Abstract
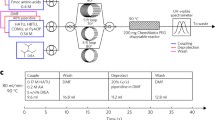
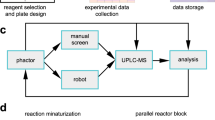
Rapid reverse-phase analytical and preparative HPLC methods havebeen developed for application to parallel synthesis libraries.Gradient methods, short columns, and high flow rates allowanalysis of over 300 compounds per day on a single system, orpurification of up to 200 compounds per day on a singlepreparative system. Hardware and software modifications allowcontinuous unattended use for maximum efficiency and throughput.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkenhohl, F., Bussche-Hunnefeld, C., Lansky, A. and Zechel, C., Combinatorial synthesis of small organicmolecules, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 35 (1996) 2289–2337.
Fruchtel, F. and Jung, G., Organic chemistry on solid supports, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 35 (1996) 17–42.
Thomson, L. and Ellman, J., Synthesis and applications of small molecule libraries, Chem. Rev., 96 (1996) 555–600.
Gordon, E.M., Gallop, M.A. and Patel, D.V., Strategy and tactics in combinatorial organic synthesis: Applications to drug discovery, Acc. Chem. Res., 29 (1996) 144–154.
Gallop, M.A., Barrett, R.W., Dower, W.J., Fodor, S.P.A. and Gordon, E.M., Applications of combinatorial technologies to drug discovery. 1. Background and peptide combinatorial libraries, J. Med. Chem., 37 (1994) 1233–1251.
Lam, K.S., Salmon, S.E., Hersh, E.M., Hruby, V.J., Kazmierski, W.M. and Knapp, R.J., A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity, Nature, 354 (1991) 82–84.
Houghten, R.A., Pinilla, C., Blondelle, S.E., Appel, J.R., Dooley, C.T. and Cuervo, J.H., Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery, Nature, 345 (1991) 84–86.
Zhao, P-L., Nachbar, R.B., Bolognese, J.A. and Chapman, K., Two new criteria for choosing sample size in combinatorial chemistry, J. Med. Chem., 39 (1996) 350–352.
Ni, Z.-J., Maclean, D., Holmes, C.P., Murphy, M.M., Ruhland, B., Jacobs, J. W., Gordon, E.M. and Gallop, M.A., Versatile approach to encoding combinatorial organic synthesis using chemically robust secondary amine tags, J. Med. Chem., 39 (1996) 1601–1608.
Kerr, J.M., Banville, S.C. and Zuckermann, R.N., Encoded combinatorial peptide libraries containing non-natural amino acids, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115 (1993) 2529–2531.
Baldwin, J.J., Burnbaum, J.J., Henderson, I. and Ohlmeyer, M.H., Synthesis of a small molecule combinatorial library encoded with molecular tags, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 117 (1995) 5588–5589.
Ohlmeyer, M.H.J., Swanson, R.N., Dillard, L.W., Reader, J.C., Asouline, G., Kobayashi, R., Wigler, M. and Still, W.C., Complex synthetic chemical libraries indexed with molecular tags, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90 (1993) 10922–10926.
Nicolaou, K.C., Xiao, X.-Y., Parandoosh, Z., Senyei, A. and Nova, M.P., Radiofrequency encoded combinatorial chemistry, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 34 (1995) 2289–2291.
Czarnik, A.W., Encoding methods in combinatorial chemistry, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 1 (1997) 60–66.
Cargill, J. and Maiefski, R., Automated combinatorial chemistry on solid phase, Lab. Robotics Autom., 8 (1996) 139–148.
DeWitt, S.H. and Czarnik, A.W., Combinatorial organic synthesis using Parke-Davis's DIVERSOMER method, Acc. Chem. Res., 29 (1996) 114–122.
Lawrence, R.M., Fryszman, O.M., Poss, M.A., Biller, S.A. and Weller, H.N., Automated preparation and purification of amides, Proc. Int. Symp. Lab. Autom. Robotics, (1995) 211–220.
Lawrence, R.M., Biller, S. A., Fryszman, O.M. and Poss, M.A., Automated synthesis and purification of amides: Exploitation of automated solid phase extraction in organic synthesis, Synthesis, (1997) 553–558.
Weller, H.N., Automated hands-on HPLC for nonspecialists, LC-GC, 10 (1992) 698–704.
Kirkland, J.J., HPLC method development: Practical aspects of increasing analysis speed while maintaining separation resolution, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 31 (1993) 493–497.
Dolan, J.W. and Snyder, L.R., Troubleshooting LC Systems, Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, 1989, pp. 486–488.
Zeng, L., Burton, L., Yung, K., Shushan, B. and Kassel, D. B., An automated analytical/preparative HPLC/MS system for the rapid characterization and purification of compound libraries, J. Chromatogr. A, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weller, H.N., Young, M.G., Michalczyk, S.J. et al. High Throughput Analysis and Purification in Support of Automated Parallel Synthesis. Mol Divers 3, 61–70 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009636725336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009636725336