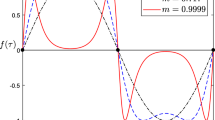
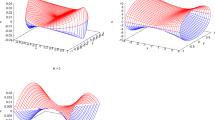
Abstract
New techniques to study Hamiltonian systems with Hamiltonian forcing are proposed. They are based on singularly weighted symplectic forms and transformations which preserve these forms. Applications pertaining to asteroid motion are outlined. These involve the presence of both Jupiter and Saturn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, R. and Marsden, J. E.: 1978,Foundations of Mechanics, Benjamin/Cumming Publ. Co.
Arnold, V. I.: 1978,Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics, Springer-Verlag.
Arnold, V. I.: 1988,Dynamical Systems III, Springer-Verlag.
Brown, E. W. and Shook, C. A.: 1931,Planetary Theory, Dover.
Cary, J. R. and Littlejohn, R. G.: 1983, ‘Noncanonical Hamiltonian mechanics and its application to magnetic field line flow’,Ann. Phys. 151, 1–34.
De la Barre, C. M.: 1993,An Investigation into the Existence of Asteroids at Saturn's Triangular Lagrangian Points, Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
De la Barre, C. M. and Kaula, W.: 1995, ‘An investigation of orbits around the triangular Lagrangian points of Saturn’, in A. E. Roy and B. Steves, eds.,From Newton to Chaos: Modern Techniques for Understanding and Coping with Chaos in N-Body Dynamical Systems, Plenum Press, in press.
De la Barre, C. M., Kaula, W. and Varadi, F.: 1995, ‘An investigation into the existence of asteroids near Saturn's triangular Lagrangian points’,Icarus, sub judice.
Érdi, B.: 1988, ‘Long periodic perturbations of Trojan asteroids’,Celest. Mech. 43, 303–308.
Érdi, B. and Varadi, F.: 1983, ‘Motion of the perihelion of Trojan asteroids’, in C. Lagerkvist and H. Rickman, eds.,Asteroids, Comets, Meteors, Uppsala University, pp. 155–159
Garfinkel, B.: 1977, ‘Theory of the Trojan asteroids. Part I’,Astron. J. 82, 368–379.
Henrard, J., Lemaître, A., Milani, A. and Murray, C. D.: 1986, ‘The reducing transformation and apocentric librators’,Celest. Mech. 38, 335–344.
Littlejohn, R. G.: 1982, ‘Hamiltonian perturbation theory in noncanonical coordinates’,J. Math. Phys.,23, 742–747.
Mikkola, S. and Innanen, K.: 1992, ‘A numerical exploration of the evolution of Trojan-type asteroidal orbits’,Astron. J. 104, 1641–1649.
Morbidelli, A. and Henrard, J.: 1991, ‘Secular resonances in the asteroid belt: Theoretical perturbation approach and the problem of their location’,Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 51, 131–167.
Sessin, W. and Ferraz-Mello, S.: 1984, ‘Motion of two planets with periods commensurable in the ratio 2:1. Solution of the Hori auxiliary systems’,Celest. Mech. 32, 307–332.
Varadi, F.: 1989,Hamiltonian Perturbation Theory Applied to Planetary Motions, Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
Varadi, F.: 1993, ‘Branching solutions and Lie series’,Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 57, 517–536.
Wisdom, J.: 1986, ‘Canonical solution of the two critical argument problem’,Celest. Mech. 38, 175–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varadi, F., De La Barre, C.M., Kaula, W.M. et al. Singularly weighted symplectic forms and applications to asteroid motion. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 62, 23–41 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692067
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00692067