Abstract
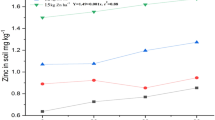
Field experiments with wheat were conducted for two years on flood plain alluvial soils to study the effectiveness of soil application of zinc sulphate and zinc oxide at 0, 15, 45, 60, 75 and 90 days after sowing. Yield and zinc uptake of wheat increased significantly with the application of zinc. Delaying the application of both zinc sulphate and zinc oxide up to 45 days of sowing did not adversly affect the zinc nutrition of wheat. However, delaying the application for 75 or 90 days after sowing eliminated the response. Zinc sulphate, when applied within 60 days of sowing performed better than zinc oxide. In a laboratory study, zinc sulphate maintained a higher level of zinc in the soil solution than zinc oxide at least over a 3-week period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora CL, Hundal HS and Takkar PN (1984) Nutrient indexing of low land rice in Ludhiana. J Agric Sci Camb 10: 277–281
Bauer A and Lindsay WL (1965) The effect of soil temperature on the availability of indigenous soil zinc. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 29: 413–420
Gambrell RP, Khalid RA, Verloo MG and Patrick WH Jr (1977) Transformations of heavy metals and plant nutrients in dredged sediments as affected by oxidation-reduction potential and pH. Vol 2, US Army Engg Waterway Exp Stn, Vicksburg, Miss, USA
Katyal JC (1980) Relative efficiencies of micronutrient sources. Fert News 23: 39–48
Katyal JC and Sharma BD (1979) Role of micronutrients in crop production. Fert News 24: 33–50
Lindsay WL (1979) Chemical equilibrium in soils. Wiley Interscience, New York
Rudgers LA, Dineterio JL, Paulson FM and Ellis R Jr (1970) Interaction among atrazine, temperature and phosphorus — induced zinc deficiency in corn. Soil Sci Soc Amer Proc 34: 240–248
Sakal R, Sinha H, Singh AP and Thakur KN (1979) A critical limit for the response of rice and wheat to applied zinc in Tarai soils. J Agric Sci Camb 93: 419–422
Sekhon GS (1982) Some experiences in soil fertility management in India. In Whither Soil Research: Proc of the 12th International Congress of Soil Science New Delhi 8–16 February, 1982
Sharma BD and Katyal JC (1986) Evaluation of amounts, methods and sources of zinc application to wheat in flood plain soils. J Agric Sci Camb 196: 41–44
Sharma BD, Takkar PN and Sadana US (1982) Evaluation of levels and methods of zinc application to rice in sodic soils. Fert Res 3: 161–167
Viets FC Jr (1966) Zinc deficiency in soil plant system. Zinc Metabolism 90–128. Chemical Abstract 67 (71814) 1968. Soil and Fert 1340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B.D., Yadvinder-Singh & Bijay-Singh Effect of time of application on the effectiveness of zinc sulphate and zinc oxide as sources of zinc for wheat. Fertilizer Research 17, 147–151 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050275
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050275