Summary
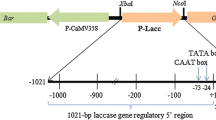
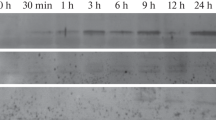
Chemically inducible gene regulation systems provide a mechanism for a temporal control of expression of transgenes. In this study expression from the herbicide safener inducible maize GST-27 promoter was tested in potato, with the aim of using this to provide inducible expression of transgenes implicated in dormancy control. A binary vector comprising 3.8 kb of the GST-27 promoter was fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene and transformed into potato. Application of the chemical inducer elevated the expression of GUS up to 40 fold in leaf tissue. However in stems, roots and tubers the GST-27 promoter caused high levels of expression of GUS in the absence of safener, demonstrating that in these tissues it acts as a constitutive promoter. A deleted promoter region of the GST-27 promoter displayed a similar expression pattern. Analysis of GUS activity in dormant and sprouting tubers showed that the GST-27 promoter was a strong constitutive promoter throughout the tuber life cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama, T. A. & N.-H. Chua, 1997. A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants.Plant Journal 11: 605–612.
Bradford, M.M., 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding.Annals of Biochemistry 72: 248–254.
Caddick, M.X., A.J. Greenland, I. Jepson, K.-P. Krause, N. Qu, K.V. Riddell, M.G. Salter, W. Schuch, U. Sonnewald & A.B. Tomsett, 1998. An ethanol inducible gene switch for plants used to manipulate carbon metabolism.Nature Biotechnology 16: 177–180.
Davies, H.V., 1998. Prospects for manipulating carbohydrate metabolism in potato tuber.Aspects of Applied Biology 52: 245–254. In: Protection and production of sugar beet and potatoes. Published by the Association of Applied Biologists.
Edwards, R., D.P. Dixon & V. Walbot, 2000. Plant glutathione S-transferases: enzymes with multiple functions in sickness and in health.Trends in Plant Sciences 5: 193–198.
Fahey, R.C. & A.R. Sunquist, 1991. Evolution of glutathione metabolism.Advances in Enzymology 64: 1–53.
Gatz, C. & I. Lenk, 1998. Promoters that respond to chemical inducers.Trends in Plant Science 3: 352–358.
Greenland, A., P. Bell, C. Hart, I. Jepson, T. Nevshemal, J. Register III & S. Wright, 1997. Reversible male sterility: a novel system for the production of hybrid corn.The Society for Experimental Biology 51: 141–147.
Holt, D.C., V.J. Lay, E.D. Clarke, A. Dinsmore, I. Jepson, S.W. Bright & A.J. Greenland, 1995. Characterisation of the safener-induced glutathione S-transferase isoform II from maize.Planta 196: 295–302.
Jefferson, R.A., 1987. Assaying chimaeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system.Plant Molecular Biology Reports 5: 387–405.
Jepson, I., V.J. Lay, D.C. Holt, S.W. Bright & A.J. Greenland, 1994. Cloning and characterisation of maize herbicide safener-induced cDNAs encoding subunits of glutathione S-transferase isoforms I, II and IV.Plant Molecular Biology 26: 1855–1866.
Jepson, I., D.C. Holt, V. Roussel, S.Y. Wright & A.J. Greenland, 1997. Transgenic plant analysis as a tool for the study of maize glutathione S-transferases. In: K.K. Hatzios (Ed.), Regulation of Enzymatic Systems Detoxifying Xenobiotics in Plants, pp. 313–323.
Jepson, I., M. Martinez & J. Sweetman, 1998. Chemical-inducible gene expression systems for plants-a review.Pesticide Science 54: 360–367.
Macleod, M.R., H. Davies, S.B. Jarvis & M.A. Taylor, 1999. Characterisation of genes isolated from a potato swelling-stolon cDNA library.Potato Research 42: 31–42.
Marrs, K.A., 1996. The functions and regulation of glutathione S-transferases in plants.Annual Review Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 47: 127–158.
Rocha-Sosa, M., U. Sonnewald, W. Frommer, M. Stratmann, J. Schell & L. Willmitzer, 1989. Both developmental and metabolic signals activate the promoter of a class I patatin gene.EMBO Journal 8: 23–29.
Shephard, H., 1996. Characterisation ofcis-elements in the GST-27 promoter ofZea mays. PhD thesis, University of Leicester.
Wilshire, J.J.J. & A.H. Cobb, 1996. A review of the physiology of potato tuber dormancy.Annals of Applied Biology 129: 553–569.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robertson, N., Paine, J.A., Sonnewald, U. et al. Expression of the chemically inducible maize GST-27 promoter in potato. Potato Res 43, 335–345 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02360539
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02360539