Abstract
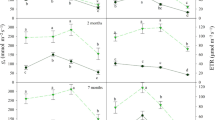
Roupala montana is an evergreen species widespread in the seasonal savannas of the central plains of Brazil. I examined the degree of coupling of photosynthetic gas-exchange characteristics, water relations and growth responses of R. montana with regard to seasonal changes in soil water availability. Despite a rainless period of over three months soil water potential at 60 cm depth reached values of only about -1.0 MPa, while pre-dawn leaf water potential (Ψl) reached about -0.4 MPa by the end of the three-month drought. Thus, R. montana had access to deep soil water in the dry period, but pre-dawn Ψl did not reach the high wet season values of -0.2 MPa. Most of the shoot growth was concluded in the onset of the rainy season. Although some individual branches might have shown some extension thereafter, most of them remained inactive during the rest of the rainy season and the subsequent dry season. New leaf production was also restricted to the first part of the wet period. R. montana remained evergreen in the dry season, but there was a 27% decrease in the number of leaves and herbivory removed about 16% of the leaf area still present in the plant. CO2-exchange rates of these leaves reached only ca. 55% of the maximum rainy season values of 14 µmol m-2 s-1. Thus, the estimated potential daily carbon gain was about 34% of the maximum by the end of the dry period. These values will be even lower, if we considered the decrease in photosynthetic rates that occurred around midday. These reductions in photosynthetic rates as a result of partial stomatal closure were measured both in the wet and dry season and they were related to increases in the evaporative demand of the atmosphere. In conclusion, the combined effect of herbivory, leaf loss and reductions in photosynthetic rates limited plant productivity in the dry season.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Felfili, J. M. & da Silva Jr., M. C. 1993. A comparative study of cerrado (sensu stricto) vegetation in Central Brazil. J. Tropical Ecol. 9: 277-289.
Fisher, F. M., Zak, J. C., Cunningham, G. L., Whitford, W. G. 1988. Water and nitrogen effects on growth and allocation paterns of creosotebush in the northern Chihuahuan Desert. J. Range Manag. 41: 387-391.
Franco, A. C. 1983. Fotossíntese e resistência foliar em Didymopanax macrocarpum.Master Thesis, Universidade de Brasília, Brazil. 79 pp.
Franco, A. C. de Soyza, A. G., Virginia, R. A., Reynolds, J. F. & Whitford, W. G. 1994. Effects of plant size and water relations on gas exchange and growth of the desert shrub Larrea tridentata. Oecologia 97: 171-178.
Franco, A. C., Nardoto, G. B. & Souza, M. P. 1996. Patterns of soil water potential and seedling survival in the cerrados of Central Brazil. Pp. 277-280. In: Pereira, R. C. & Nasser, L. C. B. (eds), Proceedings do 1st International Symposium on Tropical Savannas: Biodiversity and sustainable production of food and fibers in the Tropical savannas. EMBRAPA-CPAC, Planaltina, Brazil.
Furley, P. A. 1985. Notes on the soils and plant communities of Fazenda Água Limpa. Ocasional Publications N. S. number 5, Department of Geography, University of Edinburgh, UK.
Goldstein, G., Sarmiento, G. & Meinzer, F. 1986. Patrones diarios y estacionales en las relaciones hídricas de àrboles siempreverdes de la sabana tropical. Acta Oecologica/Oecologia Plantarum 7: 107-119.
Johnson, C. E., Franco, A. C. & Caldas, L. S. 1983. Fotossíntese e resistência foliar em espécies nativas do cerrado: metodologia e resultados preliminares. Revista Brasileira de Botânica 6: 91-97.
Lajtha, K. & Whitford, W. G. 1989. The effect of water and nitrogen amendments on phtosynthesis, leaf demography, and resource-use efficiency in Larrea tridentata, a desert evergreen shrub. Oecologia 80: 341-348.
Machado, J.-L. & Tyree, M. L. 1994. Patterns of hydraulic architecture andwater relations of two tropical canopy trees with contrasting leaf phenologies: Ochroma pyramidaleand Pseudobombax septenatum.Tree Physiol. 14: 219-240.
Medina, E. & Francisco, M. 1994. Photosynthesis and water relations of savanna tree species differing in leaf phenology. Tree Physiol. 14: 1367-1381.
Moraes, J. A. P. V., Perez, S. C. J. G. A. & Carvalho Jr., L. F. 1989. Curso diário e sazonal do potencial de água e da resist ência estomática em plantas de um cerradão. Ann. Missouri Bot. Garden 27: 13-23.
Nilsen, E. T., Sharifi, M. R., Rundel, P. W., Jarrel, W. m & Virginia, R. A. 1983. Diurnal and seasonal water relations of the desert phreatophyte Prosopis glandulosa(honey mesquite) in the Sonoran Desert of California. Ecology 64: 1381-1393.
Prado, C. H. B. A. 1994. Capacidade fotossintética de algumas espécies lenhosas do cerrado sob condições de campo. PhD thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, Brazil. 131 pp.
Ratter, J. A. & Dargie, T. C. D. 1992. An analysis of the floristic composition of 26 cerrado areas in Brazil. Edinburgh J. Bot. 49: 235-250.
Sarmiento, G., Goldstein, G. & Meinzer F. 1985. Adaptive strategies ofwoody species in neotropical savannas. Biol. Rev. 60: 315-355.
Silva, G. T., Sato, M. N. & Miranda, H. S. 1996. Mortalidade de plantas lenhosas em um campo sujo de cerrado submetido a queimadas prescritas. Pp. 93-101. In: Miranda, H. S., Saito, C. H. & Dias, B. F. de S. (eds). Impactos de Queimadas em áreas de Cerrado e Restinga. UnB, ECL, Brazil.
Sobrado, M. A. 1996. Leaf photosynthesis and water loss as influenced by leaf age and seasonal drought in an evergreen tree. Photosynthetica 32: 563-568.
Tuohy, J.M., J. A. B. Prior & G. R. Stewart. 1991. Photosynthesis in relation to leaf nitrogen and phosphorus content in Zimbabwean trees. Oecologia 88: 378-382.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, A.C. Seasonal patterns of gas exchange, water relations and growth of it Roupala montana, an evergreen savanna species. Plant Ecology 136, 69–76 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009763328808
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009763328808