Summary
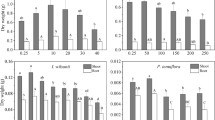
Two sandculture experiments were conducted with wheat (Triticum aestivum) to determine the effects of (1) osmotic potential (Ψπ) and (2) fluctuating boron (B) concentrations on B availability (toxicity), shoot growth and leaf concentrations of B of wheat. The first experiment consisted of growing wheat to the spike emergence stage in sandcultures irrigated with a complete nutrient solution containing 1.0, 7.5, and 15.0 mg Bl−1 and having Ψπ values of −0.02, −0.07, −0.12, and −0.17 MPa produced by CaCl2−NaCl additions. Statistically, shoot weight was independently influenced by the B and Ψπ treatments but not by their interaction. Only the B treatment had a significant effect on leaf boron concentrations; the B x Ψπ interaction was nonsignificant with respect to leaf B concentrations.
The second experiment was designed to determine if growth and B uptake of wheat responds to the time integrated mean (TIM) concentration of B. This experiment consisted of four fixed-B concentrations and four fluctuating-B concentrations designed to produce two TIM concentrations (3.9 and 7.4 mg Bl−1) approached low to high and vice versa. With respect to shoot weight, there was no statistical difference among treatments having the same TIM concentration during the 10 week experiment. However, shoot B concentrations differed greatly; they were higher when the B concentration was progressively increased over the 10 week period. Leaf B concentrations (Y leaf at flowering), while not as high as the shoot B concentrations, were also higher under the treatment of increasing B concentration, indicating B uptake rates are higher for mature plants than for seedlings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers R S and Wescot D W 1976 FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29. Water Quality for Agriculture. FAO Rome.
Bernstein L and Pearson G A 1954 Influence of integrated moisture stress achieved by varying the osmotic pressure of culture solutions on growth of tomato and pepper plants. Soil Sci. 77, 355–368.
Bingham F T 1982 Chapter 25. Boron. pp. 431–447.In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Eds. A L Pageet al. Agronomy Monograph No. 9, ASA-SSSA, Maddison, WI.
Bingham F T, Strong J E and Keren R 1985 Boron tolerance of Mexican wheat. Proc. International Workshop on Salt-Affected Soils of Latin America, Maracay, Venezuela, Oct. 23–30, 1983, pp 71–79.
Bingham F T, Strong J E, Rhoades J D and Keren R 1984 An application of the Maas-Hoffman salinity response model for boron toxicity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49, 672–674.
Ingvalson R D, Rhoades J D and Page A L 1976 Correlation of alfalfa yield with various index of salinity. Soil Sci. 122, 145–153.
Keren R and Bingham F T 1984 Boron in water, soils, and plants. Adv. Soil Sci., Springer-Verlag, New York, Inc., New York.
Maas E V 1986 Sait tolerance of plants. Applied Agricultural Res. I, 12–26.
Maas E V and Hoffman C J 1977 Crop salt tolerance—Current assessment. J. Irrig. and Drainage Div., ASCE, Vol. 103, No. (IR2): 115–134.
Rhoades J D 1982 Reclamation and management of salt-affected soils after drainage. Proc. of the First Annual Western Provincial Conf. Rationalization of Water and Soil Res. and Management. Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, Nov. 29–Dec. 2, 1982.
Rhoades J D 1984 Water today and tomorrow. Proc. Speciality Conf. sponsored by Irrig. and Drainage Div., ASCE, Flagstaff, Arizona, July 24–26, 1984.
Wilcox L V and Durum W H 1967 Quality of irrigation waters.In Irrigation of Agricultural Lands. Eds. R M Hagan and T C Edminster. pp 104–122. Am. Soc. Agron, Madison, WI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bingham, F.T., Strong, J.E., Rhoades, J.D. et al. Effects of salinity and varying boron concentrations on boron uptake and growth of wheat. Plant Soil 97, 345–351 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02383224
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02383224