Abstract
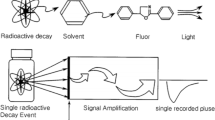
Advances in liquid scintillation counting (LSC) technologies, such as imporved scintillation cocktail formulations and alpha-beta radiation discrimination, make LSC suitable for applications in uranium process chemistry. Ease of use, low cost, and the huge dynamic range of LSC are distinct advantages for analytical support of actinide processing. All uranium isotopes decay primarily with alpha radiation emission. The immediate short-lived daughters of238U are234Th and234Pa. These nuclides are beta emitters having energy bands that overlap the uranium bands in a liquid scintillation spectrum. The resolution of these overlapping bands by alpha-beta radiation discrimination is useful for uranium quantification and purity verification. Protactinium-234 is a high-energy beta emitter that can be further identified and quantified from it's Cherenkov radiation. Energy spectra were collected on the Packard 2500AB liquid scintillator analyzer for uranyl solutions in diisopropylnaphthalene and pseudocumene based scintillator cocktails. Calibration curves were prepared for nitric, hydrochloric, and sulfuric acid media. Base titrations demonstrated the effect of acid quenching on those system. Ion exchange and water soluble polymer extraction studies are readily followed using liquid scintillation methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. J. MCDOWELL, Alpha Liquid Scintillation Counting; Past, Present, and Future, in: Liquid Scintillation Counting; Recent Applications and Development, Vol. 1, C. T. PENG, D. L. HORROCKS, E. L. ALPEN (Eds), Academic Press, New York, 1980, p. 315.
J. WIEL, T. HEGGE, Advances in Scintillation Cocktails, and J. Thomson, Di-isopropylnaphthalene-A New Solvent for Liquid Scintillation Counting, both in Liquid Scintillation, Counting and Organic Scintillators, H. ROSS, J. E. NOAKES, J. D. SPAULDING (Eds), Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, Michigan, 1991, p. 51, and p. 19.
DAZHU YANG, Study on Determination of Np, Pu and Am with Extraction-Liquid Scintillation Counting and Its Application to Assay of Transuranium Elements in High-Level Radioactive Waste, Ph. D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Bejing, Peoples Republic of China, 1990.
E. J. BOUWER, J. W. MCKLVENN, W. J. MCDOWELL, Nucl. Technol. 42 (1979) 102.
E. R. HINTON, Jr., T. T. ADAMS, L. A. BURCHFIELD, Gross Alpha Counting of Air Filters Using a Pulse-Shape Discriminating Alpha Liquid Scintillation Counter, Application Note, Packard Instrument Company, 1992.
JON LONKING, J. Amer. Water Works Assoc., (July 1988) 84.
JEFFREY S. CRAIN, B. L. MIKESELL, Appl. Spectrosc. 46 (1992) 10.
D. L. HORROCKS, Nuclear. Inst. Methods, 117 (1974) 589.
Gmelin Handbook of Inorganic Chemistry, U Supplement Vol. D3, Anion Exchange, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1982.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bower, K., Angel, A., Gibson, R. et al. Alpha-beta discrimination liquid scintillation counting for uranium and its daughters. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Articles 181, 97–107 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037551
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02037551