Abstract.
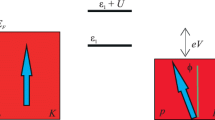
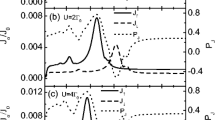
We investigate the quantum transport through a mesoscopic device consisting of an open, lateral double-quantum-dot coupled by time oscillating and spin-polarization dependent tunneling which results from a static magnetic field applied in the tunneling junction. In the presence of a non-vanishing bias voltage applied to two attached macroscopic leads both spin and charge currents are driven through the device. We demonstrate that the spin and charge currents are controllable by adjusting the gate voltage, the frequency of driving field and the magnitude of the magnetic field as well. An interesting resonance phenomenon is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Wolf et al., Science 294, 1488 (2001)
G.A. Prinz, Science 282, 1660 (1998)
The density of states for spin-up and spin-down electrons is nearly identical, but the energy of states is shifted with respect to each other. This energy-shift results in an unequal filling of the bands, which causes the different characters of spin-up and spin-down carriers at the Fermi level
A. Brataas, Y. Tserkovnyak, G.E.W. Bauer, B. Halperin, Phys. Rev. B 66, 060404 (2002)
B. Wang, J. Wang, H. Guo, cond-mat/0208475 (2002)
Q.-f. Sun, H. Guo, J. Wang, cond-mat/0212293 (2002)
Y. Meir, N.S. Wingreen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2512 (1992)
M. Buttiker, Phys. Rev. B 27, 6178 (1983)
A.P. Jauho et al., Phys. Rev. B 50, 5528 (1994)
B.G. Wang et al., Phys. Rev. B 65, 073306 (2002)
D.C. Langreth, in Liner and Nonlinear Electron Transport in Solids, Vol. 17 of Nato Advanced Study Institute, Series B: Physics, edited by J.T. Devreese, V.E. Van Doren
Q.-F. Sun, J. Wang, T.-H. Lin, Phys. Rev. B 59, 13126 (1999)
N.S. Wingreen, K.W. Jacobsen, J.W. Wilkins, Phys. Rev. B 40, 11834 (1989)
If temperature is too high, spin-current will be diminished due to thermal fluctuations
W. Yin, J.Q. Liang et al., Acta Phys. Sin. 52, 1862 (2003) (in Chinese)
Similar results are obtained by numerical simulation for the finite-temperature case
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Liang, JQ. Spin-polarized transport through a coupled double-dot . Eur. Phys. J. B 43, 421–427 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00072-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2005-00072-0