH in hypothalamic neurons in primary cultures. Dev. Brain Res. 89:155–160.
Charli, J. L., Baeza, M. A., Uriostegui, B., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1996). Rapid down regulation of adenohypophyseal pyroglutamyl peptidase II activity by arachidonic acid. 10th International Congress of Endocrinology, San Francisco, CA.
Cockle, A. M., and Smyth, D. G. (1987). Specific processing of the thyrotropin releasing prohormone in rat brain and spinal cord. Eur. J. Biochem. 165:693–698.
Covarrubias, L., Uribe, R. M., Méndez, M., Charli, J. L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1988). Neuronal TRH synthesis: Developmental and circadian TRH mRNA levels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 151:615–622.
Covarrubias, L., Redondo, J. L., Vargas, M. A., Uribe, R. M., Méndez, M., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Charli, J. L. (1994). In vitro TRH release from hypothalamus slices varies during the diurnal cycle. Neurochem. Res. 19:845–850.
Cruz, C., Charli, J. L., Vargas, M. A., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1991). Neuronal localization of pyroglutamate aminopeptidase II in primary cultures of fetal mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 6:1594–1601.
Czekay, G., and Bauer, K. (1993). Identification of the thyrotropin releasing hormone-degrading ectoenzyme as a metallopeptidase. J. Biochem. 290:921–926.
Davidson, H. W., Rhodes, C. J., and Hutton, J. C. (1988). Intraorganellar calcium and pH control of proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature 333:93–96.
Day, R., Schafer, M. K. H., Watson, S. J., Chrétien, M., and Seidah, N. G. (1992). Distribution and regulation of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2 in rat pituitary. Mol. Endocrinol. 6:485–497.
De Gortari, P., Fernández-Guardiola, A., Martínez, A., Cisneros, M., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1995). Changes in TRH and its degrading enzyme pyroglutamate peptidase II, during the development of kindling. Brain Res. 679:144–150.
De Greef, W. J., and Visser, T. J. (1981). Evidence for involvement of hypothalamic dopamine and thyrotrophin-releasing hormone in suckling-induced release of prolactin. J. Endocrinol. 91:213–223.
Desarathy, Y., and Fanburg, B. L. (1991). Involvement of second messenger systems in stimulation of angiotensin converting enzyme of bovine endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 148:327–335.
Dyess, E. M., Segerson, T. P., Liposits, Z., Paull, W. D., Kaplan, M. M., Wu, P., Jackson, I. M. D., and Lechan, R. M. (1988). Triiodothyronine exerts direct cell-specific regulation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Endocrinology 123:2291–2297.
Elmore, M. A., Griffiths, E. C., O'Connor, B., and O'Cuinn, G. (1990). Further characterization of the substrate specificity of a TRH hydrolysing pyroglutamate aminopeptidase from guinea-pig brain. Neuropeptides 15:31–36.
Erdos, E. G., Wagner, B., Harbury, C. B., Painter, R. G., Skidgel, R. A. N., and Fa, X. G. (1989). Down regulation and inactivation of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 enkephalinase in human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 264:14519–14523.
Faivre-Bauman, A., Loudes, C., Barret, A., Tixier-Vidal, A., and Bauer, K. (1986). Possible role of neuropeptide degrading enzyme on thyroliberin secretion in fetal hypothalamic cultures grown in serum free medium. Neuropeptides 7:125–138.
Faivre-Bauman, A., Loudes, C., Barret, A., Patte, C., and Tixier-Vidal, A. (1988). Ontogenesis of peptidylglycyl α-amidation activity in the mouse hypothalamus in vivo and in serum-free medium cultures. Relation with thyroliberin (TRH) accumulation and release in vitro. Dev. Brain Res. 40:261–267.
Franks, S., Mason, H. D., Shennan, K. I. J., and Sheppard, M. C. (1984). Stimulation of prolactin secretion by oestradiol in the rat is associated with increased hypothalamic release of thyrotropin releasing hormone. J. Endocrinol. 103:257–261.
Friedman, T. C., and Wilk, S. (1985). The effect of inhibitors of prolyl endopeptidase and pyroglutamyl peptidase hydrolase on TRH degradation in rat serum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 132:787–793.
Friedman, T. C., Loh, Y. P., Cawley, N. X., Birch, N. P., Huang, S. S., Jackson, I. M., and Nillni, E. A. (1995). Processing of pro-TRH by bovine intermediate lobe secretory vesicle membrane PC1 and PC2 enzymes. Endocrinology 136:4462–4472.
Fink, G., Koch, Y., and Ben-Aroya, N. (1983). TRH in hypophysial portal blood: characteristics of release and relationship to thyrotropin and prolactin secretion. In Griffiths, E. C., and Bennett, G. W. (eds.), Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone, Raven Press, New York, pp. 127–144.
Garat, B., Miranda, J., Charli, J. L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1985). Presence of a membrane bound pyroglutamyl aminopeptidase degrading thyroliberin releasing hormone in rat brain. Neuropeptides 6:27–40.
Gershengorn, M. C. (1992). Post-transcriptional regulation of TRH receptor messenger RNA by TRH. In Progress in Endocrinology, Proc. 9th Int. Congr. Endocrinol., Nice, pp. 299–302.
Gollasch, M., Kleuss, C., Hescheler, J., Witting, B., and Schultz, G. (1993). Gi2 and protein kinase C are required for thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced stimulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in rat pituitary GH3 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:6265–6269.
Grosvenor, C. E., and Mena, F. (1980). Evidence that thyrotropin-releasing hormone and a hypothalamic prolactin-releasing factor may function in the release of prolactin in the lactating rat. Endocrinology 107:863–868.
Haisenleder, D. J., Orotlano, G. A., Dalkin, A. C., and Marschall, J. C. (1992). Differential actions of TRH pulses in the expression of prolactin and TSH subunit messenger ribonucleic acid in rat pituitary cells in vitro. Endocrinology 130:2915–2923.
Hefco, E., Krulich, L., Illner, P., and Larsen, P. R. (1975). Effect of acute exposure to cold on the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid system. Endocrinology 97:1185–1195.
Hollenberg, A. N., Monden, T., Flynn, T. R., Boers, M. E., Cohen, O., and Wondisford, F. E. (1995). The human thyrotropin releasing hormone gene is regulated by thyroid hormone through two distinct classes of negative thyroid hormone response elements. Mol. Endocrinol. 9:540–550.
Horsthemke, B., Leblanc, P., Kordon, C., Wattiaux-de Conink, S., Wattiaux, R., and Bauer, K. (1984). Subcellular distribution of particle-bound neutral peptidases capable of hydrolyzing gonadoliberin, thyroliberin, enkephalin and substance P. Eur. J. Biochem. 139:315–320.
Hsieh, K. P., and Martin, T. F. J. (1992). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors activate phospholipase C by coupling to the guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins Gq and G11. Mol. Endocrinol. 6:1673–1681.
Jackson, I. M. D. (1995). TRH and CRH. What's the message? Endocrinology 136:2793–2794.
Joseph-Bravo, P., Loudes, C., Charli, J. L., and Kordon, C. (1979). Subcellular distribution of brain peptidases degrading luteinizing hormone releasing hormone and thyrotropin releasing hormone. Brain Res. 166:321–329.
Joseph-Bravo, P., Charli, J. L., and Covarrubias, L. (1989). Metabolism of thyrotropin releasing hormone. In Velasco, M., Israel, A., Romero, E., and Silva, H. (eds.), Recent Advances in Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 215–220.
Joseph-Bravo, P., Fresan, M. E., Cisneros, M., Vargas, M. A., and Charli, J. L. (1994). Pyroglutamyl peptidase II activity is not in the processes of bulbospinal TRHergic neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 178:243–246.
Kakucska, I., Qi, Y., and Lechan, R. M. (1995). Changes in adrenal status affect hypothalamic TRH gene expression in parallel with CRH. Endocrinology 136:2795–2808.
Koller, K. J., Wolff, R. S., Warden, M. K., and Zoeller, R. T. (1987). Thyroid hormones regulate levels of thyrotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in the paraventricular nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:7329–7333.
Kovács, K. J., and Sawchenko, P. E. (1996). Sequence of stress-induced alterations in indices of synaptic and transcriptional activation in parvocellular neurosecretory neurons. J. Neurosci. 16:262–273.
Kubek, M. J., Knoblach, B. S., Shariff, N. A., Burt, D. R., Buterbaugh, G. G., and Fuson, K. S. (1993). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene expression and receptors are differentially modified in limbic seizures. Ann. Neurol. 33:70–75.
Lamberts, S. W. J., and MacLeod, R. M. (1990). Regulation of prolactin secretion at the level of the lactotroph. Physiol. Rev. 70:279–325.
Ladram, A., Bulant, M., Delfour, A., Montagne, J. J., Vaudry, H., and Nicolas, P. (1994). Modulation of the biological activity of thyrotropin releasing hormone by alternate processing of pro-TRH. Biochimie 76:320–328.
Lechan, R. M., and Toni, R. (1992). Thyrotropin releasing hormone neuronal systems in the central nervous system. In Nemeroff, C. B. (ed.), Neuroendocrinology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 279–330.
Lechan, R., Wu, P., Jackson, I. M. D., Wolf, H., Cooperman, S., Mandel, G., and Goodman, R. H. (1986). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone precursor: Characterization in rat brain. Science 231:159–161.
Lee, S. L., Stewart, K., and Goodman, R. (1988). Structure of the gene encoding rat thyrotropin releasing hormone. J. Biol. Chem. 263:16604–16609.
Lee, S. L., Yang, I.-M., and Lin, A. (1993). A multifunctional site in the promoter of the rat thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) gene binds c-Jun, CREB, and the thyroid hormone receptor. The Endocrine Society 75th Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, NV, p. 532.
Liu, J. L., and Patel, Y. C. (1995). Glucocorticoids inhibit somatostatin gene expression through accelerated degradation of somatostatin messenger ribonucleic acid in human thyroid medullary carcinoma (TT) cells. Endocrinology 136:2389–2396.
Luo, L., Bruhn, T., and Jackson, I. M. D. (1995). Glucocorticoids stimulate thyrotropin releasing gene expression in cultural hypothalamic neurons. Endocrinology 136:4945–4959.
Malfroy, B., Swertz, J. P., Guyon, A., Roques, B. P., and Schwartz, J. C. (1978). High affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature 294:558–560.
Méndez, M., Cruz, C., Joseph-Bravo, P., Wilk, S., and Charli, J.-L. (1990). Evaluation of the role of prolylendopeptidase and pyroglutamyl peptidase I in the metabolism of LHRH and TRH in brain. Neuropeptides 17:55–62.
Martin, T. F. J., and Kowalchyk, J. A. (1984a). Evidence for the role of calcium and diacylglycerol as dual second messengers in thyrotropin-releasing hormone action: Involvement of diacylglycerol. Endocrinology 115:1517–1526.
Martin, T. F. J., and Kowalchyk, J. A. (1984b). Evidence for the role of calcium and diacylglycerol as dual second messengers in thyrotropin-releasing hormone action: Involvement of Ca+2. Endocrinology 115:1527–1536.
Merchenthaler, I., and Liposits, Z. (1994). Mapping of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neuronal systems of rat forebrain projecting to the median eminence and the OVLT. Immunocytochemistry combined with retrograde labeling at the light and electron microscopic levels. Acta Biol. Hung. 45:361–374.
Miyamoto, T., Suzuki, S., and Degroot, L. J. (1993). High affinity and specificity of dimeric binding of thyroid hormone receptors to DNA and their ligand dependent association. Mol. Endocrinol. 7:224–231.
Murdoch, G. H., Waterman, M., Evans, R. M., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1985). Molecular mechanisms of phorbol ester, thyrotropin-releasing hormone and growth factor stimulation of prolactin gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 260:11852–11858.
Nillni, E. A., Friedman, T. C., Todd, R. B., Birch, N. P., Loh, Y. P., and Jackson, I. M. D. (1995). Prothyrotropin-releasing hormone processing by recombinant PC1. J. Neurochem. 65:2462–2472.
O'Connor, B., and O'Cuinn, G. (1984). Localization of a narrow-specificity thyroliberin hydrolyzing pyroglutamate aminopeptidase in synaptosomal membranes of guinea-pig brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 144:271–278.
O'Leary, R., and O'Connor, B. (1995). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J. Neurochem. 65:953–963.
Ouafik, L. H., Giraud, P., Slers, P., Dutour, A., Castanas, E., Boudouresque, F., and Oliver, C. (1987). Evidence for high peptide α-amidating activity in the pancreas from neonatal rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:261–264.
Paek, I., and Axel, R. (1987). Glucocorticoids enhance stability of human growth hormone mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:1496–1507.
Ponce, G., Charli, J.-L., Pasten, J. A., Aceves, C., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1988). Tissue-specific regulation of pyroglutamate aminopeptidase II activity by thyroid hormones. Neuroendocrinology 48:211–213.
Pu, L. P., Ma, W., Barker, J. L., and Loh, Y. P. (1996). Differential coexpression of genes encoding prothyrotropin-releasing hormone (Pro-TRH) and prohormone convertases (PC1 and PC2) in rat brain neurons: Implications for differential processing of pro-TRH. Endocrinology 137:1233–1241.
Rage, F., Lazaro, J.-B., Benyassi, A., Arancibia, S., and Tapia-Arancibia, L. (1994). Rapid changes in somatostatin and TRH mRNA in whole rat hypothalamus in response to acute cold exposure. J. Neuroendocrinol. 6:19–23.
Ramsdell, J. S., and Tashjian, A. H., Jr. (1985). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and epidermal growth factor stimulate prolactin synthesis by a pathway(s) that differs from that used by phorbol esters: Dissociation of actions by calcium dependency and additivity. Endocrinology 117:2050–2060.
Rondeel, J. M. M., De Greef, W. J., Van der Schoot, P., Karels, B., Klootwijk, W., and Visser, T. J. (1988). Effect of thyroid status and paraventricular area lesions on the release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone and catecholamines into hypophysial portal blood. Endocrinology 123:523–527.
Sánchez, E., Charli, J.-L., Morales, C., Corkidi, G., Seidah, N., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Uribe, R. M. (1996). Expression of the proprotein convertases PC1 and PC2 mRNAs in thyrotropin releasing hormone neurons of the rat paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus. Brain Res. 761:77–86.
Schauder, B., Schomburg, L., Kohrle, J., and Bauer, K. (1994). Cloning of a CDNA encoding an ectoenzyme that degrades thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:9534–9538.
Schomburg, L., and Bauer, K. (1995). Thyroid hormones rapidly and stringently regulate the messenger RNA levels of the thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) receptor and the TRH degrading ectoenzyme. Endocrinology 136:3480–3485.
Segerson, T. P., Kauer, J., Wolfe, H. C., Mobtaker, H., Wu, P., Jackson, I. M. D., and Lechan, R. M. (1987). Thyroid hormone regulates TRH biosynthesis in the paraventricular nucleus of the rat hypothalamus. Science 238:78–80.
Seidah, N., Marcinkiewicz, M., Benjannet, S., Gaspar, L., Beaubien, G., Mattei, M., Lazure, C., Mbikay, M., and Chretien, M. (1991). Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, furin, and Kex2; Distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol. Endocrinol. 5:111–122.
Simard, M., Pekary, A. E., Smith, V. P., and Hersman, J. M. (1989). Thyroid hormones modulate thyrotropin-releasing hormone biosynthesis in tissues outside the hypothalamic-pituitary axis of male rats. Endocrinology 125:524–531.
Smith, M. A., Shinya, M., Kim, S.-Y., and Kvetansnky, R. (1995). Stress increases brain-derived neurotropic factor messenger ribonucleic acid in the hypothalamus and pituitary. Endocrinology 136:3743–3750.
Stevenin, B., and Lee, S. L. (1995). Hormonal regulation of the thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) gene. Endocrinologist 5:286–296.
Taylor, W. L., and Dixon, J. E. (1978). Characterization of a pyroglutamate aminopeptidase from rat serum that degrades thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J. Biol. Chem. 253:6934–6940.
Taylor, T., Wondisford, F. E., Blaine, T., and Weintraub, B. D. (1990). The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus has a major role in thyroid hormone feedback regulation of thyrotropin synthesis and secretion. Endocrinology 126:317–324.
Torres, H., Charli, J.-L., González-Noriega, A., Vargas, M. A., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1986). Subcellular distribution of the enzymes degrading thyrotropin releasing hormone and metabolites in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 9:103–110.
Uribe, R. M., Pasten, J., Ponce, G., Méndez, M., Covarrubias, L., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Charli, J.-L. (1991). Some events of TRH metabolism are regulated in lactating and cycling rats. Neuroendocrinology 54:493–498.
Uribe, R. M., Redondo, J. L., Charli, J.-L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1993). Suckling and cold stress rapidly and transiently increase TRH mRNA in the paraventricular nucleus. Neuroendocrinology 58:140–145.
Uribe, R. M., Joseph-Bravo, P., Ponce, G., Cisneros, M., Aceves, C., and Charli, J. L. (1994). Influence of thyroid status on TRH metabolism in rat olfactory bulb. Peptides 15:435–439.
Uribe, R. M., Pérez-Martínez, L., Covarrubias, M. L., Gómez, O. B., Covarrubias, L., Charli, J.-L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1995). Neural regulation of TRH biosynthesis. Neurosci. Lett. 201:41–44.
Uribe, R. M., Jasso, P., Morales, C., de Gortari, P., Charli, J.-L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1996). In situ hybridization histochemical analysis of pyroglutamyl peptidase II mRNA distribution in the rat brain. 26th Annual Meeting, Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC.
van Haateran, G. A. C., Linkels, E., Klootwijk, W., van Toor, H., Rondeel, J. M. M., Themmen, A. P. N., de Jong, F. H., Valentijn, K., Vaudry, H., Bauer, K., Visser, T. J., and de Greef, W. J. (1995). Starvation-induced changes in the hypothalamic content of prothyrotropin releasing hormone (proTRH) mRNA and the hypothalamic release of proTRH-derived peptides: Role of the adrenal gland. J. Endocrinol. 145:143–153.
Vargas, M. A., Méndez, M., Cisneros, M., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Charli, J. L. (1987). Regional distribution of the membrane bound pyroglutamate aminopeptidase degrading TRH in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 79:1476–1492.
Vargas, M. A., Herrera, J., Uribe, R. M., Charli, J.-L., and Joseph-Bravo, P. (1992). Ontogenesis of pyroglutamyl peptidase II activity in rat brain, adenohypophysis and pancreas. Dev. Brain Res. 66:251–256.
Vargas, M. A., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Charli, J. L. (1994). Thyrotropin-releasing hormone down regulates pyroglutamyl aminopeptidase II activity in adenohypophyseal cells. Neuroendocrinology 60:323–330.
Vargas, M. A., Bourdais, J., Sánchez, S., Uriostegui, B., Moreno, E., Joseph-Bravo, P., and Charli, J.-L. Multiple hypothalamic factors regulate pyroglutamyl peptidase II in cultures of adenohypophyseal cells: Role of the cAMP pathway. J. Neuroendoc. (in press).
Wilk, S., and Wilk, E. (1989). Pyroglutamyl peptidase II, a thyrotropin releasing hormone degrading enzyme: Purification and specificity studies of the rabbit brain enzyme. Neurochem. Int. 15:81–89.
Yamada, M., Rogers, D., and Wilber, J. F. (1989). Exogenous triiodothyronine lowers thyrotropin-releasing hormone concentrations in the specific hypothalamic nucleus (paraventricular) involved in thyrotropin regulation and also in posterior nucleus. Neuroendocrinology 50:560–563.
Yamada, M., Radovick, S., Wondisford, R. E., Nakayama, Y., Weingraub, B. D., and Wilber, J. F. (1990). Cloning and structure of human genomic DNA and hypothalamic cDNA encoding human prepro thyrotropin-releasing-hormone. Mol. Endocrinol. 4:551–556.
Yang-Yen, H.-F., Chambard, J. C., Sun, Y. L., Smeal, T., Scmidt, T. J., Drouin, J., and Karin, M. (1990). Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: Mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell 62:1205–1215.
Zoeller, R. T., and Fletcher, D. L. (1994). A single administration of ethanol simultaneously increases c-fos mRNA and reduces c-jun mRNA in the hypothalamus and hippocampus. Mol. Brain. Res. 24:185–191.
Zoeller, R. T., Wolf, R. S., and Koller, K. J. (1988). Thyroid hormone regulation of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding thyrotropin (TSH)-releasing hormone is independent of the pituitary gland and TSH. Mol. Endocrinol. 2:248–252.
Zoeller, R. T., Kabeer, N., and Albers, H. E. (1990). Cold exposure elevates cellular levels of mRNA encoding TRH in paraventricular nucleus despite elevated levels of thyroid hormones. Endocrinology 127:2955–2962.
Zoeller, R. T., Simonyi, A., Butnariu, O., and Fletcher, K. L. (1995). Effects of acute ethanol administration and cold exposure on the hypothalamic pituitary axis. Endocrine 3:39–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph-Bravo, P., Uribe, R.M., Vargas, M.A. et al. Multifactorial Modulation of TRH Metabolism. Cell Mol Neurobiol 18, 231–247 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022521020840
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022521020840