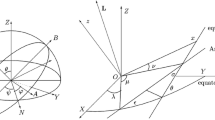
Abstract
This paper is the entire report of the IAU Working Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements of the Planets and Satellites, including three annexes. Tables give the recemmended values for the directions of the north poles of rotation and the prime meridians of the planets and satellites. Reference surfaces for mapping these bodies are described. The annexes discuss the guiding principles, given in the body of the report, present explanatory notes, and provide a bibliography of the rotational elements and reference surfaces of the planets and satellites, definitions, and algebraic expressions of relevant parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Anderson, J. D.: 1976, ‘The gravity field of Jupiter’, in: T. Gehrels (ed.),Jupiter, University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 113.
Anderson, L. E. and Fix, J. D.: 1973, ‘Pluto: New photometry and a determination of the axis of rotation’,Icarus 20, 279.
Ash, M. E., Shapiro, I. I., and Smith, W. B.: 1971, ‘The system of planetary masses’,Science 174, 551.
Beerer, Joseph G.: 1976, 1979, personal communications.
Belton, M. J. S., Wallace, L., Hayes, S. H., and Price, M. J.: 1979, ‘Nepture's rotation period: a correction and a speculation on the effect of the disk brightness distribution’, submitted toIcarus.
Born, G. H. and Duxbury, T. C.: 1975, ‘The Motions of Phobos and Deimos from Mariner 9 TV data’,Celes. Mech. 12, 77.
Brown, L. W.: 1975, ‘Saturn radio emission near 1 MHz’,Astrophys. J. 198, L89.
Brown, R. A. and Goody, R. M.: 1977, ‘The rotation of Uranus’,Astrophys. J. 217, 680.
Christy, J. W. and Harrington, R. S.: 1978, ‘The satellite of Pluto’,Astron. J. 83, 8, 1005.
Colombo, G.: 1965, ‘Rotational period of the planet Mercury’,Nature 208, 575.
Cruikshank, D. P., Pilcher, C. B., and Morrison, D.: 1976, ‘Pluto: Evidence for methane frost’,Science 194, 835.
Cruikshank, D. P.: 1978a, ‘On the rotation period of Neptune’,Astrophys. J. 220, 57.
Cruikshank, D. P.: 1978b, ‘Physical properties of the satellites of Saturn’, in: D. M. Hunter and D. Morrison (eds.),The Saturn System, NASA Conference Publication 2068, 237.
Danielson, R. E., Tomasko, M. G., and Savage, B. D.: 1972, ‘High Resolution imagery of Uranus obtained by Stratoscope II’,Astrophys. J. 178, 887.
Davies, M. E. and Batson, R. M.: 1975, ‘Surface coordinates and cartography of Mercury’,J. Geophys. Res. 80, 7, 2417.
Davies, M. E. and Katayama, F. Y.: 1976,The Control Net of Mercury: November 1976, The Rand Corporation, R-2089-NASA.
Davies, M. E., Katayama, F. Y., and Roth, J. A.: 1978,Control Net of Mars: February 1978, The Rand Corporation, R-2309-NASA.
Davies, M. E., Hauge, T. A., Katayama, F. Y., and Roth, J. A.: 1979,Control Networks for the Galilean Satellites: November 1979, The Rand Corporation, R-2532-JPL/NASA.
de Vaucouleurs, G., Davies, M. E., and Sturms, F. M. Jr.: 1973, ‘Mariner 9 areographic coordinate system’,J. Geophys. Res. 80, 20, 4395.
Dollfus, A.: 1970, ‘New optical measurements of the diameters of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune’,Icarus 12, 101.
Dunham, D. W.: 1971,The Motions of the Satellites of Uranus, Ph.D. dissertation, Yale University.
Duxbury, Thomas C.: 1979, personal communication.
Dyce, R. B., Pettengill, G. H., and Shapiro, I. I.: 1967, ‘Radar determination of the rotations of Venus and Mercury’,Astron. J. 72, 351.
Eichelberger, W. S. and Newton A.: 1926, ‘The orbit of Neptune's satellite and the pole of Neptune's equator’,Astron. Pap. Am. Ephem. IX, 281.
Elliot, J. L., Dunham, E., Mink, D. J., and Churns, J.: 1979, ‘The radius and ellipticity of Uranus from its occultation of SAO 158 687’, submitted toAstrophys. J.
Franklin, F. A., Avis, C. C., Columbo, G., and Shapiro, I. I.: 1980, ‘The geometric oblateness of Uranus’,Astrophys. J. (in press).
Freeman, K. C. and Lyngå, G.: 1970, ‘Data for Neptune from occultation observations,Astrophys. J. 160, 767.
Garcia, H. A.: 1972, ‘The mass and figure of Saturn by photographic astronomy of its satellites’,Astron. J. 77, 684–691.
Gill, J. R. and Gault, B. L.: 1968, ‘A new determination of the orbit of Triton, pole of Neptune's equator, and mass of Neptune’,Astron. J. 73, S95.
Goldstein, R. M.: 1966, in: A. Dollfus (ed.),Radar Studies of Venus, Moon, and Planets, North Holland Publishing Co., Amsterdam.
Harrington, R. S. and Christy, J. W.: 1980, ‘The satellite of Pluto-II’,Astron. J. 85, 2.
Hayes, S. H. and Belton, M. J. S.: 1977, ‘The rotational periods of Uranus and Neptune’,Icarus 32, 383.
Howard, H. T., Tyler, G. L., Fjeldbo, G., Kliore, A. J., Levy, G. S., Brunn, D. L., Dickinson, R., Edelson, R. E., Martin, W. L., Postal, R. B., Seidel, B., Sesplaukis, T. T., Shirley, D. L., Stelzried, C. T., Sweetnam, D. N., Zygielbaum, A. I., Esposito, P. B., Anderson, J. D., Shapiro, I. I., Reasenberg, R. D.: 1974a, ‘Venus: mass, gravity field, atmosphere, and ionosphere as measured by the Mariner 10 dual-frequency radio system’,Science 183, 4131, 1297.
Howard, H. T., Tyler, G. L., Esposito, P. B., Anderson, J. D., Reasenberg, R. D., Shapiro, I. I., Fjeldbo, G., Kliore, A. J., Levy, G. S., Brunn, D. L., Dickinson, R., Edelson, R. E., Martin, W. L., Postal, R. B., Seidel, B., Sesplaukis, T. T., Shirley, D. L., Stelzried, C. T., Sweetnam, D. N., Wood, G. E., Zygielbaum, A. I.: 1974b, ‘Mercury: Results on mass, radius, ionosphere, and atmosphere from Mariner 10 dual-frequency radio signals’,Science 185, 4146, 179.
Jurgens, R. F.: 1970, ‘Some preliminary results of the 70-CM radar studies of Venus’,Radio Science 5, 2, 435.
Klaasen, K. P.: 1976, ‘Mercury's rotation axis and period’,Icarus 28, 469.
Kozai, Y.: 1957, ‘On the astronomical constants of Saturnian satellite systems’,Ann. Tokyo Astron. Obs. 2nd ser.,5, 73–106.
Kozai, Y.: 1976, ‘Masses of satellites and oblateness parameters of Saturn’,Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 28, 675.
Lieske, J. H.: 1979, ‘Poles of the Galilean satellites’,Astron. Astrophys. 75, 158.
Mayo, A. A., Blackshear, W. T., Tolson, R. H., Michael, W. H., Jr., Kelly, G. M., Brenkle, J. P., and Komarek, T. A.: 1977, ‘Lander locations, Mars physical ephemeris, and solar system parameters: determination from Viking lander tracking data’,J. Geophys. Res. 82, 28, 4297.
Michael, W. H., Jr.: 1979, ‘Viking lander tracking contributions to Mars mapping’,The Moon and Planets 20, 149–152.
Morrison, D., Cruikshank, D. P., and Burns, J. A.: 1977, ‘Introducing the satellites’, in: J. A. Burns (ed.),Planetary Satellites, University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
Munch, G. and Hippelein, H.: 1979, ‘The effects of seeing on the reflected spectrum of Uranus and Neptune’, submitted toAstron. Astrophys.
Null, G. W.: 1976, ‘Gravity field of Jupiter and its satellites from Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 tracking data’,Astron. J. 81, 12, 1153.
Pascu, Dan: 1978, personal communication.
Peale, S. J.: 1972, ‘Determination of parameters related to the interior of Mercury’,Icarus 17, 168.
Peale, S. J.: 1977, ‘Rotation histories of the natural satellites’, in: J. A. Burns (ed.),Planetary Satellites, University of Arizona Press, Tucson.
Pettengill, G. H. and Dyce, R. B.: 1965, ‘A radar determination of the rotation of the planet Mercury’,Nature 206, 1240.
Pollack, J. B., Veverka, J., Noland, M., Sagan, C., Duxbury, T. C., Acton, C. H. Jr., Born, G. H., Hartmann, W. K., and Smith, B. A.: 1973, ‘Mariner 9 television observations of Phobos and Deimos, 2’,J. Geophys. Res. 78, 20, 4313.
Reese, E. J.: 1971, ‘Recent photographic measurements of Saturn’,Icarus 15, 466.
Riddle, A. C. and Warwick, J. W.: 1976, ‘Redefinition of System III longitude’,Icarus 27, 457.
Seidelmann, P. K. and Divine, N.: 1977, ‘Evaluation of Jupiter longitudes in System III (1965)’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 4, 2, 65.
Shapiro, I. I.: 1967a, ‘Theory of the radar determination of planetary rotations’,Astron. J. 72, 1309.
Shapiro, I. I.: 1967b, ‘Resonance rotation of Venus’,Science 157, 423.
Shapiro, I. I., Campbell, D. B., and deCampli, W. M.: 1979, ‘Nonresonance rotation of Venus?’,Astrophys. J. 230, L123.
Sinclair, A. T.: 1974, ‘A theory of the motion of Iapetus’,Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 169, 591–605.
Sinclair, A. T.: 1977, ‘The Orbits of Tethys, Dione, Rhea, Titan and Iapetus’,Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 180, 447–459.
Sinclair, A. T., 1978, personal communication.
Sinclair, A. T. and Davis, M. E.: 1979, personal correspondence.
Slavsky, D. and Smith, H. J.: 1978, ‘The rotation period of Neptune’,Astrophys. J. Lett. 226, L49.
Smith, B. A. and Reese, E. J.: 1968, ‘Mercury's rotation period: photographic configuration’,Science 162, 1275.
Smith, B. A., Soderblom, L. A., Beebe, R., Boyce, J., Briggs, G., Carr, M., Collins, S. A., Cook, A. F., II, Danielson, G. E., Davies, M. E., Hunt, G. E., Ingersoll, A., Johnson, T. V., Masursky, H., McCauley, J., Morrison, D., Owen, T., Sagan, C., Shoemaker, E. M., Strom, R., Suomi, V. E., and Veverka, J.: 1979, ‘The Galilean satellites and Jupiter: Voyager 2 Imaging Science results’,Science 206, 4421, 927.
Smith, H. J. and Slavsky, D.: 1978,The Rotation Period of Neptune, presented at the Tenth Annual DPS/AAS Meeting, Pasadena, November 1, 1978.
Smith, H. J. and Slavsky, D. B.: 1979, ‘Rotation period of Uranus’,Bull. Am. Astr. Soc. 11, 3, 568.
Tjuflin, Y. S.: 1978,Results of Photogrammetric Plotting Space Imagery Obtained from the Soviet Unmanned Interplanetary Laboratories Aimed for the Moon and Planets Exploration, ISP Commission III Symposium, Moscow, July 31–August 5, 1978.
Trafton, L.: 1977, ‘Uranus' rotational period’,Icarus 32, 402.
Trauger, J. T., Roesler, F. L. and Münch, G.: 1978, ‘A redetermination of the Uranus rotation period’,Astrophys. J. 219, 1079.
Williams, James G.: 1979, personal communication.
Woltjer, J.: 1928, ‘The motion of Hyperion’,Ann. van de Sterrewacht te Leiden 16, 3, 1–139.
Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Ephemeris, Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, 1961.
Transactions of the International Astronomical Union, Vol. 11B, Proceedings of the Eleventh General Assembly, Berkeley, 1961, Academic Press, N.Y., 1961.
Transactions of the International Astronomical Union, Vol. 14B, Proceedings of the Fourteenth General Assembly, Brighton, 1970, D. Reidel Publishing Company, The Netherlands, 1971.
Transactions of the International Astronomical Union, Vol. 15B, Proceedings of the Fifteenth General Assembly, Sydney, 1973, D. Reidel Publishing Company, The Netherlands, 1974.
Transactions of the International Astronomical Union, Vol. 16B, Proceedings of the Sixteenth General Assembly, Grenoble, 1976, D. Reidel Publishing Company, The Netherlands, 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davies, M.E., Abalakin, V.K., Cross, C.A. et al. Report of the IAU Working Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements of the Planets and Satellites. Celestial Mechanics 22, 205–230 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01229508
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01229508